Revenue represents the total income generated from the sale of goods or services before any expenses are deducted. Tracking your revenue accurately is essential for assessing business performance and making informed financial decisions. Explore the article to learn strategies for boosting revenue and maximizing profitability.
Table of Comparison
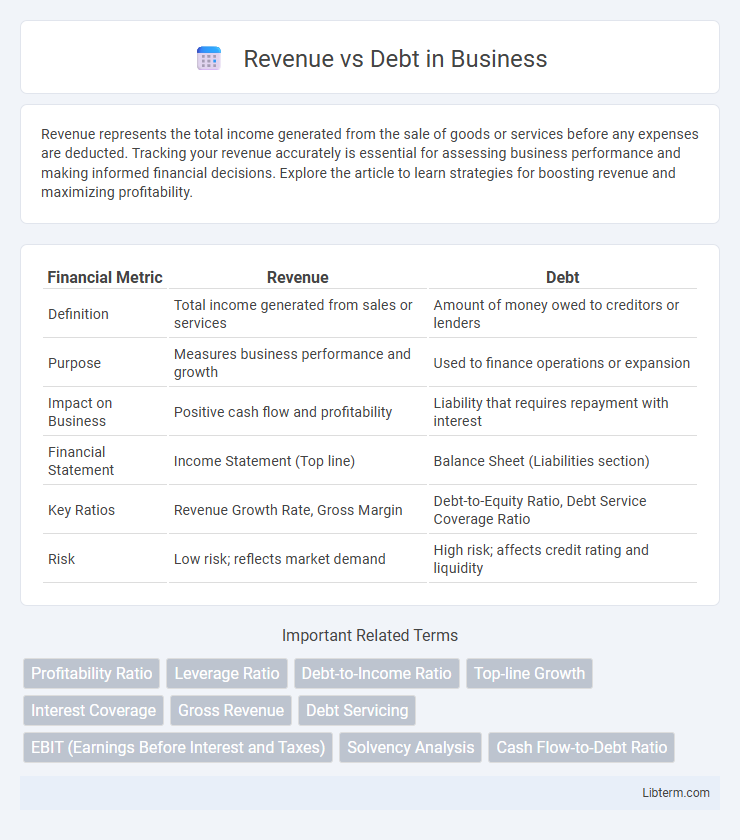
| Financial Metric | Revenue | Debt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total income generated from sales or services | Amount of money owed to creditors or lenders |
| Purpose | Measures business performance and growth | Used to finance operations or expansion |
| Impact on Business | Positive cash flow and profitability | Liability that requires repayment with interest |
| Financial Statement | Income Statement (Top line) | Balance Sheet (Liabilities section) |
| Key Ratios | Revenue Growth Rate, Gross Margin | Debt-to-Equity Ratio, Debt Service Coverage Ratio |
| Risk | Low risk; reflects market demand | High risk; affects credit rating and liquidity |
Introduction to Revenue and Debt
Revenue represents the total income generated by a company from its core business operations, serving as a key indicator of financial health and growth potential. Debt refers to the money borrowed by an organization that must be repaid over time, often including interest, and impacts liquidity and risk management. Understanding the balance between revenue and debt is crucial for effective financial planning and sustaining business operations.
Defining Revenue: Key Concepts
Revenue represents the total income generated by a company from its core business activities, including sales of goods and services before any expenses are deducted. It serves as a critical indicator of a company's financial performance and operational efficiency. Understanding revenue is essential for evaluating a company's ability to cover its debts and sustain long-term growth.
Understanding Debt: Types and Sources
Debt comprises various types such as secured loans, unsecured loans, bonds, and lines of credit, each varying by collateral requirements and repayment terms. Sources of debt financing include banks, credit unions, bond markets, and private lenders, offering businesses and individuals options tailored to their financial needs. Understanding the specific terms, interest rates, and risk associated with each debt type is crucial for effective financial management and maintaining healthy revenue-to-debt ratios.
Revenue vs Debt: Core Differences
Revenue represents the total income generated by a company from its business activities, while debt refers to the borrowed funds that a company must repay with interest. Revenue is a measure of operational success and cash inflow, highlighting profitability potential, whereas debt indicates financial obligations and leverage, impacting liquidity and credit risk. Understanding the balance between revenue and debt is crucial for assessing a company's financial health and long-term sustainability.
The Role of Revenue in Business Growth
Revenue serves as the primary driver of business growth by providing the necessary funds to invest in innovation, expand operations, and enhance competitive advantage. Healthy revenue streams improve cash flow, enabling companies to manage and repay debt more effectively while supporting sustainable scaling. Strong revenue growth signals business viability to investors and lenders, facilitating access to better financing terms and increased capital availability.
The Impact of Debt on Financial Health
Debt significantly affects a company's financial health by increasing financial leverage and risk, which can strain revenue streams if interest payments exceed earnings. High debt levels often lead to reduced credit ratings, limiting access to capital and increasing borrowing costs, thereby constraining operational growth. Maintaining an optimal debt-to-revenue ratio is crucial for sustaining liquidity, ensuring long-term solvency, and enhancing overall financial stability.
Revenue Generation Strategies
Revenue generation strategies focus on increasing cash inflows through diversified sales channels, optimized pricing models, and enhanced customer engagement. Implementing subscription services, upselling, and cross-selling can significantly boost revenue streams, improving financial stability. Effective revenue growth directly impacts a company's ability to manage and reduce debt by increasing available capital for debt servicing.
Managing and Reducing Debt
Effective management of revenue plays a crucial role in reducing debt by ensuring consistent cash flow and prioritizing high-interest liabilities for timely repayments. Allocating a portion of revenue towards a structured debt reduction plan allows businesses and individuals to progressively lower outstanding balances, minimizing financial risk. Regularly analyzing revenue streams and adjusting budgets accordingly enhances the ability to meet debt obligations while maintaining operational stability.
Revenue and Debt in Financial Decision-Making
Revenue represents the total income generated by a company, serving as a critical indicator of operational performance and cash flow availability. Debt involves borrowed capital that must be managed carefully to maintain financial stability and optimize capital structure. In financial decision-making, balancing revenue growth against debt obligations ensures sustainable expansion and minimizes risk exposure.
Balancing Revenue and Debt for Sustainable Success
Balancing revenue and debt is critical for maintaining financial stability and promoting sustainable success in any business. Optimal revenue growth must be aligned with manageable debt levels to ensure liquidity and operational flexibility without risking solvency. Effective debt management strategies combined with diversified revenue streams enhance creditworthiness and long-term profitability.
Revenue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com