A spot contract is an agreement to buy or sell an asset immediately at the current market price, typically settling within two business days. This type of contract is commonly used in forex, commodities, and securities trading where quick execution and delivery are essential. Explore the article to understand how a spot contract can benefit your trading strategy.
Table of Comparison
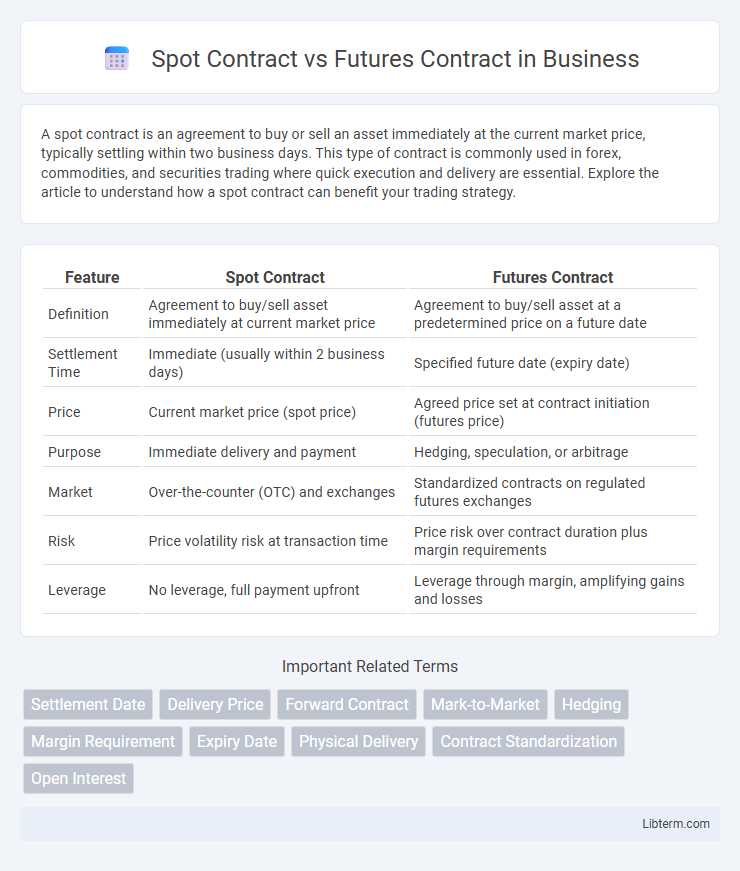
| Feature | Spot Contract | Futures Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agreement to buy/sell asset immediately at current market price | Agreement to buy/sell asset at a predetermined price on a future date |
| Settlement Time | Immediate (usually within 2 business days) | Specified future date (expiry date) |
| Price | Current market price (spot price) | Agreed price set at contract initiation (futures price) |
| Purpose | Immediate delivery and payment | Hedging, speculation, or arbitrage |
| Market | Over-the-counter (OTC) and exchanges | Standardized contracts on regulated futures exchanges |
| Risk | Price volatility risk at transaction time | Price risk over contract duration plus margin requirements |
| Leverage | No leverage, full payment upfront | Leverage through margin, amplifying gains and losses |
Introduction to Spot and Futures Contracts
Spot contracts involve the immediate exchange of assets at current market prices, enabling traders to buy or sell commodities, currencies, or securities with instant delivery. Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date, commonly used for hedging or speculative purposes in commodities, forex, and financial markets. The distinction between spot and futures markets lies in timing and purpose: spot contracts settle immediately, while futures contracts allow price locking and risk management over time.
Key Differences Between Spot and Futures Contracts
Spot contracts involve the immediate purchase and delivery of assets at current market prices, whereas futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell assets at a predetermined price on a future date. Spot transactions settle instantly, providing immediate ownership transfer, while futures contracts require margin deposits and are settled at contract expiration or through offsetting trades. Risk exposure differs as spot contracts reflect current market risks, while futures allow hedging against price volatility through leverage and contract standardization.
How Spot Contracts Work
Spot contracts involve the immediate exchange of financial instruments or commodities at current market prices, with settlement typically occurring within two business days. These contracts reflect real-time supply and demand, allowing traders to lock in prices and transfer ownership instantly. Spot markets facilitate liquidity by enabling prompt transactions without the delays associated with future settlement dates.
Understanding Futures Contracts
Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date, providing a way to hedge against price volatility or speculate on price movements. Unlike spot contracts, which involve immediate delivery and settlement of assets, futures contracts settle at maturity, often without the physical exchange of the underlying asset through cash settlement. These contracts are traded on regulated exchanges, featuring margin requirements and daily mark-to-market processes that manage counterparty risk and ensure contract integrity.
Advantages of Spot Contracts
Spot contracts offer immediate settlement and ownership transfer, providing quick access to assets without the complexities of margin requirements typical in futures contracts. They allow traders to benefit from current market prices with no obligation to future delivery, minimizing exposure to price volatility risk inherent in futures markets. Spot trading facilitates straightforward transactions, making it ideal for hedgers and investors seeking instant asset acquisition and liquidity.
Benefits of Futures Contracts
Futures contracts offer benefits such as price hedging, allowing traders to lock in prices and manage risk against market volatility. They provide standardized terms and high liquidity on regulated exchanges, facilitating easier trade execution and transparency. Additionally, leverage in futures trading enables greater capital efficiency by controlling large positions with relatively small margin deposits.
Risks Associated with Spot Contracts
Spot contracts involve the immediate exchange of assets at the current market price, exposing traders to price volatility and liquidity risks due to rapid market fluctuations. Unlike futures contracts, spot contracts lack built-in risk management tools such as hedging or margin requirements, increasing the potential for significant financial loss in unstable markets. The absence of contractual time frames in spot trading also leads to settlement risks, especially in less regulated or illiquid markets.
Risks Involved in Futures Contracts
Futures contracts carry significant risks including market volatility that can lead to substantial financial losses due to margin calls and leverage effects. Unlike spot contracts settled immediately at the current market price, futures contracts involve future obligations that may not align with market movements, increasing exposure to price fluctuations. Counterparty risk and the potential for contract default also heighten the risk profile in futures trading compared to spot transactions.
Spot vs Futures: Which Is Right for You?
Spot contracts enable immediate purchase or sale of assets at current market prices, providing straightforward transactions and instant ownership transfer. Futures contracts involve agreeing on a price today for asset delivery at a specified date, offering hedging opportunities and potential leverage but requiring margin and risk management. Choosing between spot and futures depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and preference for immediate ownership versus speculative or hedging strategies.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Spot and Futures Contracts
Choosing between spot and futures contracts depends on an investor's risk tolerance, market outlook, and investment horizon. Spot contracts offer immediate settlement and lower complexity, suitable for those seeking direct ownership and quick transactions. Futures contracts provide leverage and hedging opportunities, appealing to traders aiming for speculative gains or risk management over longer timeframes.
Spot Contract Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com