Anonymization is the process of removing or masking personal identifiers from data to protect individual privacy while maintaining data utility. This technique is crucial for compliance with data protection regulations and minimizing the risk of sensitive information exposure. Discover how effective anonymization can safeguard your data and empower secure analysis in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
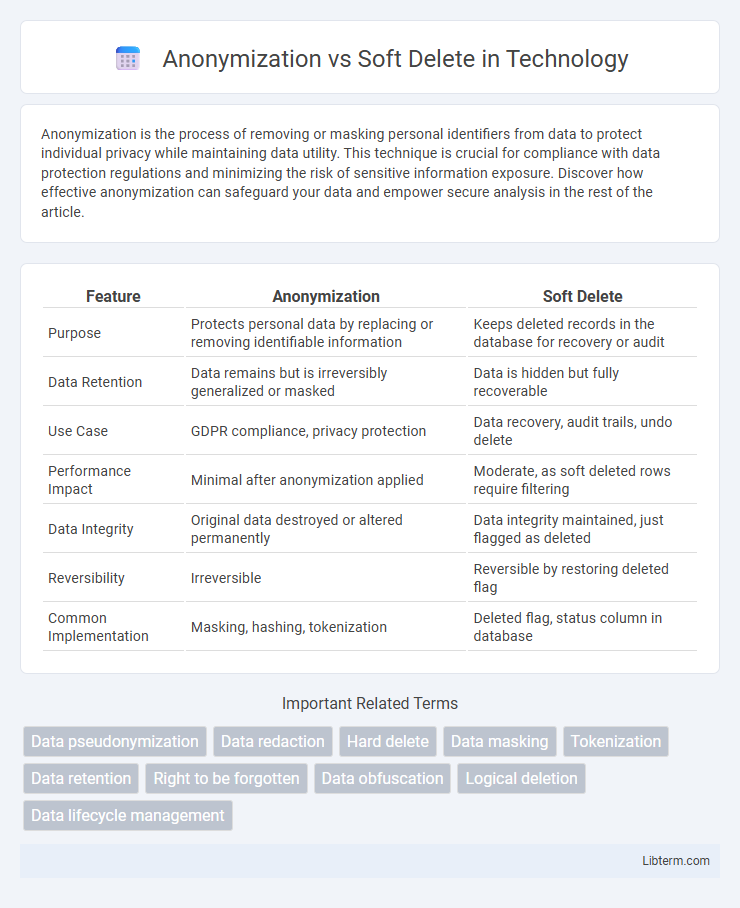
| Feature | Anonymization | Soft Delete |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects personal data by replacing or removing identifiable information | Keeps deleted records in the database for recovery or audit |
| Data Retention | Data remains but is irreversibly generalized or masked | Data is hidden but fully recoverable |
| Use Case | GDPR compliance, privacy protection | Data recovery, audit trails, undo delete |
| Performance Impact | Minimal after anonymization applied | Moderate, as soft deleted rows require filtering |
| Data Integrity | Original data destroyed or altered permanently | Data integrity maintained, just flagged as deleted |
| Reversibility | Irreversible | Reversible by restoring deleted flag |
| Common Implementation | Masking, hashing, tokenization | Deleted flag, status column in database |
Introduction to Data Privacy: Anonymization vs Soft Delete
Data privacy techniques like anonymization and soft delete play crucial roles in protecting sensitive information within databases. Anonymization removes or masks personally identifiable information (PII) to prevent re-identification, ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Soft delete, on the other hand, flags data as deleted without physically removing it, enabling data recovery while requiring careful management to mitigate privacy risks.
Defining Anonymization in Data Management
Anonymization in data management refers to the process of irreversibly removing personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets to protect individual privacy while retaining the usefulness of the data. Unlike soft delete, which marks data as inactive without removing it, anonymization ensures no direct or indirect identifiers can be traced back to an individual, complying with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Effective anonymization techniques include data masking, pseudonymization, and aggregation, which enable secure data analytics without exposing sensitive information.
Understanding Soft Delete: How It Works
Soft delete marks records as inactive or deleted by setting a specific flag or timestamp without removing data from the database, preserving data integrity for audit or recovery purposes. This method ensures that deleted items remain accessible for compliance checks while appearing hidden in regular queries through filtering mechanisms. Anonymization, by contrast, irreversibly removes or masks personally identifiable information to protect privacy but does not retain original data for restoration.
Key Differences Between Anonymization and Soft Delete
Anonymization replaces personal data with irreversible, non-identifiable information to protect privacy, while soft delete marks records as inactive without removing data, allowing recovery and auditing. Anonymization ensures compliance with data protection regulations by permanently eliminating identifiable information, whereas soft delete retains full data for operational continuity and potential restoration. The key difference lies in anonymization's focus on privacy and data protection versus soft delete's emphasis on reversible data management.
Use Cases: When to Choose Anonymization
Anonymization is ideal for compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR when retaining user privacy is crucial while maintaining analytical value. It is best used in scenarios requiring irreversible data masking, like medical records or customer feedback, ensuring that personal identifiers cannot be reconstructed. Soft delete suits temporary recovery needs, whereas anonymization supports long-term privacy-preserving data retention and safe data sharing with third parties.
Use Cases: When to Opt for Soft Delete
Soft delete is ideal for applications requiring reversible data removal, such as user account deactivation, where data recovery may be necessary to comply with customer support or legal requests. It supports auditing and historical data analysis by preserving records without displaying them in active queries, crucial for financial or healthcare systems maintaining data integrity. Opt for soft delete when regulatory frameworks demand data retention with limited access rather than permanent erasure, ensuring compliance while safeguarding operational flexibility.
Legal and Compliance Implications
Anonymization removes personally identifiable information (PII) irreversibly, ensuring compliance with strict data protection regulations like GDPR by minimizing data retention risks. Soft delete retains the data in a non-active state, allowing potential recovery but requiring robust access controls and clear retention policies to meet legal obligations. Organizations must balance data utility and privacy, as anonymization supports regulatory mandates for data minimization while soft delete may expose them to compliance risks if deleted data remains accessible.
Impact on Data Retrieval and Recovery
Anonymization irreversibly removes personally identifiable information (PII), making data recovery impossible while preserving dataset usability for analysis without privacy risks. Soft delete retains the original data masked as deleted, enabling straightforward data retrieval and recovery but posing potential privacy concerns if access controls are weak. Choosing between anonymization and soft delete impacts system design, balancing compliance with data privacy regulations and operational needs for data restoration.
Security Risks and Best Practices
Anonymization removes or masks personal data to protect user identity, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches and non-compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR. Soft delete retains data in the system but marks it as deleted, which poses security risks if unauthorized access occurs or if restoration processes are inadequate. Best practices include combining anonymization for sensitive data with secure access controls and audit logs to ensure comprehensive data protection throughout the data lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Choosing between anonymization and soft delete depends on your organization's data privacy requirements and compliance obligations. Anonymization irreversibly removes personally identifiable information to protect user privacy, making it ideal for reducing risks in data processing and sharing. Soft delete retains data by marking it inactive or hidden, facilitating recovery and audit trails while maintaining compliance with data retention policies.
Anonymization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com