A final product represents the completed result of a manufacturing or creative process, ready for distribution or consumption. It embodies the quality, functionality, and design that meet customer expectations, ensuring satisfaction and brand loyalty. Explore the rest of the article to discover how final products impact your business success and innovation.
Table of Comparison
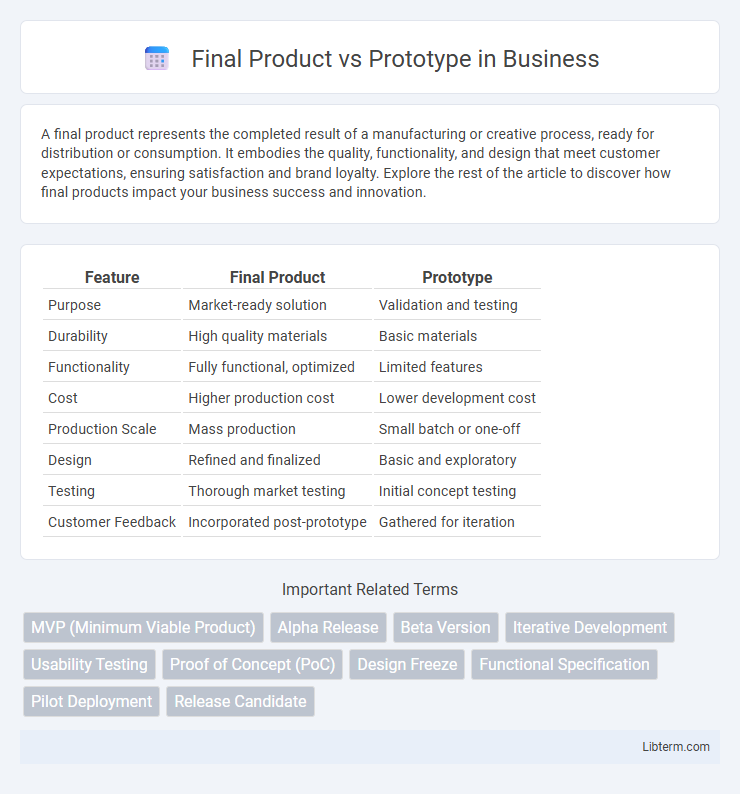
| Feature | Final Product | Prototype |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Market-ready solution | Validation and testing |
| Durability | High quality materials | Basic materials |
| Functionality | Fully functional, optimized | Limited features |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower development cost |
| Production Scale | Mass production | Small batch or one-off |
| Design | Refined and finalized | Basic and exploratory |
| Testing | Thorough market testing | Initial concept testing |
| Customer Feedback | Incorporated post-prototype | Gathered for iteration |
Understanding Prototypes and Final Products
Prototypes serve as preliminary models designed to test concepts, functionality, and design before mass production, allowing for iterative improvements and risk reduction. Final products represent the fully developed, market-ready versions that meet quality standards, user requirements, and regulatory compliance. Understanding the distinction between prototypes and final products is essential for efficient product development, resource allocation, and successful market launch.
Key Differences: Prototype vs Final Product
A prototype serves as an early model used for testing design concepts, functionality, and usability, whereas the final product is the fully developed version ready for mass production and consumer use. Prototypes often have limited features and may use different materials, while the final product meets all quality, safety, and performance standards. The key difference lies in prototypes being iterative, experimental versions, while the final product represents the refined, market-ready solution.
Purpose and Goals of Prototypes
Prototypes serve to validate design concepts, test functionality, and gather user feedback early in the development process, enabling iterative improvements. The goal of a prototype is to identify potential issues and refine features before investing resources into the final product. Unlike the final product, prototypes are not fully polished or production-ready but are essential for reducing risks and ensuring alignment with user needs.
The Role of Final Products in the Market
The final product serves as the market-ready solution, embodying refined features, tested functionality, and compliance with industry standards, differentiating itself from the prototype's experimental nature. It plays a critical role in customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and revenue generation by addressing user needs and providing reliable performance. Market feedback on the final product drives continuous improvement and innovation, positioning companies competitively within their sectors.
Design Changes from Prototype to Final Product
Design changes from prototype to final product often involve refining functionality, improving materials, and enhancing user experience based on prototype testing feedback. Prototypes typically use temporary or lower-cost components, whereas the final product integrates durable, production-grade materials and optimized manufacturing processes. Adjustments in ergonomics, aesthetics, and compliance with safety standards are common to ensure the final product meets market demands and regulatory requirements.
Testing and Feedback: Prototype Stage
The prototype stage focuses on testing functionality and gathering user feedback to identify design flaws and areas for improvement. Iterative testing during this phase enables developers to make adjustments before finalizing the product, reducing risks and costs associated with post-production changes. User feedback collected from prototypes helps refine usability, performance, and overall user experience.
Quality Assurance in Final Product Development
Final product development incorporates rigorous quality assurance processes to ensure reliability, performance, and compliance with industry standards, unlike prototypes which primarily focus on concept validation. Quality assurance in the final product involves systematic testing, defect tracking, and process optimization to achieve consistent production output and customer satisfaction. This comprehensive approach reduces risk, enhances product durability, and supports regulatory certification essential for market release.
Cost Implications: Prototype vs Final Product
Prototype development typically involves higher per-unit costs due to small production runs, specialized materials, and iterative testing requirements. Final product manufacturing benefits from economies of scale, streamlined processes, and bulk purchasing, significantly reducing unit costs. Understanding these cost differences is crucial for budgeting and pricing strategies during product development.
Speed to Market: Iteration and Launch
Prototypes accelerate speed to market by enabling rapid iteration and testing, allowing teams to identify and fix design flaws early. The final product requires comprehensive development and quality assurance, which extends launch timelines. Efficient prototyping reduces time-to-launch, empowering faster market entry and customer feedback integration.
Importance of Prototypes in Product Success
Prototypes play a crucial role in bridging the gap between conceptual designs and final products, allowing developers to identify design flaws and gather user feedback early in the development process. This iterative testing significantly enhances product quality, reduces costly errors, and accelerates time-to-market by validating functionality and usability before full-scale production. Investing in robust prototyping increases the likelihood of market success by aligning the product closely with customer needs and expectations.
Final Product Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com