Pentesting identifies vulnerabilities by simulating cyberattacks on your systems to highlight security weaknesses. Red Teaming goes further by mimicking real-world attackers, testing your defenses from multiple angles to evaluate response effectiveness. Explore the full article to understand how these approaches safeguard your digital assets.
Table of Comparison
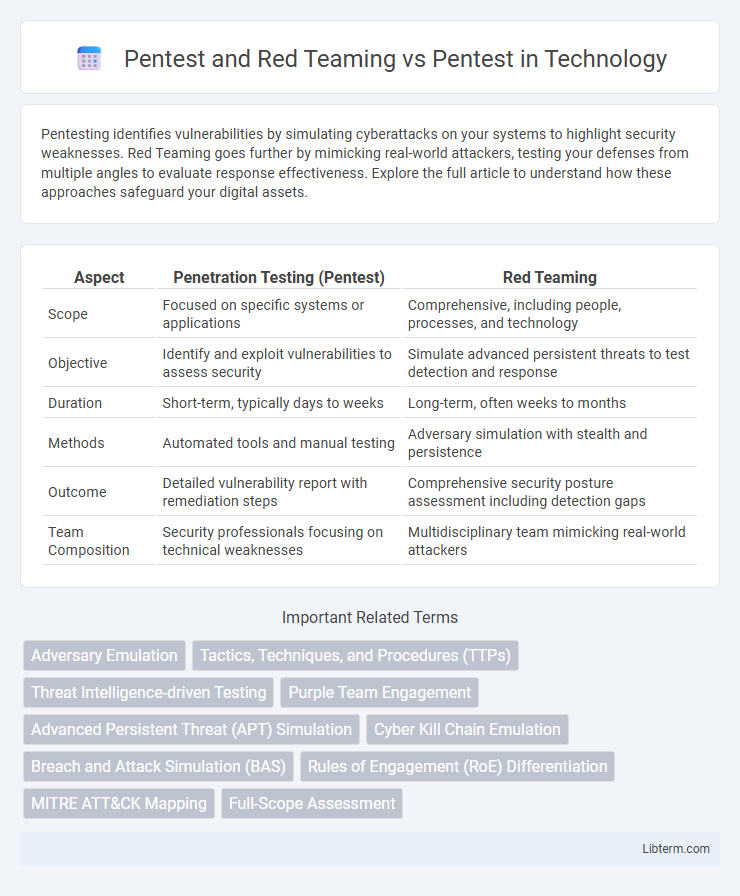
| Aspect | Penetration Testing (Pentest) | Red Teaming |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Focused on specific systems or applications | Comprehensive, including people, processes, and technology |
| Objective | Identify and exploit vulnerabilities to assess security | Simulate advanced persistent threats to test detection and response |
| Duration | Short-term, typically days to weeks | Long-term, often weeks to months |
| Methods | Automated tools and manual testing | Adversary simulation with stealth and persistence |
| Outcome | Detailed vulnerability report with remediation steps | Comprehensive security posture assessment including detection gaps |
| Team Composition | Security professionals focusing on technical weaknesses | Multidisciplinary team mimicking real-world attackers |
Understanding Pentest: Core Concepts
Pentest involves systematically identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities in IT systems to evaluate security defenses, typically focusing on predefined targets within a limited scope. Core concepts include reconnaissance, vulnerability scanning, exploitation, and reporting, aimed at uncovering weaknesses before attackers do. Unlike Red Teaming, which simulates real-world adversaries using multi-layered tactics across broader environments, pentesting emphasizes technical vulnerability assessment and compliance validation.
Defining Red Teaming: A Broader Approach
Red Teaming represents a broader cybersecurity strategy that simulates real-world adversaries to evaluate an organization's overall security posture beyond traditional Pentest scope. Unlike Pentesting, which primarily targets specific vulnerabilities in systems or applications, Red Teaming encompasses multi-faceted tactics including social engineering, physical security breaches, and detection evasion to assess how well defenses respond under authentic attack scenarios. This holistic approach uncovers gaps in people, processes, and technology, offering comprehensive insights for enhancing an enterprise's cybersecurity resilience.
Pentest vs Red Teaming: Key Differences
Pentest focuses on identifying specific vulnerabilities through simulated cyberattacks, often limited to predefined scopes and methodologies. Red Teaming provides a comprehensive, adversary-style assessment that tests an organization's detection and response capabilities across multiple attack vectors over an extended period. Key differences include the scope, objectives, and depth: pentests target technical flaws, while red teams mimic real-world attackers to evaluate overall security posture.
Objectives and Scope: Pentest Compared to Red Teaming
Penetration testing (Pentest) primarily focuses on identifying specific vulnerabilities within predefined systems or applications through controlled, short-term assessments targeting known attack vectors. Red Teaming adopts a broader and more realistic adversarial approach, simulating advanced persistent threats (APT) to evaluate an organization's overall security posture, including detection and response capabilities across people, processes, and technology. Unlike Pentest's narrow scope, Red Teaming encompasses multi-vector attacks over extended periods, aiming to expose gaps in defense mechanisms and improve organizational resilience.
Methodologies: How Pentesters and Red Teamers Operate
Pentesters typically follow structured methodologies such as OWASP or NIST guidelines, focusing on identifying vulnerabilities through automated scanning and manual testing within a defined scope and timeframe. Red Teamers employ adversary simulation techniques, mimicking real-world attackers using tactics from frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK, emphasizing stealth, persistence, and multi-phase operations across broader organizational environments. Both roles require deep technical expertise, but Red Teaming prioritizes holistic security assessment and defensive posture evaluation beyond the vulnerability-focused approach of traditional penetration testing.
Tools and Techniques: Technology Stack Comparison
Pentest primarily leverages automated vulnerability scanners, static and dynamic application security testing tools, and network analyzers to identify known security flaws efficiently. Red Teaming employs a broader technology stack including custom exploit frameworks, social engineering toolkits, and advanced persistent threat (APT) simulation platforms to mimic real-world attack scenarios and evade detection. While Pentesting tools focus on vulnerability identification and remediation, Red Team techniques emphasize stealth, lateral movement, and post-exploitation persistence across diverse systems.
Value Proposition: Business Impact of Each Approach
Pentesting identifies specific vulnerabilities and provides a clear, prioritized list of actionable security flaws, enabling swift remediation to reduce immediate risks. Red Teaming offers a comprehensive simulation of real-world attacks, exposing systemic weaknesses, testing defenses, and evaluating incident response effectiveness, delivering valuable insights into an organization's security posture. Businesses benefit from pentesting's focused risk reduction while leveraging red teaming to understand and improve overall security resilience against advanced threats.
Reporting and Results: Deliverables in Pentest vs Red Teaming
Pentest deliverables typically include detailed vulnerability reports with clear remediation steps aimed at improving specific system defenses. Red Teaming reports provide comprehensive attack narratives, highlighting real-world exploit paths and security gaps across people, processes, and technologies. While pentest results focus on technical fixability, red team deliverables emphasize strategic risk management and executive-level insights.
Choosing the Right Assessment: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right assessment between Pentest and Red Teaming depends on the organization's security goals, budget, and the scope of vulnerabilities to explore. Pentests focus on identifying specific vulnerabilities in systems through simulated attacks, while Red Teaming provides a comprehensive threat simulation, testing detection and response capabilities across multiple attack vectors. Organizations should consider factors such as risk tolerance, regulatory requirements, and the need for holistic security insights to select the most effective assessment approach.
Integrating Pentest and Red Teaming into Security Strategy
Integrating Pentest and Red Teaming into a security strategy enhances an organization's defense by combining vulnerability identification with realistic attack simulations to uncover complex security gaps. Pentest focuses on pinpointing weaknesses in specific systems or applications, while Red Teaming emulates sophisticated adversary tactics across multiple attack vectors to test overall security resilience. Together, these approaches provide comprehensive insights that inform proactive risk management and strengthen incident response capabilities.
Pentest and Red Teaming Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com