Gamma radiation, a form of high-energy electromagnetic waves, penetrates materials more deeply than alpha or beta particles, making it essential in medical imaging and cancer treatment. Understanding gamma sources and safety measures is crucial to protect yourself from potential health risks. Explore the article further to learn how gamma radiation impacts technology and health in your daily life.
Table of Comparison
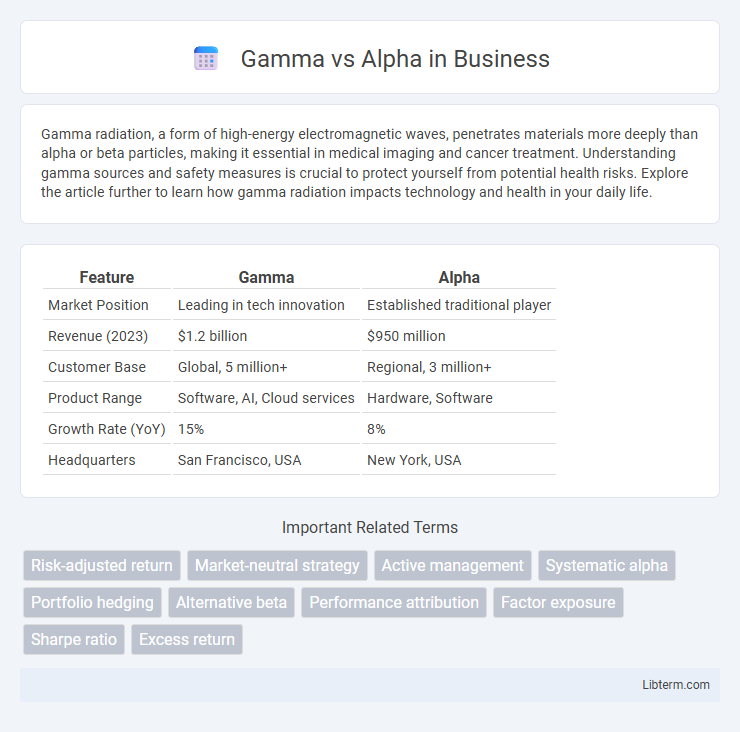
| Feature | Gamma | Alpha |
|---|---|---|
| Market Position | Leading in tech innovation | Established traditional player |
| Revenue (2023) | $1.2 billion | $950 million |
| Customer Base | Global, 5 million+ | Regional, 3 million+ |
| Product Range | Software, AI, Cloud services | Hardware, Software |
| Growth Rate (YoY) | 15% | 8% |
| Headquarters | San Francisco, USA | New York, USA |
Understanding Gamma and Alpha: Key Definitions
Gamma represents the rate of change in an option's delta relative to the underlying asset's price movements, measuring convexity and indicating the sensitivity of delta to price fluctuations. Alpha quantifies an investment's excess return compared to a benchmark index, reflecting the value added by active portfolio management. Understanding Gamma and Alpha is crucial for balancing risk and return in options trading and portfolio performance evaluation.
The Science Behind Gamma and Alpha Brainwaves
Gamma and Alpha brainwaves represent distinct neural oscillations linked to cognitive functions and mental states. Gamma waves, typically ranging from 30 to 100 Hz, are associated with high-level information processing, attention, and working memory. Alpha waves, oscillating between 8 and 12 Hz, correlate with relaxed alertness and inhibitory control, facilitating efficient neural communication and sensory gating.
Functional Differences: Gamma vs. Alpha
Gamma and Alpha proteins differ significantly in their functional roles within cellular processes. Gamma proteins primarily modulate signal transduction pathways, influencing cellular responses and communication, while Alpha proteins are mainly involved in structural integrity and enzymatic activities essential for metabolism. The distinct localization and interaction partners of Gamma versus Alpha proteins underline their specialized contributions to maintaining cellular homeostasis and function.
How Gamma and Alpha Affect Cognitive Performance
Gamma brain waves, typically ranging from 30-100 Hz, are closely linked to high-level cognitive functions such as memory recall, information processing speed, and attentional focus. Alpha waves, occurring between 8-12 Hz, play a crucial role in relaxation and mental coordination, facilitating a calm but alert state that enhances creative problem solving and reduces mental fatigue. Research indicates that optimal cognitive performance involves a dynamic balance between heightened gamma activity for active thinking and increased alpha activity for restorative mental states.
Gamma vs. Alpha in Meditation and Mindfulness
Gamma brain waves exhibit higher frequency patterns linked to enhanced cognitive functions and deep meditation states, whereas Alpha waves are slower and associated with relaxed alertness and mindfulness practices. During meditation, Gamma activity correlates with increased neuroplasticity and heightened sensory perception, while Alpha waves promote calming focus and stress reduction. Research highlights that experienced meditators often show elevated Gamma wave synchronization, suggesting deeper mental integration compared to the predominantly Alpha-dominated states of novice mindfulness practitioners.
Influence of Gamma and Alpha on Emotional Regulation
Gamma and Alpha brainwaves play distinct roles in emotional regulation, with Gamma waves associated with higher cognitive functioning, attention, and integrating emotional experiences to foster resilience. Alpha waves contribute to relaxation and calmness, reducing stress and promoting emotional balance by inhibiting unnecessary neural activity. The interaction between Gamma and Alpha waves supports adaptive emotional processing and effective stress management.
Technological Methods for Measuring Gamma and Alpha
Technological methods for measuring gamma and alpha radiation utilize specialized detectors tailored to each type's unique properties. Gamma radiation is commonly quantified using scintillation detectors or semiconductor detectors such as high-purity germanium (HPGe) detectors, which offer high-resolution gamma spectroscopy. Alpha detection often employs solid-state nuclear track detectors (SSNTDs) or silicon surface barrier detectors, capable of precisely identifying alpha particle emissions due to their limited penetration power.
Enhancing Gamma and Alpha Brainwaves: Techniques and Tips
Enhancing gamma and alpha brainwaves boosts cognitive function and relaxation, with techniques like mindfulness meditation and neurofeedback training proving effective. Studies show focused attention and sensory stimulation increase gamma wave activity, enhancing memory and information processing. For alpha waves, practices such as deep breathing exercises and rhythmic light or sound exposure promote calmness and creativity by inducing a relaxed yet alert mental state.
Clinical Relevance: Gamma and Alpha in Mental Health
Gamma and Alpha brain waves play crucial roles in mental health, with Gamma waves linked to cognitive functioning, memory, and information processing, while Alpha waves contribute to relaxation and stress reduction. Elevated Gamma activity is often observed in conditions like schizophrenia and anxiety, indicating heightened neural activity and sensory processing. Conversely, reduced Alpha wave patterns are associated with depression and chronic stress, suggesting impaired relaxation and emotional regulation.
Future Research and Applications of Gamma vs. Alpha
Future research on Gamma vs. Alpha focuses on enhancing comparative analysis to uncover unique functional roles and interaction mechanisms within neural networks. Advanced imaging techniques and machine learning algorithms are being developed to precisely map Gamma and Alpha wave dynamics in cognitive processes and neurological disorders. Emerging applications include tailored neurofeedback therapies and brain-computer interfaces leveraging differential Gamma and Alpha activity for improved mental health diagnostics and treatment efficacy.
Gamma Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com