Service-based businesses prioritize delivering exceptional customer experiences through personalized solutions and ongoing support. These businesses focus on building long-term relationships by understanding client needs and offering customized services that drive value and satisfaction. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a service-based approach can enhance your business success.
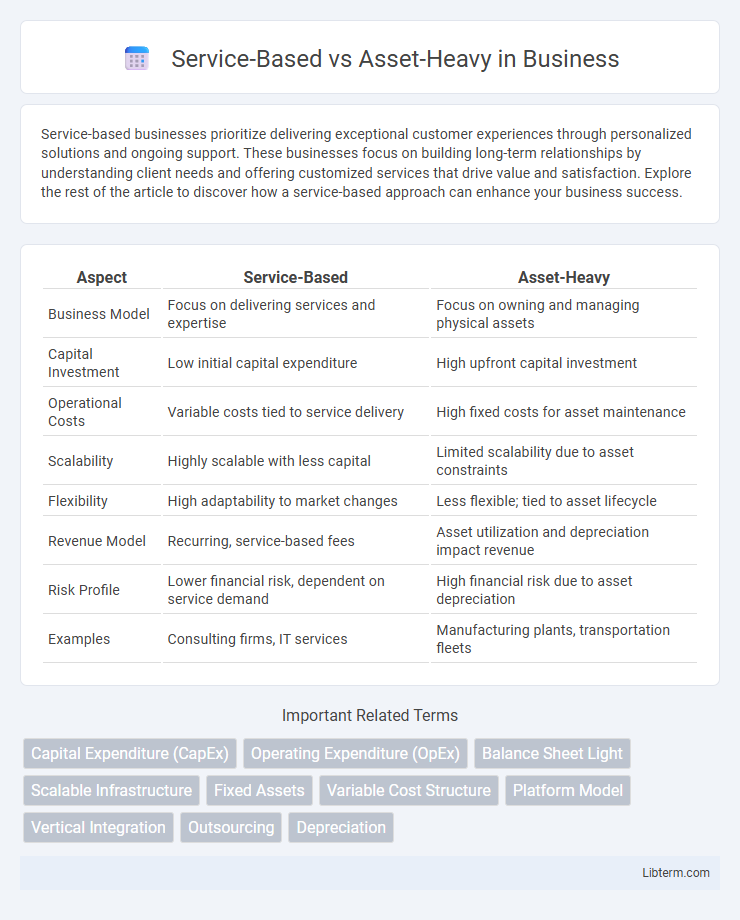
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Service-Based | Asset-Heavy |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Focus on delivering services and expertise | Focus on owning and managing physical assets |
| Capital Investment | Low initial capital expenditure | High upfront capital investment |
| Operational Costs | Variable costs tied to service delivery | High fixed costs for asset maintenance |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with less capital | Limited scalability due to asset constraints |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to market changes | Less flexible; tied to asset lifecycle |
| Revenue Model | Recurring, service-based fees | Asset utilization and depreciation impact revenue |
| Risk Profile | Lower financial risk, dependent on service demand | High financial risk due to asset depreciation |
| Examples | Consulting firms, IT services | Manufacturing plants, transportation fleets |
Introduction to Service-Based and Asset-Heavy Models
Service-based models prioritize delivering intangible value through customer-centric solutions, relying heavily on human capital, technology, and expertise rather than physical assets. Asset-heavy models focus on significant investments in tangible resources such as machinery, facilities, and infrastructure to produce and deliver goods. Understanding these frameworks helps businesses align operational strategies with financial, scalability, and risk management goals.
Key Differences Between Service-Based and Asset-Heavy Approaches
Service-based models emphasize flexibility, operational efficiency, and customer-centric solutions by leveraging intangible resources such as expertise and technology platforms. Asset-heavy approaches rely heavily on physical assets like machinery, equipment, or real estate, leading to higher capital expenditure and maintenance costs but offering greater control over production processes. Key differences include investment intensity, scalability, risk exposure, and the balance between operational agility and asset control.
Advantages of Service-Based Businesses
Service-based businesses benefit from lower capital investment and reduced fixed costs compared to asset-heavy models, enabling greater financial flexibility and scalability. They often achieve faster market entry and adaptability due to the reliance on human expertise and technology rather than physical assets. Enhanced customer relationships and recurring revenue streams boost long-term profitability and resilience in dynamic market conditions.
Benefits of Asset-Heavy Business Models
Asset-heavy business models offer significant control over production, enabling higher quality assurance and customization of products. Owning physical assets such as manufacturing plants, equipment, and real estate leads to increased operational stability and long-term cost efficiencies. This model also provides substantial barriers to entry for competitors, fostering sustained competitive advantage and asset appreciation over time.
Challenges Faced by Service-Based Companies
Service-based companies face challenges such as managing fluctuating demand and ensuring consistent quality across diverse client needs. High dependency on skilled labor creates difficulties in scaling operations and maintaining workforce stability. Limited physical assets increase vulnerability to market competition and reduce collateral options for financing growth.
Drawbacks of Asset-Heavy Operations
Asset-heavy operations often require substantial capital investment in physical infrastructure such as manufacturing plants, machinery, and inventory, leading to high fixed costs and reduced financial flexibility. The dependence on tangible assets increases vulnerability to market fluctuations and technological obsolescence, causing potential asset write-downs and stranded costs. Maintenance, depreciation, and underutilization of assets further erode profitability and complicate scaling or pivoting to new business models.
Scalability Comparison: Service-Based vs Asset-Heavy
Service-based models offer superior scalability by leveraging flexible resources and easily adjustable operational structures, allowing rapid market expansion without significant capital investment. In contrast, asset-heavy models require substantial upfront investments in physical assets, which limit quick scalability and increase fixed costs. The scalability advantage of service-based businesses enables faster adaptation to market demand fluctuations and supports sustained growth with lower financial risk.
Industry Examples of Each Business Model
Tech companies like Netflix and Spotify exemplify service-based models by delivering streaming media through subscription services without owning physical assets. In contrast, manufacturing giants such as General Motors and Boeing operate asset-heavy models requiring substantial investment in factories, machinery, and inventory. Retail chains like Walmart blend both approaches, maintaining extensive physical stores alongside e-commerce platforms to balance asset intensity and service delivery.
Financial Implications and Risk Management
Service-based business models typically require lower capital expenditure, leading to improved cash flow and reduced debt levels compared to asset-heavy models, which demand substantial upfront investment in physical assets. Asset-heavy companies face higher depreciation costs and greater exposure to asset obsolescence, increasing financial risk and necessitating robust risk management strategies including asset valuation and maintenance planning. Service-based firms often benefit from scalable operations with lower fixed costs, mitigating financial risk through flexibility and adaptability in volatile markets.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Choosing the right business model depends on your company's core competencies and market demands. Service-based models prioritize flexibility, scalability, and lower upfront capital expenditure by focusing on customer-centric offerings and recurring revenue streams. Asset-heavy models require significant investment in physical assets, offering control over production and potentially higher profit margins, but entail greater operational risks and fixed costs.
Service-Based Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com