A spot contract involves the immediate purchase or sale of assets, such as commodities, currencies, or securities, at the current market price. This type of transaction settles "on the spot," typically within two business days, making it ideal for traders seeking quick execution without delay. Explore the rest of the article to understand how spot contracts can impact your trading strategies.
Table of Comparison
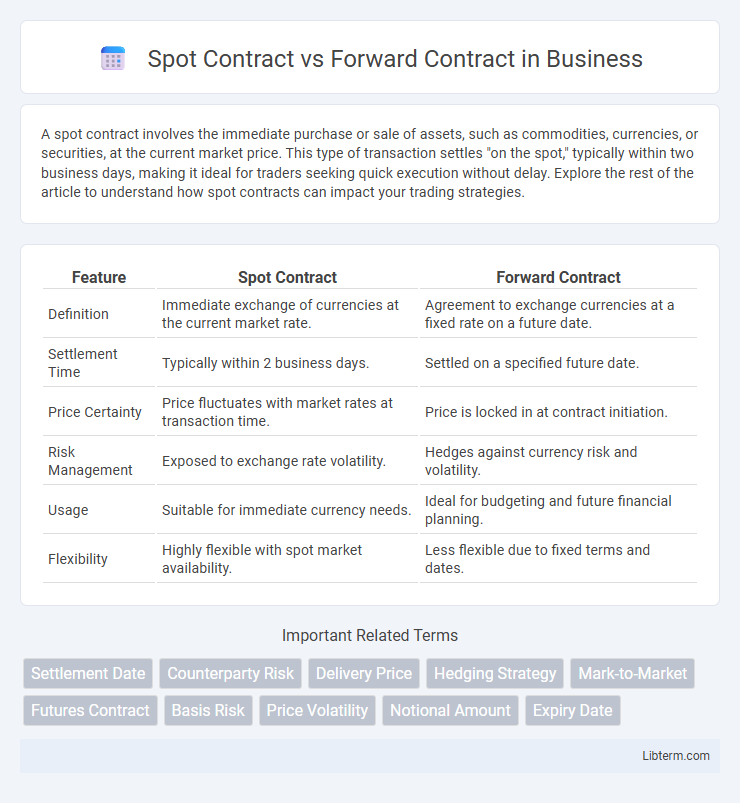
| Feature | Spot Contract | Forward Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immediate exchange of currencies at the current market rate. | Agreement to exchange currencies at a fixed rate on a future date. |
| Settlement Time | Typically within 2 business days. | Settled on a specified future date. |
| Price Certainty | Price fluctuates with market rates at transaction time. | Price is locked in at contract initiation. |
| Risk Management | Exposed to exchange rate volatility. | Hedges against currency risk and volatility. |
| Usage | Suitable for immediate currency needs. | Ideal for budgeting and future financial planning. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible with spot market availability. | Less flexible due to fixed terms and dates. |
Introduction to Spot and Forward Contracts
Spot contracts involve the immediate exchange of financial instruments or commodities at the current market price, with settlement typically occurring within two business days. Forward contracts are customized agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specified future date, offering risk management against price fluctuations. Both contracts are fundamental tools in trading and risk hedging within financial markets and commodities trading.
Key Differences Between Spot and Forward Contracts
Spot contracts involve the immediate exchange of currencies or commodities at the current market price, with settlement typically occurring within two business days. Forward contracts are customized agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a future date, allowing parties to hedge against price fluctuations. The key differences include settlement timing, price certainty, and flexibility, where spot contracts provide instant transaction execution, while forward contracts offer risk management through future price locks.
How Spot Contracts Work
Spot contracts involve the immediate purchase or sale of a financial instrument, currency, or commodity at the current market price, known as the spot price. Settlement typically occurs within two business days, allowing for rapid transfer of ownership and payment between parties. These contracts are crucial in forex trading, commodity markets, and securities for executing transactions based on real-time market conditions.
How Forward Contracts Work
Forward contracts involve a customized agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a future date, allowing businesses to hedge against price volatility. These contracts are settled at maturity, with no initial payment, providing flexibility in terms of contract size, maturity, and underlying asset. Unlike spot contracts that execute immediately at current market prices, forward contracts lock in prices to manage risk in commodities, currencies, or financial instruments.
Advantages of Spot Contracts
Spot contracts offer immediate settlement and delivery, providing liquidity and minimizing counterparty risk by avoiding future price fluctuations. They enable traders and businesses to capitalize on current market prices, ensuring transparent and straightforward transactions. Spot contracts are particularly advantageous in volatile markets where rapid execution and payment are critical for operational efficiency.
Advantages of Forward Contracts
Forward contracts offer the advantage of locking in prices for future transactions, providing businesses with protection against price volatility and currency fluctuations. These customized, over-the-counter agreements allow parties to tailor terms specific to their needs, including quantity, delivery date, and price. By eliminating uncertainty, forward contracts enhance financial planning and risk management for companies involved in international trade and commodity markets.
Risks Associated with Spot Contracts
Spot contracts carry significant risks including price volatility, as transactions occur immediately at current market rates, exposing parties to sudden unfavorable price shifts. Liquidity risk is also present due to the requirement for immediate settlement, which can strain cash flows or operational capacity. Unlike forward contracts, spot contracts lack the ability to hedge future price uncertainties, increasing exposure to market fluctuations.
Risks Associated with Forward Contracts
Forward contracts carry inherent risks including counterparty risk, where the other party may default on the agreement, leading to financial loss. Market risk is significant due to price fluctuations between the contract initiation and settlement date, potentially resulting in unfavorable exchange rates. Liquidity risk is also present because forward contracts are typically customized and not traded on standard exchanges, making them harder to exit or transfer before maturity.
Spot vs Forward Contracts: Which to Choose?
Spot contracts involve immediate settlement and delivery of assets at current market prices, ideal for transactions requiring quick execution and minimal uncertainty. Forward contracts lock in prices for future delivery dates, offering protection against price volatility and facilitating customized risk management in volatile markets. Choosing between spot and forward contracts depends on liquidity needs, risk tolerance, and market outlook to optimize financial strategy.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Contract for Your Needs
Selecting between a spot contract and a forward contract depends on your risk tolerance and market expectations. Spot contracts suit immediate transactions with current market rates, while forward contracts hedge against future price fluctuations by locking in rates. Understanding your financial goals and market volatility is essential for making the most strategic contract choice.
Spot Contract Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com