A rights issue allows existing shareholders to purchase additional shares at a discounted price, helping companies raise capital efficiently. This method prevents share dilution for current investors while providing funds for expansion or debt reduction. Explore the full article to understand how a rights issue could impact your investment strategy.
Table of Comparison
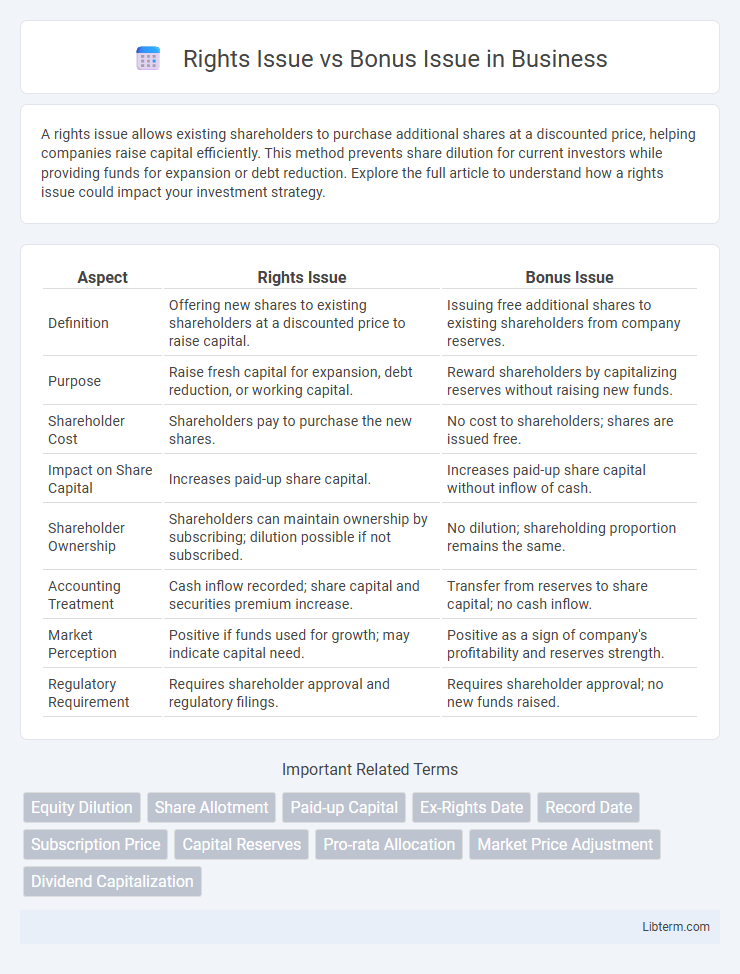
| Aspect | Rights Issue | Bonus Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Offering new shares to existing shareholders at a discounted price to raise capital. | Issuing free additional shares to existing shareholders from company reserves. |
| Purpose | Raise fresh capital for expansion, debt reduction, or working capital. | Reward shareholders by capitalizing reserves without raising new funds. |
| Shareholder Cost | Shareholders pay to purchase the new shares. | No cost to shareholders; shares are issued free. |
| Impact on Share Capital | Increases paid-up share capital. | Increases paid-up share capital without inflow of cash. |
| Shareholder Ownership | Shareholders can maintain ownership by subscribing; dilution possible if not subscribed. | No dilution; shareholding proportion remains the same. |
| Accounting Treatment | Cash inflow recorded; share capital and securities premium increase. | Transfer from reserves to share capital; no cash inflow. |
| Market Perception | Positive if funds used for growth; may indicate capital need. | Positive as a sign of company's profitability and reserves strength. |
| Regulatory Requirement | Requires shareholder approval and regulatory filings. | Requires shareholder approval; no new funds raised. |
Introduction to Rights Issue and Bonus Issue
Rights Issue allows existing shareholders to purchase additional shares at a discounted price within a specific period, enabling companies to raise fresh equity capital without diluting ownership significantly. Bonus Issue involves the issuance of free shares to existing shareholders based on their current holdings, effectively capitalizing reserves and increasing the total number of shares while maintaining the company's market capitalization. Both are corporate actions used to adjust share capital, with Rights Issue aimed at financing and Bonus Issue focused on rewarding shareholders.
Definition and Key Differences
A rights issue is a way for companies to raise capital by offering existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase additional shares at a discounted price, maintaining their proportional ownership. A bonus issue involves distributing additional shares free of charge to existing shareholders, converting a portion of reserves into share capital without raising new funds. Key differences include that rights issues entail fresh capital inflow and shareholder payment, whereas bonus issues increase share quantity without any cash transaction or capital infusion.
Purpose and Objectives
Rights issues aim to raise fresh capital from existing shareholders by offering discounted shares, primarily to fund expansion, reduce debt, or improve working capital. Bonus issues distribute additional shares to current shareholders without raising new funds, serving to reward shareholders and increase share liquidity. Both strategies adjust share structure but differ fundamentally in capital generation and shareholder benefit objectives.
Mechanism and Process
Rights issue allows existing shareholders to purchase additional shares at a discounted price within a specific time frame, enhancing capital infusion by raising fresh equity directly from current investors. The company sends entitlement letters detailing the offer proportionate to existing holdings, enabling shareholders to either subscribe, sell, or renounce their rights. Bonus issue involves issuing free additional shares to existing shareholders based on their current holdings, capitalizing reserves without raising new funds, and requires board and shareholder approval before distribution.
Impact on Share Capital
Rights Issue increases share capital by offering existing shareholders the option to purchase additional shares, resulting in fresh equity infusion and potential dilution of ownership. Bonus Issue reallocates reserves to issue free shares to existing shareholders, increasing the number of shares without raising new capital or changing the overall equity value. Rights Issues affect the company's capital structure by raising new funds, whereas Bonus Issues primarily impact share distribution without altering the total share capital value.
Effects on Shareholder Value
Rights issues dilute shareholder value if existing shareholders do not exercise their rights, as new shares are issued at a discount, potentially lowering the stock price. Bonus issues increase the number of shares held by shareholders without additional cost, preserving value but diluting earnings per share (EPS). Both actions impact market perception; rights issues can signal capital raising needs, while bonus issues may indicate confidence in future profits.
Eligibility Criteria for Shareholders
Rights issues require shareholders to hold shares on the record date to be eligible for purchasing additional shares at a discounted rate, ensuring only existing investors can participate. Bonus issues grant additional shares to current shareholders in proportion to their existing holdings, with eligibility determined by the shareholder's status on the record date without any payment required. Both methods rely on the shareholder register as of the record date to establish eligibility but differ fundamentally in the financial commitment from shareholders.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Rights Issue allows existing shareholders to purchase additional shares at a discounted price, providing companies with a significant capital influx without incurring debt, but it may dilute share value and require shareholder funding. Bonus Issue rewards shareholders by distributing free shares proportional to their holdings, enhancing liquidity and shareholder confidence without additional investment, yet it does not raise new capital and may lead to share price dilution. Both methods impact shareholding patterns differently, with Rights Issue potentially altering control dynamics, while Bonus Issue primarily adjusts market perception and stock liquidity.
Tax Implications
Rights issues often trigger tax liabilities as they may be regarded as a capital gains event when shares are sold, with the premium value or discount impacting cost basis calculations. Bonus issues usually do not result in immediate tax consequences since they are treated as a capital adjustment, increasing the number of shares held without altering the total cost of investment. Investors must monitor local tax regulations closely, as treatment can vary significantly by jurisdiction, influencing portfolio tax planning strategies.
Rights Issue vs Bonus Issue: Summary Comparison
Rights Issue allows existing shareholders to purchase additional shares at a discounted price, providing capital infusion to the company, whereas Bonus Issue involves the free distribution of additional shares to shareholders from the company's reserves without raising new funds. Rights Issue dilutes shareholding if shareholders do not subscribe, while Bonus Issue increases share quantity without changing ownership percentage. Key differences include capital raising in Rights Issue versus share capitalization in Bonus Issue, impacting the company's balance sheet and shareholder equity differently.
Rights Issue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com