Integrating new technologies into existing systems requires careful planning and strategic execution to ensure seamless functionality and minimal disruption. Leveraging advanced integration tools can optimize performance and improve data flow across platforms, enhancing overall efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to discover proven methods and best practices for successful integration tailored to your needs.
Table of Comparison
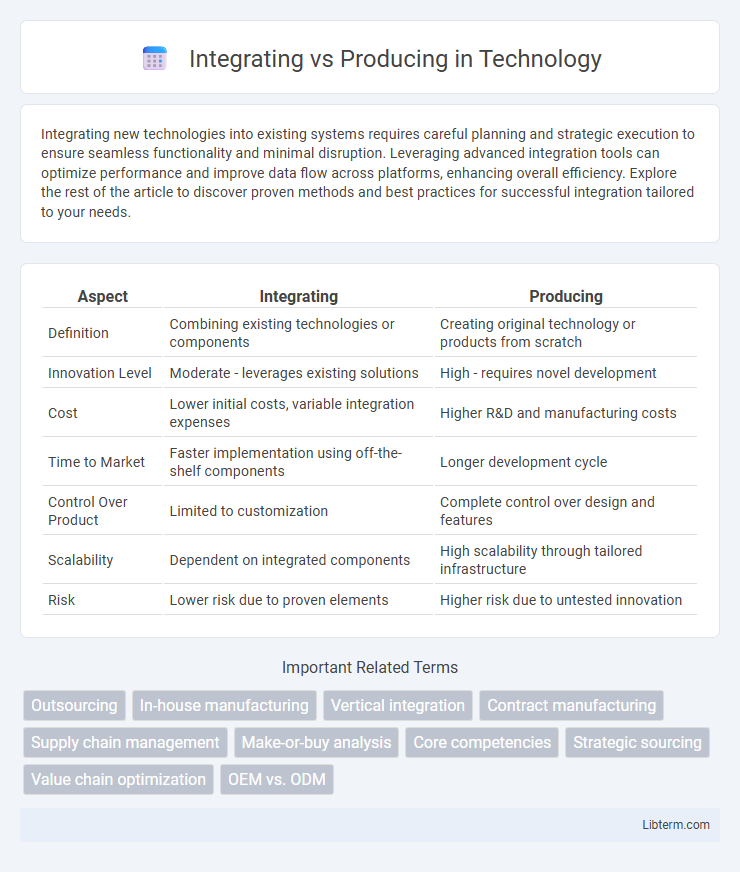
| Aspect | Integrating | Producing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining existing technologies or components | Creating original technology or products from scratch |
| Innovation Level | Moderate - leverages existing solutions | High - requires novel development |
| Cost | Lower initial costs, variable integration expenses | Higher R&D and manufacturing costs |
| Time to Market | Faster implementation using off-the-shelf components | Longer development cycle |
| Control Over Product | Limited to customization | Complete control over design and features |
| Scalability | Dependent on integrated components | High scalability through tailored infrastructure |
| Risk | Lower risk due to proven elements | Higher risk due to untested innovation |
Understanding Integration and Production
Understanding integration involves combining various components or systems to function cohesively, enhancing interoperability and overall efficiency. Production focuses on the creation or manufacturing of goods and services, emphasizing output quality and process optimization. Effective integration supports seamless production workflows by aligning resources, technologies, and operations.
Key Differences Between Integrating and Producing
Integrating involves combining existing components or systems into a cohesive whole, emphasizing compatibility and coordination, whereas producing centers on creating new products or content from raw materials or ideas, highlighting innovation and originality. Integrating prioritizes system interoperability, reducing redundancy, and optimizing workflows, while producing focuses on manufacturing efficiency, quality control, and resource management. Key differences lie in their objectives: integration aims to unify and streamline, whereas production aims to generate and deliver tangible outputs.
Benefits of Integration in Modern Workflows
Integration in modern workflows enhances efficiency by automating data exchange between systems, reducing manual errors and saving time. Seamless connectivity across tools fosters real-time collaboration, enabling faster decision-making and improved project outcomes. Businesses experience cost savings and scalability by unifying platforms, streamlining operations, and optimizing resource allocation.
Advantages of In-House Production
In-house production offers greater control over quality standards, enabling companies to maintain consistent product specifications and swiftly address issues. It reduces dependency on external suppliers, minimizing risks related to supply chain disruptions and lead times. Cost savings emerge from eliminating third-party margins and fostering innovation through close collaboration among internal teams.
Scalability: Integration vs. Production
Integration offers scalability by unifying diverse systems, enabling seamless data flow and reducing redundant processes, which improves operational efficiency across expanding environments. Production scalability relies on optimizing resource allocation and modular design to handle increased output without compromising quality or performance. Balancing integration and production scalability ensures robust growth by leveraging interconnected systems and scalable manufacturing or service processes.
Cost Analysis: Integrating vs. Producing
Cost analysis reveals that integrating existing components often reduces upfront expenses and shortens production timelines due to leveraging pre-made assets. Producing in-house entails higher initial costs driven by development, tooling, and quality assurance requirements but can lead to greater control and long-term savings. Selecting between integrating and producing hinges on evaluating trade-offs between immediate expenditure and strategic investment in proprietary capabilities.
Resource Allocation Strategies
Integrating strategies focus on efficient allocation of existing resources to enhance collaboration and reduce redundancy, optimizing overall operational workflows. Producing strategies prioritize investing in new resources and capabilities to expand production capacity and meet increasing demand. Balancing resource allocation between integration and production ensures sustainable growth and maximizes return on investment.
Quality Control: Which Approach Wins?
Integrating third-party components demands rigorous quality control measures to ensure compatibility and reliability, while producing in-house allows for direct oversight and customization of quality standards. Studies reveal that companies producing internally often achieve higher defect detection rates and faster issue resolution, though integration offers cost and time efficiency. Ultimately, quality control effectiveness hinges on robust testing protocols and transparent communication regardless of the approach.
Case Studies: Successful Integration vs. Production Models
Case studies in technology reveal that successful integration models often emphasize seamless compatibility and real-time data exchange between existing systems, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime. In contrast, production models showcase the benefits of end-to-end control and scalability in manufacturing environments, driving faster output with consistent quality. Organizations leveraging integration prioritize interoperability, while those focused on production optimize for throughput and resource utilization.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business
Selecting between integrating and producing hinges on balancing cost efficiency, scalability, and control over the product. Businesses aiming for rapid market entry often prefer integrating existing technologies, while those seeking unique differentiation prioritize producing in-house solutions. Evaluating resource availability, time-to-market demands, and long-term strategic goals ensures the optimal approach for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Integrating Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com