A product extension merger allows companies to expand their product lines by integrating complementary offerings from another business, enhancing market reach and customer appeal. This strategy leverages brand recognition and distribution channels to create a more diverse portfolio with reduced risk. Discover how a product extension merger can transform Your business's growth potential in the full article.
Table of Comparison
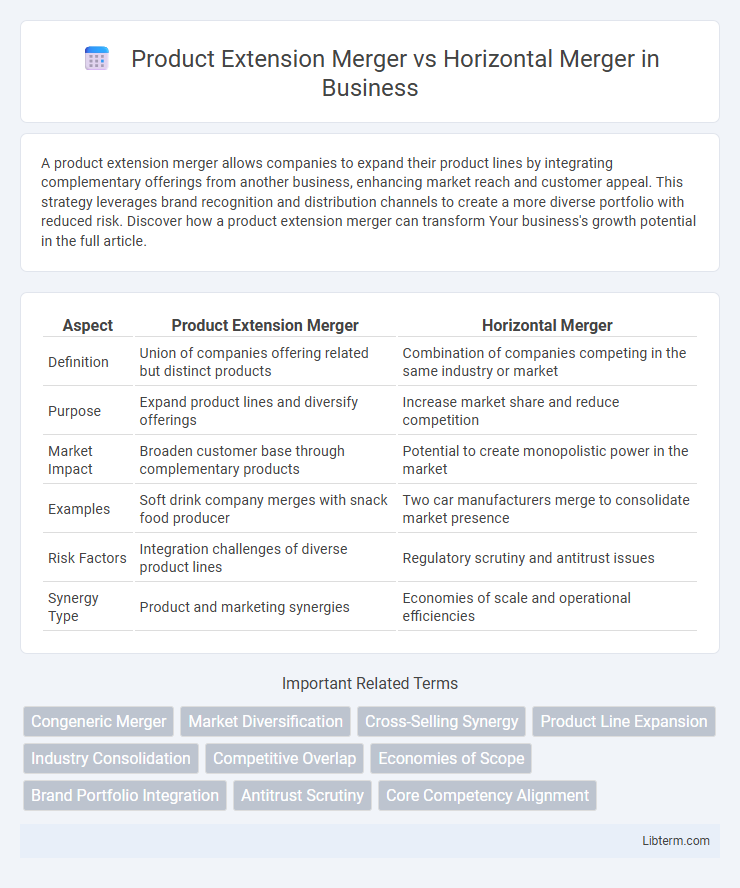
| Aspect | Product Extension Merger | Horizontal Merger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Union of companies offering related but distinct products | Combination of companies competing in the same industry or market |
| Purpose | Expand product lines and diversify offerings | Increase market share and reduce competition |
| Market Impact | Broaden customer base through complementary products | Potential to create monopolistic power in the market |
| Examples | Soft drink company merges with snack food producer | Two car manufacturers merge to consolidate market presence |
| Risk Factors | Integration challenges of diverse product lines | Regulatory scrutiny and antitrust issues |
| Synergy Type | Product and marketing synergies | Economies of scale and operational efficiencies |
Introduction to Merger Types
Product extension mergers involve companies combining to expand their product lines within the same industry, enhancing market reach and customer base without drastic changes in production processes. Horizontal mergers occur between firms operating at the same stage of production in the same industry, aiming to increase market share, reduce competition, and achieve economies of scale. Both merger types strategically align resources but differ in focus: product extension mergers broaden product variety, while horizontal mergers consolidate market position.
Defining Product Extension Merger
Product Extension Merger occurs when two companies offering related products within the same market combine to expand their product lines and customer base, enhancing market reach without direct competition overlap. This type of merger allows firms to capitalize on complementary offerings, thereby increasing cross-selling opportunities and operational synergies. In contrast, a Horizontal Merger involves the unification of companies producing identical or highly similar products, aiming primarily to increase market share and reduce competition.
Understanding Horizontal Merger
Horizontal mergers involve the combination of companies operating in the same industry and at the same stage of production, aiming to increase market share and reduce competition. This contrasts with product extension mergers, where firms merge to expand their product lines within related markets rather than directly competing products. Understanding horizontal mergers is crucial for analyzing market consolidation, potential anti-competitive effects, and the strategic growth opportunities they present.
Key Differences Between Product Extension and Horizontal Mergers
Product extension mergers involve companies operating at different stages of production or in related product lines, aiming to expand their product offerings and diversify market reach, while horizontal mergers occur between firms in the same industry and at the same production stage to increase market share and reduce competition. Product extension mergers help firms leverage complementary products to enhance customer base and reduce distribution costs, whereas horizontal mergers primarily focus on economies of scale and consolidating industry power. Key differences include the strategic intent behind the merger--product diversification versus market consolidation--and the degree of overlap in product lines and market presence.
Strategic Objectives of Product Extension Mergers
Product extension mergers aim to expand a company's product line by combining firms that operate in related but distinct product areas, enhancing market reach and customer base without directly competing. These mergers strategically leverage complementary products to achieve cross-selling opportunities, increase product variety, and improve customer loyalty. They differ from horizontal mergers, which consolidate companies competing in the same product category to achieve economies of scale and reduce competition.
Strategic Objectives of Horizontal Mergers
Horizontal mergers aim to increase market share, achieve economies of scale, and reduce competition by combining companies operating in the same industry and at the same stage of the production process. These mergers enable firms to consolidate resources, expand their customer base, and enhance pricing power, thereby improving overall competitiveness. In comparison, product extension mergers primarily focus on diversifying the product line within the same market to attract a broader customer spectrum without direct consolidation of competitors.
Benefits of Product Extension Mergers
Product extension mergers enable companies to expand their product portfolios by combining complementary products, enhancing market reach and customer base without direct competition overlap. These mergers drive revenue growth through cross-selling opportunities and diversify risks by targeting varied consumer segments. Businesses benefit from shared resources and increased brand recognition, leading to improved competitive advantage in related markets.
Advantages of Horizontal Mergers
Horizontal mergers offer significant advantages, including increased market share and reduced competition by combining firms operating within the same industry segment. These mergers allow companies to achieve economies of scale and scope, resulting in cost efficiencies and enhanced bargaining power with suppliers. Furthermore, horizontal mergers often facilitate greater innovation and resource sharing, leading to improved product offerings and competitive positioning.
Challenges and Risks for Each Merger Type
Product extension mergers face challenges in integrating diverse product lines and aligning marketing strategies, risking brand dilution and customer confusion. Horizontal mergers encounter risks related to regulatory scrutiny, market monopolization concerns, and difficulties in harmonizing corporate cultures. Both merger types demand careful management of operational redundancies and employee retention to prevent productivity losses.
Choosing the Right Merger Strategy for Business Growth
Product extension mergers expand a company's product line within the same market, enhancing customer reach and leveraging existing brand loyalty. Horizontal mergers combine firms operating in the same industry and market stage, increasing market share and operational efficiencies. Choosing the right merger strategy depends on growth objectives, whether targeting product diversification or market consolidation for competitive advantage.
Product Extension Merger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com