B2B2C is a business model that combines elements of both B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-consumer) approaches, enabling companies to reach end consumers through their business partners. This model allows businesses to leverage partnerships for broader market access while maintaining direct influence over customer experience and product delivery. Explore the full article to understand how B2B2C strategies can enhance your market reach and drive growth effectively.
Table of Comparison
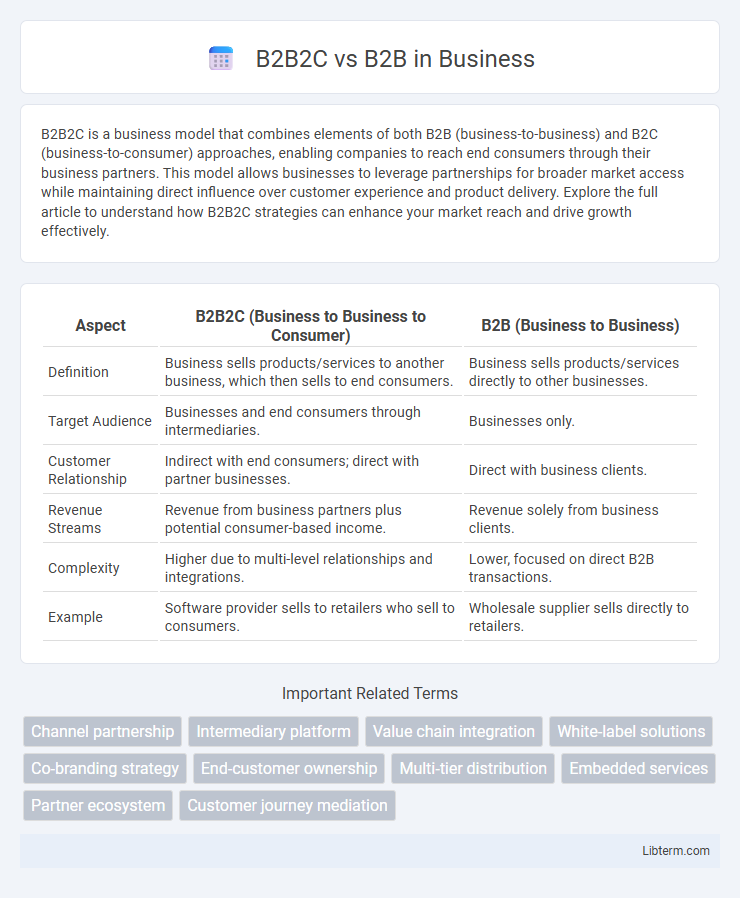
| Aspect | B2B2C (Business to Business to Consumer) | B2B (Business to Business) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business sells products/services to another business, which then sells to end consumers. | Business sells products/services directly to other businesses. |
| Target Audience | Businesses and end consumers through intermediaries. | Businesses only. |
| Customer Relationship | Indirect with end consumers; direct with partner businesses. | Direct with business clients. |
| Revenue Streams | Revenue from business partners plus potential consumer-based income. | Revenue solely from business clients. |
| Complexity | Higher due to multi-level relationships and integrations. | Lower, focused on direct B2B transactions. |
| Example | Software provider sells to retailers who sell to consumers. | Wholesale supplier sells directly to retailers. |
Overview of B2B2C and B2B Business Models
B2B2C (Business-to-Business-to-Consumer) combines elements of both B2B and B2C by allowing companies to sell products or services through intermediaries directly to end consumers, creating an extended value chain. This model leverages partnerships where businesses collaborate to reach consumer markets more effectively, enhancing distribution and customer experience. In contrast, the B2B (Business-to-Business) model strictly involves transactions between businesses, focusing on supplying goods or services without direct consumer engagement.
Key Differences Between B2B2C and B2B
B2B2C involves businesses selling products or services to other businesses that then sell directly to consumers, integrating both intermediary and end-user interactions, whereas B2B focuses solely on transactions between businesses. Key differences include the customer engagement model, with B2B2C emphasizing a hybrid relationship chain that combines business partnerships and direct consumer engagement, while B2B prioritizes business collaboration and bulk transactions. Additionally, B2B2C strategies often require more complex marketing and customer experience management to cater to both intermediaries and end customers, unlike B2B's straightforward, business-focused approach.
How B2B2C Works: Business-to-Business-to-Consumer Explained
B2B2C (Business-to-Business-to-Consumer) operates by connecting businesses directly with consumers through an intermediary business, enabling manufacturers or service providers to reach end-users efficiently. This model combines B2B's emphasis on partnerships with B2C's customer-centric approach, creating a seamless flow from product creation to consumer delivery. Companies leverage B2B2C to expand market reach, enhance customer experience, and streamline distribution by collaborating closely with other businesses that interface directly with consumers.
Primary Advantages of B2B2C
B2B2C (Business-to-Business-to-Consumer) models offer enhanced customer reach by combining B2B sales efficiency with direct consumer engagement, resulting in higher market penetration and brand loyalty. This approach enables businesses to leverage partner networks for distribution while maintaining control over customer experience and data analytics. B2B2C also facilitates faster feedback loops and personalized marketing strategies, driving increased sales growth compared to traditional B2B models.
Core Benefits of B2B
B2B (Business-to-Business) models streamline operations by facilitating direct relationships between companies, enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing costs. Core benefits include scalable networking opportunities, improved procurement processes, and stronger long-term partnerships that drive innovation and competitive advantage. In contrast, B2B2C integrates consumer-facing elements but relies heavily on the foundational strengths of B2B for business growth.
Challenges in B2B2C Compared to B2B
B2B2C models face unique challenges compared to B2B due to the added complexity of managing both business clients and end consumers simultaneously, requiring sophisticated coordination across multiple touchpoints. This multi-layered engagement demands advanced data integration and personalized marketing strategies to address diverse user needs while maintaining consistent brand experiences. Furthermore, B2B2C businesses often encounter increased operational costs and logistical hurdles related to supply chain management and customer support, intensifying overall management complexity.
Customer Experience in B2B2C vs B2B
B2B2C models enhance customer experience by directly engaging end consumers through a seamless integration of business partnerships, allowing for personalized service and faster feedback loops compared to traditional B2B setups. Unlike B2B, where customer interaction is indirect and mediated by client businesses, B2B2C provides greater control over branding, product customization, and support, fostering stronger loyalty and satisfaction. Leveraging advanced CRM systems and data analytics in B2B2C strategies improves customer insights and tailors experiences more effectively than the typically transactional nature of B2B relationships.
Revenue Generation and Monetization Models
B2B2C models generate revenue by integrating both business and consumer transactions, leveraging partnerships to expand market reach and share monetization across stakeholders. Revenue streams in B2B2C include subscription fees, transaction commissions, and value-added services, creating diversified income channels beyond direct sales to businesses. In contrast, B2B models focus primarily on wholesale pricing, licensing fees, or service contracts, limiting monetization to the business client without direct consumer engagement.
Real-World Examples of B2B2C and B2B Companies
Amazon Web Services exemplifies B2B by providing cloud infrastructure solutions directly to businesses. In contrast, Shopify operates under a B2B2C model, offering e-commerce platforms to merchants who then sell products to end consumers. Both models leverage digital platforms but differ in how they engage with the consumer; B2B focuses solely on business clients, while B2B2C incorporates a dual engagement with businesses and their customers.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider for Your Business
Choosing the right model between B2B2C and B2B depends on your business goals, customer reach, and operational complexity. B2B2C integrates direct consumer access through business partners, enhancing customer insights and engagement, while B2B focuses purely on supplier-to-business transactions, offering streamlined processes and cost efficiencies. Evaluate your target market scalability, control over customer experience, and resource capacity to determine which approach aligns best with your strategic growth objectives.
B2B2C Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com