Supply Chain Management (SCM) optimizes the flow of goods, information, and finances from raw materials to final products, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. By integrating processes across suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, SCM ensures timely delivery and improved customer satisfaction. Discover how your business can leverage SCM strategies to gain a competitive edge by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
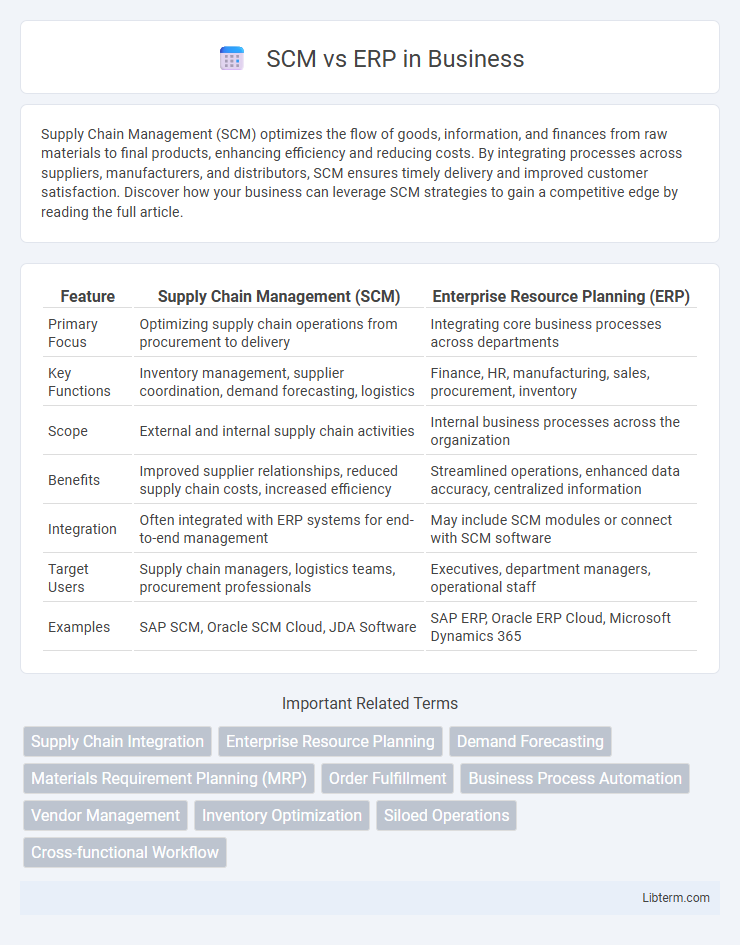
| Feature | Supply Chain Management (SCM) | Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Optimizing supply chain operations from procurement to delivery | Integrating core business processes across departments |
| Key Functions | Inventory management, supplier coordination, demand forecasting, logistics | Finance, HR, manufacturing, sales, procurement, inventory |
| Scope | External and internal supply chain activities | Internal business processes across the organization |
| Benefits | Improved supplier relationships, reduced supply chain costs, increased efficiency | Streamlined operations, enhanced data accuracy, centralized information |
| Integration | Often integrated with ERP systems for end-to-end management | May include SCM modules or connect with SCM software |
| Target Users | Supply chain managers, logistics teams, procurement professionals | Executives, department managers, operational staff |
| Examples | SAP SCM, Oracle SCM Cloud, JDA Software | SAP ERP, Oracle ERP Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
Introduction to SCM and ERP
Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves the coordination of all activities related to sourcing, production, and logistics to optimize the flow of goods and services. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) integrates core business processes, including finance, human resources, and manufacturing, into a unified system to improve organizational efficiency. Both SCM and ERP systems enhance operational performance but focus on different aspects of the business infrastructure.
Key Definitions: What Are SCM and ERP?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) refers to the coordinated oversight of all activities involved in sourcing, procurement, manufacturing, and logistics to optimize the entire supply chain flow. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an integrated software platform that consolidates core business processes--including finance, human resources, and inventory management--into a unified system for improved data accuracy and operational efficiency. Both SCM and ERP systems play crucial roles in enhancing organizational productivity but focus on different facets of business operations.
Core Functions of SCM vs ERP
Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems primarily focus on the optimization of procurement, production, inventory management, and logistics to enhance the flow of goods and information across the supply chain. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business processes including finance, human resources, manufacturing, and sales, providing a unified platform for data management and operational efficiency. SCM emphasizes external supply chain coordination and demand forecasting, whereas ERP centralizes internal business operations for comprehensive resource planning.
Main Differences Between SCM and ERP
SCM (Supply Chain Management) focuses on optimizing the flow of goods, information, and finances across the entire supply chain, from suppliers to customers, enhancing inventory management, demand forecasting, and supplier coordination. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) integrates core business processes across departments such as finance, HR, manufacturing, and sales into a unified system for improved data accuracy and operational efficiency. The main difference lies in SCM's supply chain-centric approach versus ERP's broad organizational resource integration and process standardization.
Integration: How SCM and ERP Work Together
SCM and ERP systems integrate seamlessly to enhance supply chain efficiency by sharing real-time data across procurement, production, and distribution processes. ERP provides a centralized platform for financials and resource planning, while SCM focuses on inventory management and supplier coordination, ensuring synchronized workflow and demand forecasting. This integration reduces operational costs, improves decision-making accuracy, and enables agile response to market changes.
Benefits of Implementing SCM
Implementing Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems enhances inventory control, reduces operational costs, and improves demand forecasting accuracy. SCM fosters real-time collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, leading to streamlined workflows and faster response times. This efficiency boosts customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability and timely delivery.
Advantages of Adopting ERP Systems
ERP systems streamline business processes by integrating various functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relationship management into a unified platform, leading to improved data accuracy and operational efficiency. Real-time data visibility and advanced analytics within ERP solutions enable better decision-making and strategic planning across departments. Enhanced collaboration and automation reduce manual errors, lower operational costs, and facilitate scalability in growing organizations.
Industry Applications: SCM vs ERP
Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems optimize procurement, logistics, and inventory processes to enhance efficiency in manufacturing, retail, and distribution industries, ensuring timely delivery and cost reduction. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions integrate core business functions like finance, HR, and production planning, supporting comprehensive operational control in sectors such as healthcare, automotive, and finance. Industry-specific SCM applications emphasize supplier collaboration and demand forecasting, while ERP focuses on centralized data management and resource allocation across departments.
Choosing the Right Solution: SCM or ERP?
Selecting between Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems depends on specific business needs; SCM excels in optimizing logistics, inventory, and supplier relations, while ERP integrates core processes like finance, HR, and production into a unified platform. Companies prioritizing end-to-end supply chain visibility and demand forecasting may benefit more from SCM solutions, whereas businesses seeking comprehensive operational control and data centralization often prefer ERP systems. Evaluating factors such as scalability, industry requirements, and integration capabilities ensures choosing the right solution to enhance efficiency and decision-making.
Future Trends in SCM and ERP Integration
Future trends in SCM and ERP integration emphasize increased adoption of AI-powered analytics to enhance demand forecasting and inventory optimization. Cloud-based platforms enable real-time data sharing across supply chains, driving agility and reducing operational costs. Blockchain technology is also poised to improve transparency and traceability, fostering trust among stakeholders in integrated SCM-ERP systems.
SCM Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com