Rolling deployment gradually updates your application by replacing instances one at a time, minimizing downtime and maintaining service availability. This approach ensures continuous delivery of new features or bug fixes without interrupting user experience. Discover how rolling deployments can optimize your release strategy and improve your system's reliability in the full article.
Table of Comparison
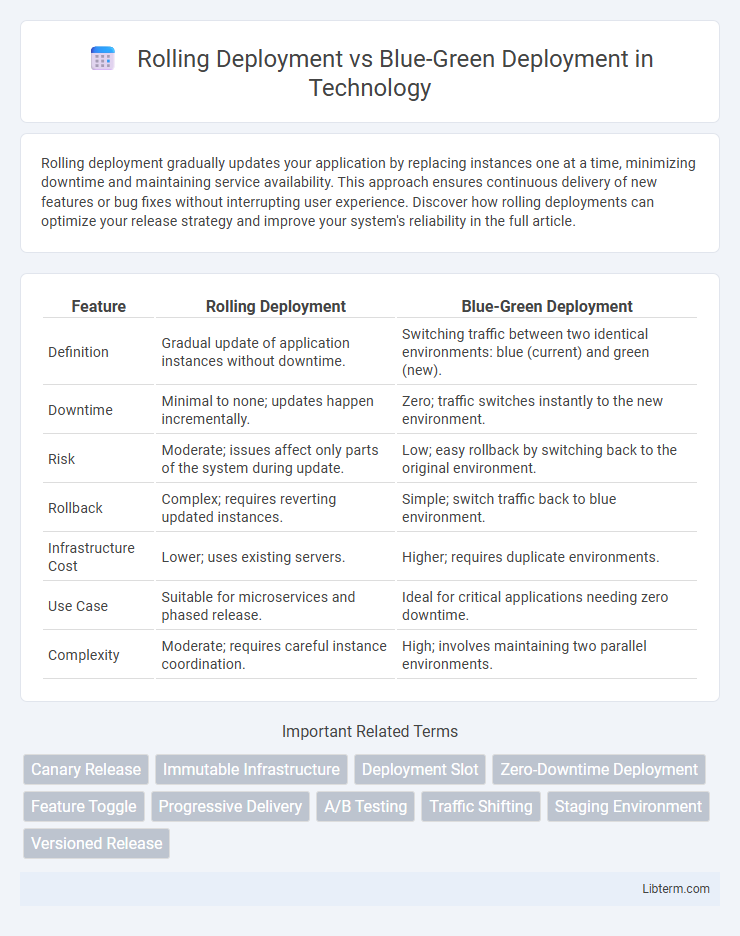
| Feature | Rolling Deployment | Blue-Green Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual update of application instances without downtime. | Switching traffic between two identical environments: blue (current) and green (new). |
| Downtime | Minimal to none; updates happen incrementally. | Zero; traffic switches instantly to the new environment. |
| Risk | Moderate; issues affect only parts of the system during update. | Low; easy rollback by switching back to the original environment. |
| Rollback | Complex; requires reverting updated instances. | Simple; switch traffic back to blue environment. |
| Infrastructure Cost | Lower; uses existing servers. | Higher; requires duplicate environments. |
| Use Case | Suitable for microservices and phased release. | Ideal for critical applications needing zero downtime. |
| Complexity | Moderate; requires careful instance coordination. | High; involves maintaining two parallel environments. |
Introduction to Deployment Strategies
Rolling deployment gradually updates application instances by replacing them one at a time, minimizing downtime and allowing continuous delivery. Blue-green deployment maintains two identical production environments, switching traffic from blue to green to achieve near-zero downtime during releases. Both strategies aim to enhance reliability and reduce risk, but rolling deployment offers progressive updates while blue-green provides instant rollbacks.
What is Rolling Deployment?
Rolling Deployment is a software release strategy where updates are gradually implemented across servers or instances, minimizing downtime and reducing risk by continuously deploying new versions in small batches. This method ensures that only a portion of the system is updated at a time, allowing for quick rollback if issues arise, and maintaining overall service availability. It contrasts with Blue-Green Deployment by avoiding the need for running two complete environments simultaneously.
What is Blue-Green Deployment?
Blue-Green Deployment is a release management strategy that maintains two identical production environments called Blue and Green, allowing seamless switching between them to minimize downtime and risk. This approach enables rapid rollback by routing traffic to the stable environment while updating the other, ensuring continuous service availability during deployment. It significantly reduces deployment risks by isolating updates and enabling thorough testing before directing live traffic to the new version.
Key Differences Between Rolling and Blue-Green Deployment
Rolling deployment updates applications incrementally across servers, minimizing downtime by gradually replacing old versions with new ones, while blue-green deployment involves maintaining two identical production environments and switching traffic entirely from the blue (old) to the green (new) environment. Rolling deployment is advantageous for continuous delivery with minimal resource overhead but may involve risk as both old and new versions run simultaneously during updates, whereas blue-green deployment ensures a complete and instant cutover that simplifies rollback but requires double infrastructure. Key differences include deployment speed, resource utilization, rollback complexity, and impact on user experience during the release process.
Advantages of Rolling Deployment
Rolling Deployment minimizes downtime by updating application instances incrementally, ensuring continuous service availability during the release process. This approach reduces risk as only a subset of instances is updated at a time, allowing quick rollback if issues arise. It also optimizes resource usage by not requiring duplicate production environments, making it cost-effective compared to Blue-Green Deployment.
Advantages of Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-Green Deployment offers zero-downtime releases by instantly switching traffic from the old environment to the fully tested new environment, minimizing user disruption. Its ability to safely roll back to the previous version in case of issues enhances reliability and reduces risk during deployment. The clear separation of production environments simplifies debugging and monitoring, improving overall stability and operational control.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Rolling Deployment
Rolling deployment faces challenges such as the risk of inconsistent application states due to partial updates across different servers, complicating rollback processes when errors occur. It often results in longer update times and increased resource consumption as old and new versions run simultaneously during the deployment phase. This approach may cause temporary service disruptions or degraded performance, impacting user experience compared to isolated environments in blue-green deployment.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-Green Deployment requires maintaining two identical production environments, leading to increased infrastructure costs and resource duplication. This approach introduces complexity in database schema changes since both environments must support backward and forward compatibility, complicating seamless transitions. Traffic switching risks causing downtime or data inconsistency if rollback mechanisms are not meticulously managed.
When to Choose Rolling vs Blue-Green Deployment
Rolling deployment is ideal for applications requiring minimal downtime and continuous delivery, especially when infrastructure capacity supports phased updates without impacting the entire system. Blue-green deployment suits environments needing instant rollback capabilities and complete environment isolation, often used when testing new releases in production with minimal risk. Choose rolling deployment for incremental updates in large-scale distributed systems and blue-green deployment for critical applications where immediate failover and zero downtime are paramount.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Deployment Strategy
Choosing the right deployment strategy depends on application complexity, risk tolerance, and downtime requirements. Rolling deployments enable gradual updates with minimal downtime, ideal for continuous delivery and frequent releases. Blue-green deployments offer instant rollback and zero downtime, best suited for critical applications demanding high availability and stability.
Rolling Deployment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com