Data integration combines data from different sources into a unified view, enhancing accuracy and accessibility for better decision-making. It streamlines workflows by eliminating data silos and ensures consistent, up-to-date information across your organization. Discover how effective data integration can transform your operations in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
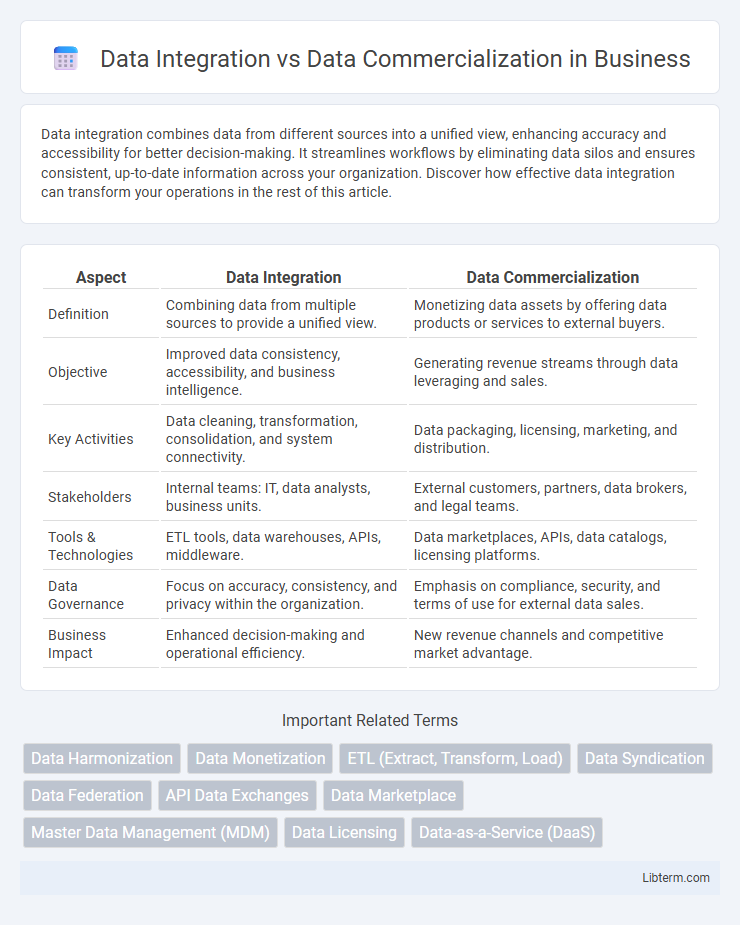
| Aspect | Data Integration | Data Commercialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining data from multiple sources to provide a unified view. | Monetizing data assets by offering data products or services to external buyers. |
| Objective | Improved data consistency, accessibility, and business intelligence. | Generating revenue streams through data leveraging and sales. |
| Key Activities | Data cleaning, transformation, consolidation, and system connectivity. | Data packaging, licensing, marketing, and distribution. |
| Stakeholders | Internal teams: IT, data analysts, business units. | External customers, partners, data brokers, and legal teams. |
| Tools & Technologies | ETL tools, data warehouses, APIs, middleware. | Data marketplaces, APIs, data catalogs, licensing platforms. |
| Data Governance | Focus on accuracy, consistency, and privacy within the organization. | Emphasis on compliance, security, and terms of use for external data sales. |
| Business Impact | Enhanced decision-making and operational efficiency. | New revenue channels and competitive market advantage. |
Introduction to Data Integration and Data Commercialization
Data integration involves combining data from multiple sources into a unified view to improve data accessibility and consistency for analytics and decision-making. Data commercialization refers to the process of monetizing data by packaging and selling it as a product or service to external customers or partners. Both practices leverage data as a strategic asset but differ in purpose, with integration focusing on internal optimization and commercialization targeting external revenue generation.
Defining Data Integration
Data Integration involves combining data from multiple sources into a unified view, enabling comprehensive analysis and decision-making within an organization. This process includes data cleansing, transformation, and consolidation to ensure consistency and accuracy across diverse datasets. Unlike Data Commercialization, which focuses on monetizing data assets, Data Integration aims to enhance operational efficiency and data accessibility.
What is Data Commercialization?
Data commercialization involves transforming raw data into valuable products or services that generate revenue, enabling organizations to unlock new business opportunities. Unlike data integration, which focuses on combining data from different sources to create a unified view, data commercialization emphasizes packaging, marketing, and distributing data assets for commercial use. Effective data commercialization requires robust data governance, compliance with privacy regulations, and strategic partnerships to maximize monetization potential.
Key Differences Between Data Integration and Data Commercialization
Data integration involves combining data from multiple sources to provide a unified view, enhancing data quality and accessibility for internal analytics and operations. Data commercialization focuses on packaging and monetizing data products or insights, targeting external customers or partners to generate revenue streams. The key differences lie in purpose--data integration is internally oriented for operational efficiency, while data commercialization aims at market-driven profit generation.
Benefits of Effective Data Integration
Effective data integration streamlines data from multiple sources into a unified, accessible system, enhancing data accuracy and consistency across the organization. It reduces operational costs by eliminating redundant data processing and accelerates decision-making through real-time data availability. Improved data integration supports scalability and compliance, fostering a robust foundation for data commercialization strategies.
Advantages of Data Commercialization for Businesses
Data commercialization enables businesses to unlock new revenue streams by transforming data assets into marketable products or services, increasing overall profitability. It enhances competitive advantage through monetizing unique datasets while fostering innovation and strategic partnerships that expand market reach. This approach also improves data governance and quality by aligning data management practices with commercial objectives, driving better decision-making and operational efficiency.
Common Challenges in Data Integration
Data integration faces common challenges such as data silos, inconsistent data formats, and the complexity of merging diverse data sources into a unified system. These issues often result in data quality problems, delayed access to actionable insights, and increased costs due to manual data cleansing and transformation. Addressing these challenges requires robust ETL tools, standardized data schemas, and scalable architectures to ensure seamless data flow across organizational platforms.
Risks and Considerations in Data Commercialization
Data commercialization involves risks such as data privacy breaches, regulatory compliance challenges, and intellectual property concerns that require careful management. Organizations must consider data quality, security measures, and consent frameworks to mitigate potential legal and ethical issues. Unlike data integration, commercialization demands ongoing monitoring of market dynamics and the impact of data monetization on brand reputation.
Best Practices for Successful Data Integration and Monetization
Effective data integration requires robust data governance, standardized data formats, and real-time data synchronization to ensure consistent and accurate information across systems. Data commercialization succeeds by identifying high-value data assets, establishing clear data ownership, and implementing secure data-sharing frameworks that comply with privacy regulations. Combining these best practices drives seamless data flow and unlocks revenue opportunities through data monetization strategies.
Future Trends in Data Integration and Commercialization
Future trends in data integration emphasize advanced AI-driven automation, real-time data processing, and enhanced interoperability across diverse platforms to enable seamless, scalable data ecosystems. Data commercialization is evolving through increased use of blockchain for secure data transactions, growing emphasis on data privacy compliance, and innovative monetization models like data-as-a-service (DaaS) platforms. Both fields converge towards maximizing data value by integrating sophisticated technologies that support dynamic data sharing and ethical data utilization in competitive markets.
Data Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com