C2B (Consumer-to-Business) is a business model where individuals offer products or services to companies, reversing the traditional B2C dynamic. This approach empowers consumers to influence market trends, pricing, and product development directly. Discover how C2B strategies can benefit Your business by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
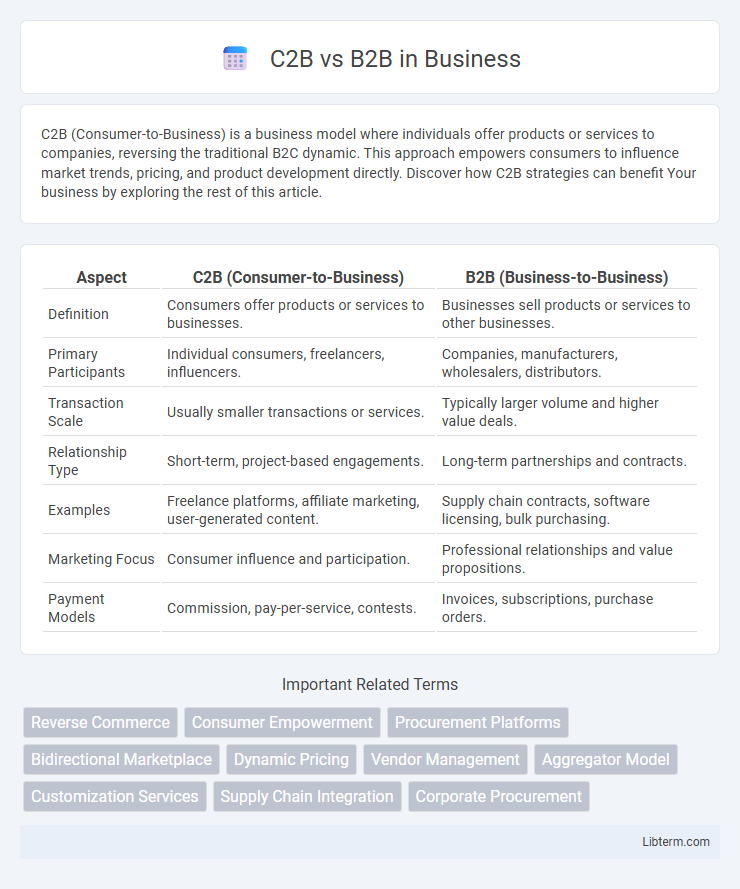
| Aspect | C2B (Consumer-to-Business) | B2B (Business-to-Business) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consumers offer products or services to businesses. | Businesses sell products or services to other businesses. |
| Primary Participants | Individual consumers, freelancers, influencers. | Companies, manufacturers, wholesalers, distributors. |
| Transaction Scale | Usually smaller transactions or services. | Typically larger volume and higher value deals. |
| Relationship Type | Short-term, project-based engagements. | Long-term partnerships and contracts. |
| Examples | Freelance platforms, affiliate marketing, user-generated content. | Supply chain contracts, software licensing, bulk purchasing. |
| Marketing Focus | Consumer influence and participation. | Professional relationships and value propositions. |
| Payment Models | Commission, pay-per-service, contests. | Invoices, subscriptions, purchase orders. |
Understanding C2B and B2B Business Models
C2B (Consumer-to-Business) and B2B (Business-to-Business) models differ fundamentally in transaction direction and target audience. C2B involves individual consumers offering products or services to businesses, common in influencer marketing and freelance platforms, whereas B2B focuses on commercial transactions between companies, emphasizing bulk sales and long-term contracts. Understanding each model's customer dynamics and value exchange mechanisms is crucial for optimizing marketing strategies and operational workflows in these distinct ecosystems.
Key Differences Between C2B and B2B
C2B (Consumer-to-Business) involves individual consumers offering products or services to businesses, emphasizing user-generated content, influencer marketing, and freelance services, while B2B (Business-to-Business) focuses on transactions between companies, typically involving bulk purchasing, supply chain logistics, and long-term contracts. C2B models prioritize consumer influence on business decisions and marketing strategies, whereas B2B centers on efficiency, scalability, and professional relationships between enterprises. The key differences lie in the direction of value exchange, target audience, and transaction complexity.
Advantages of the C2B Model
The C2B model empowers consumers by allowing them to set prices and dictate terms, enhancing customer satisfaction and engagement. Businesses benefit from direct feedback and personalized marketing data, improving product development and targeting accuracy. This model also reduces traditional operational costs, offering greater flexibility and scalability in meeting consumer demands.
Benefits of the B2B Approach
The B2B approach delivers enhanced scalability and long-term partnerships, driving consistent revenue streams through bulk transactions and strategic contracts. Businesses benefit from higher order values, professional procurement processes, and tailored solutions that improve operational efficiency and ROI. This approach also facilitates better market insights and collaborative innovation by fostering close relationships between companies.
Common Examples of C2B and B2B Transactions
C2B transactions typically include freelance platforms where individuals offer services to businesses, such as graphic design or content creation on Upwork, and influencer marketing where consumers promote brands on social media. B2B transactions commonly involve wholesale suppliers providing products to retailers, SaaS companies selling software solutions to enterprises, and manufacturers supplying raw materials to production companies. Both C2B and B2B models facilitate unique value exchanges but target different market roles, emphasizing consumer-to-business versus business-to-business interactions.
Challenges Faced in C2B and B2B Models
Challenges faced in C2B models include managing diverse consumer demands and ensuring data privacy while integrating user-generated content and feedback into business strategies. B2B models often struggle with longer sales cycles, complex decision-making processes, and the need for strong relationship management to maintain client trust and loyalty. Both models require tailored technological solutions to address scalability issues and optimize transaction efficiency.
Technology’s Role in C2B vs B2B Operations
Technology in C2B operations empowers consumers through digital platforms that facilitate direct feedback, product customization, and peer-to-peer interactions, enhancing customer engagement and data collection. In contrast, B2B technology focuses on streamlining complex supply chains, automating procurement processes, and integrating enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to improve operational efficiency and long-term partnerships. Advanced analytics, AI, and cloud computing play pivotal roles in both C2B and B2B environments but are tailored to meet the distinct demands of consumer-driven innovation versus large-scale business transactions.
Marketing Strategies for C2B and B2B
Marketing strategies for C2B (Consumer-to-Business) emphasize influencer partnerships, user-generated content, and personalized digital campaigns to empower consumers in brand promotion. In contrast, B2B (Business-to-Business) marketing relies on relationship-building through account-based marketing, in-depth content marketing, and targeted LinkedIn outreach to connect with decision-makers. Both approaches optimize engagement by leveraging data analytics to tailor messaging and improve conversion rates.
Future Trends: C2B and B2B Evolution
Future trends in C2B and B2B models highlight increased integration of AI-driven personalization, enabling businesses to tailor offerings based on consumer-generated data. The evolution of blockchain technology is reshaping trust and transparency in B2B transactions while facilitating secure C2B interactions through decentralized platforms. Enhanced mobile and IoT connectivity will further blur the lines between these models, driving innovative hybrid marketplaces that leverage real-time consumer input and supplier collaboration.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Choosing the right business model between Consumer-to-Business (C2B) and Business-to-Business (B2B) depends on your target audience and transaction dynamics. C2B models excel in leveraging individual consumer value, such as influencer marketing or freelance platforms, while B2B focuses on large-scale transactions and long-term relationships between companies. Analyzing customer needs, sales cycles, and revenue potential is essential for selecting a model that maximizes profitability and operational efficiency.
C2B Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com