Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) is a unit of measurement that standardizes employee workload by converting part-time hours into full-time equivalents, facilitating accurate workforce planning and budgeting. Understanding FTE helps organizations optimize resource allocation and assess productivity more effectively. Discover how mastering FTE calculations can improve Your business management in the full article ahead.
Table of Comparison
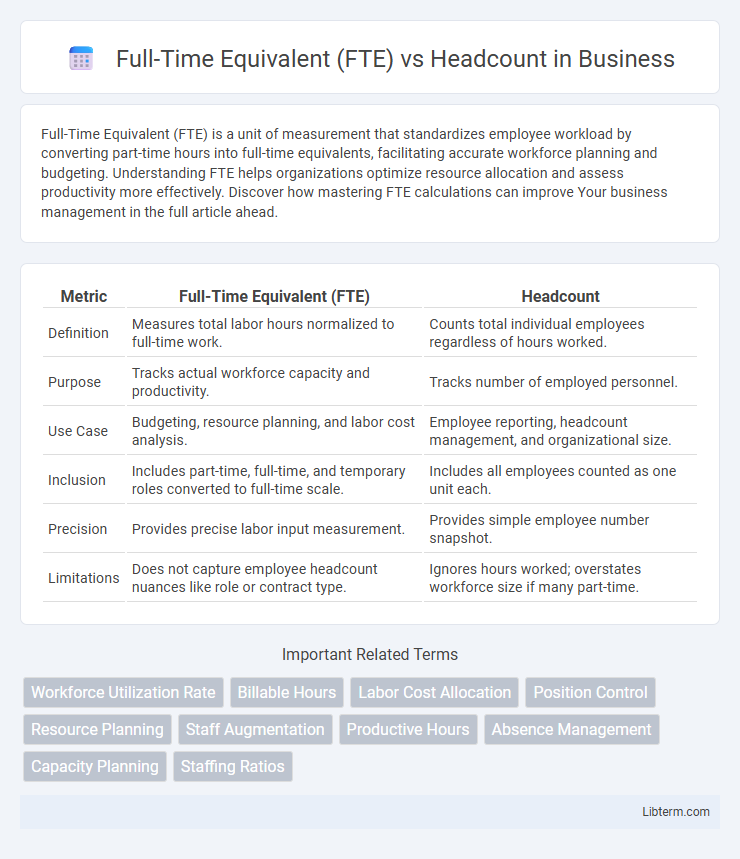
| Metric | Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) | Headcount |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures total labor hours normalized to full-time work. | Counts total individual employees regardless of hours worked. |
| Purpose | Tracks actual workforce capacity and productivity. | Tracks number of employed personnel. |
| Use Case | Budgeting, resource planning, and labor cost analysis. | Employee reporting, headcount management, and organizational size. |
| Inclusion | Includes part-time, full-time, and temporary roles converted to full-time scale. | Includes all employees counted as one unit each. |
| Precision | Provides precise labor input measurement. | Provides simple employee number snapshot. |
| Limitations | Does not capture employee headcount nuances like role or contract type. | Ignores hours worked; overstates workforce size if many part-time. |
Understanding Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) measures workforce capacity by converting part-time and full-time hours into a standardized unit representing one full-time employee's workload. This metric enables organizations to analyze labor resources more accurately than simple headcount by reflecting actual hours worked rather than the number of individuals employed. Understanding FTE is essential for workforce planning, budgeting, and assessing productivity across different employment arrangements.
Defining Headcount in Workforce Metrics
Headcount in workforce metrics refers to the total number of individual employees working for an organization, regardless of their work hours or employment status. Unlike Full-Time Equivalent (FTE), which standardizes labor input by converting part-time hours into full-time units, headcount simply counts each employee as one unit. Accurate headcount data is essential for understanding the total workforce size, planning resources, and managing organizational structures.
Key Differences Between FTE and Headcount
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) measures the total workload of employees, converting part-time hours into full-time employee equivalents, providing a standardized metric for labor capacity. Headcount represents the actual number of individual employees, regardless of their full-time or part-time status, emphasizing workforce size rather than workload. Unlike headcount, FTE offers a clearer insight into productivity and resource allocation by reflecting labor input based on hours worked instead of simply counting employees.
Why FTE Matters for Resource Planning
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) provides a standardized measure of workforce capacity by converting part-time and variable hours into a full-time workload equivalent, ensuring accurate resource allocation. Unlike headcount, which counts each employee regardless of hours worked, FTE reflects the actual labor input, allowing for precise budgeting and forecasting. This metric is crucial for optimizing staffing levels, managing labor costs, and aligning workforce capabilities with project demands.
When to Use Headcount vs FTE
Headcount measures the total number of employees, ideal for understanding workforce size and staffing levels, while Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) quantifies labor based on hours worked relative to full-time hours, useful for budgeting and productivity analysis. Use headcount when tracking individual employee numbers or compliance with headcount-based regulations, and rely on FTE for assessing workforce capacity, financial forecasting, or comparing part-time and full-time labor contributions. Employers aiming to balance resource allocation and labor cost efficiency should distinguish between headcount and FTE metrics to make informed staffing decisions.
Calculating FTE: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) starts by determining the total hours worked by all employees during a specific period and dividing this by the standard full-time hours for that period, typically 40 hours per week. For example, if the standard full-time workweek is 40 hours and part-time employees together work 80 hours, the FTE equals 2 (80 divided by 40). This precise calculation allows organizations to measure workforce capacity more accurately than headcount, which only counts individuals regardless of their time contributions.
Common Industry Applications of FTE and Headcount
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) and Headcount metrics serve distinct roles in workforce analysis across industries such as healthcare, education, and manufacturing. FTE provides a standardized measure of labor input by converting part-time hours into full-time workload equivalents, enabling precise budgeting, staffing, and productivity assessment. Headcount offers a straightforward count of employees, crucial for compliance reporting, diversity tracking, and organizational planning.
Impact on Budgeting and Payroll
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) provides a standardized measurement of workforce hours, enabling more accurate budgeting and payroll forecasting compared to headcount, which simply counts employees regardless of work hours. Using FTE helps organizations align labor costs with actual working time, ensuring payroll expenses reflect true resource allocation. This approach reduces budget discrepancies by accounting for part-time and variable-hour employees, resulting in more precise financial planning.
Challenges in Reporting FTE and Headcount
Challenges in reporting Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) and headcount arise from inconsistent definitions across organizations and industries, complicating data comparisons. FTE calculations require accurate tracking of part-time, temporary, and variable-hour employees, which can lead to errors if time reporting systems are inadequate. Headcount metrics often overlook variations in work hours and employment types, resulting in skewed workforce analysis and misinformed decision-making.
Best Practices for Workforce Measurement
Accurate workforce measurement requires distinguishing Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) from headcount, as FTE standardizes employee hours into full-time units, enabling better resource allocation and cost analysis. Best practices include using FTE for budgeting and productivity metrics while relying on headcount for understanding total employee numbers and diversity tracking. Combining both metrics ensures a comprehensive view of labor capacity and workforce composition, aiding strategic decision-making.
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com