Insourcing enhances operational control by utilizing internal resources to manage projects and processes, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings. This strategy empowers your organization to leverage in-house expertise, maintain quality standards, and quickly adapt to changing business needs. Discover how insourcing can transform your company's workflow and competitive advantage in the full article.
Table of Comparison
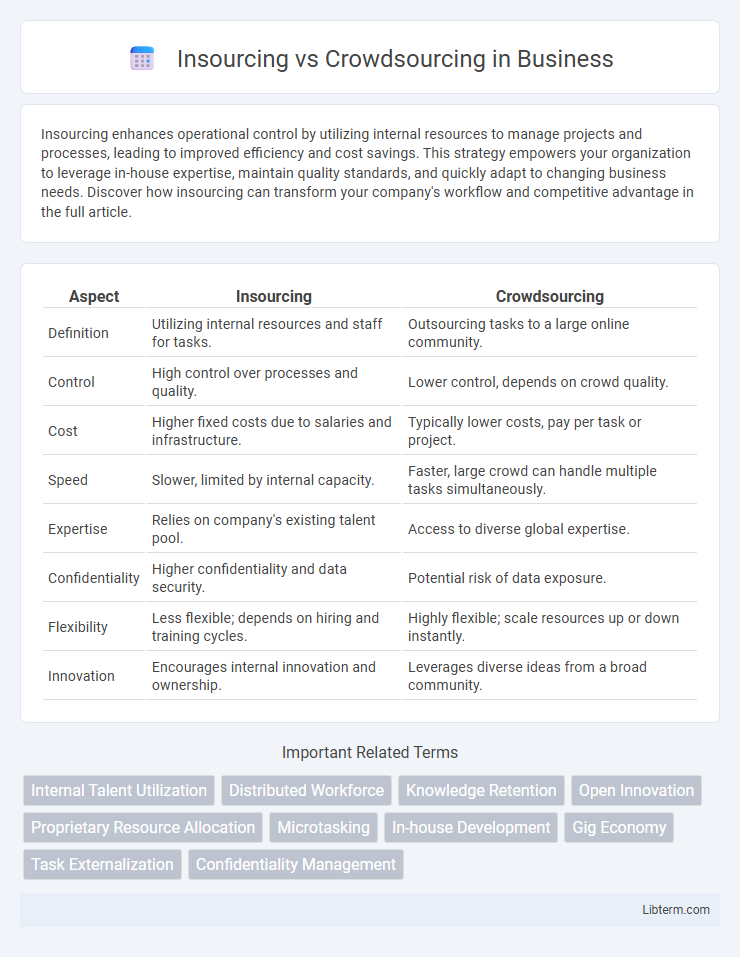
| Aspect | Insourcing | Crowdsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Utilizing internal resources and staff for tasks. | Outsourcing tasks to a large online community. |
| Control | High control over processes and quality. | Lower control, depends on crowd quality. |
| Cost | Higher fixed costs due to salaries and infrastructure. | Typically lower costs, pay per task or project. |
| Speed | Slower, limited by internal capacity. | Faster, large crowd can handle multiple tasks simultaneously. |
| Expertise | Relies on company's existing talent pool. | Access to diverse global expertise. |
| Confidentiality | Higher confidentiality and data security. | Potential risk of data exposure. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; depends on hiring and training cycles. | Highly flexible; scale resources up or down instantly. |
| Innovation | Encourages internal innovation and ownership. | Leverages diverse ideas from a broad community. |
Introduction to Insourcing and Crowdsourcing
Insourcing involves utilizing internal resources and employees to complete tasks, ensuring control over quality and confidentiality while fostering team expertise. Crowdsourcing leverages the collective intelligence and skills of a broad, external community to solve problems or gather input, often accelerating innovation and reducing costs. Both approaches offer distinct advantages depending on project scope, desired control, and resource availability.
Core Definitions: What Sets Insourcing and Crowdsourcing Apart?
Insourcing refers to the practice of utilizing an organization's internal resources, employees, and expertise to complete tasks or projects, ensuring direct control and alignment with company standards. Crowdsourcing involves outsourcing tasks to a large, often undefined group of external contributors via online platforms, leveraging diverse skills and rapid problem-solving at scale. The key distinction lies in insourcing's reliance on internal capabilities versus crowdsourcing's open, decentralized approach to harnessing external talent.
Key Advantages of Insourcing
Insourcing offers greater control over project quality, timelines, and proprietary information by utilizing internal resources and expertise. It enhances team cohesion and alignment with company culture, leading to improved communication and faster decision-making. Cost predictability and direct management of employee performance further contribute to efficient resource allocation and accountability.
Major Benefits of Crowdsourcing
Crowdsourcing offers access to a vast, diverse talent pool that accelerates innovation and problem-solving by leveraging collective intelligence. It reduces operational costs and enhances scalability by outsourcing tasks to qualified contributors worldwide. This approach fosters creative solutions and rapid iteration, driving business agility and competitive advantage.
Challenges and Limitations of Insourcing
Insourcing often faces challenges such as higher operational costs and limited access to diverse skill sets compared to crowdsourcing. Organizations may struggle with scalability and flexibility when relying solely on internal teams, leading to potential bottlenecks in project execution. Additionally, insourcing can result in resource constraints and slower innovation due to fewer external inputs and perspectives.
Drawbacks and Risks Associated with Crowdsourcing
Crowdsourcing presents risks such as reduced control over quality and consistency due to the diverse and decentralized nature of contributors, leading to potential variability in output. Intellectual property concerns arise from sharing sensitive information with an uncontrolled external workforce, increasing the risk of data breaches or misuse. Moreover, crowdsourcing can result in communication challenges and coordination difficulties, which may delay project timelines and complicate the management of contributions.
Cost Implications: Insourcing vs Crowdsourcing
Insourcing typically involves higher fixed costs due to salaries, training, and infrastructure, which can limit scalability but ensures tighter quality control. Crowdsourcing reduces overhead by leveraging a distributed workforce paid per task, offering cost efficiency and flexibility for variable workloads. However, managing crowdsourced projects may incur indirect costs such as quality assurance and coordination efforts.
Quality Control and Project Management Comparison
Insourcing offers direct quality control through centralized oversight, enabling consistent adherence to company standards and immediate issue resolution. Crowdsourcing presents challenges in maintaining uniform quality due to the diverse skill levels and decentralized nature of contributors, often requiring robust project management platforms to monitor progress and enforce guidelines. Effective project management in insourcing relies on internal teams with clear roles, whereas crowdsourcing demands scalable coordination tools and rigorous vetting processes to manage dispersed contributors efficiently.
Use Cases: When to Choose Insourcing or Crowdsourcing
Insourcing is ideal for projects requiring deep organizational knowledge, strict data security, and high-quality control, such as product development, customer service, or proprietary research. Crowdsourcing excels in tasks that benefit from diverse input and scalability, like idea generation, market research, or large-scale data labeling. Choose insourcing for long-term, specialized expertise and crowdsourcing for cost-effective, rapid innovation and broad problem-solving.
Future Trends and Final Considerations
Future trends in insourcing emphasize enhanced control, data security, and specialized expertise within organizations, driven by advancements in AI and automation to optimize internal processes. Crowdsourcing continues to evolve with greater integration of blockchain for transparent collaboration, AI-driven talent matching, and expanded global participation enabling diverse innovation. Final considerations highlight balancing cost-efficiency with quality, recognizing hybrid models that combine insourcing's reliability and crowdsourcing's scalability as the most effective strategy for dynamic business environments.
Insourcing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com