Collaboration enhances creativity and efficiency by combining diverse skills and perspectives to achieve common goals. Effective communication and mutual respect are essential to foster a productive collaborative environment. Discover how you can leverage collaboration to drive success in your projects by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
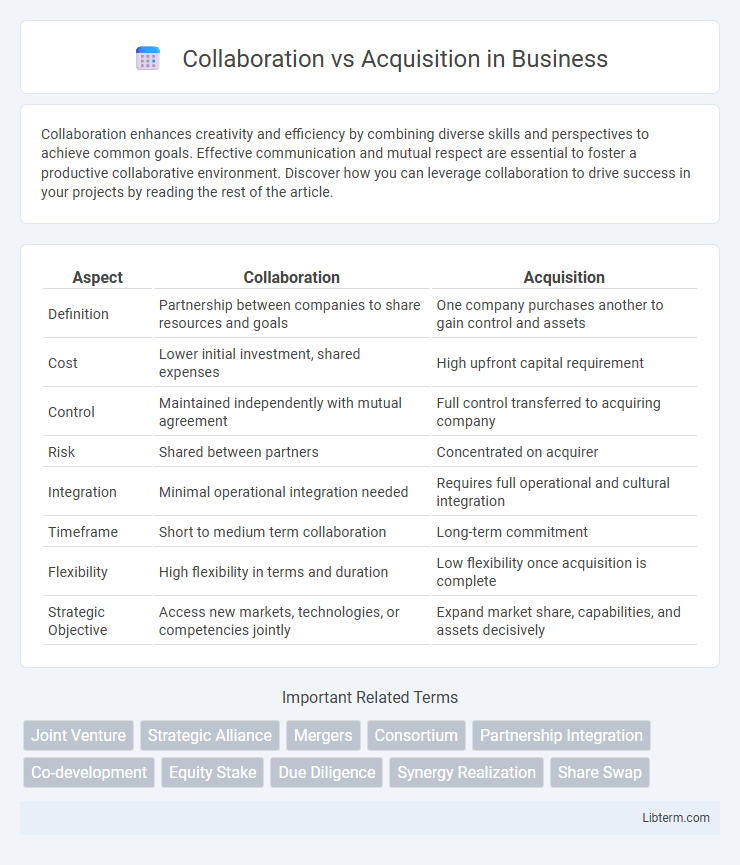
| Aspect | Collaboration | Acquisition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between companies to share resources and goals | One company purchases another to gain control and assets |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, shared expenses | High upfront capital requirement |
| Control | Maintained independently with mutual agreement | Full control transferred to acquiring company |
| Risk | Shared between partners | Concentrated on acquirer |
| Integration | Minimal operational integration needed | Requires full operational and cultural integration |
| Timeframe | Short to medium term collaboration | Long-term commitment |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in terms and duration | Low flexibility once acquisition is complete |
| Strategic Objective | Access new markets, technologies, or competencies jointly | Expand market share, capabilities, and assets decisively |
Understanding Collaboration and Acquisition
Collaboration involves two or more organizations working together toward shared goals while maintaining their independence, fostering innovation, resource sharing, and flexibility. Acquisition entails one company purchasing another, leading to full control and integration of the acquired entity's assets, operations, and workforce. Understanding collaboration versus acquisition requires analyzing factors such as strategic objectives, risk tolerance, resource commitment, and desired level of operational control.
Key Differences Between Collaboration and Acquisition
Collaboration involves two or more organizations working together to achieve common goals while maintaining their independence, whereas acquisition occurs when one company purchases another, resulting in full ownership and control. Key differences include the level of control, where collaboration emphasizes shared decision-making and resource pooling, and acquisition entails complete integration of operations. Collaboration typically allows for flexibility and mutual benefit, while acquisition often focuses on consolidation and strategic expansion.
Strategic Advantages of Collaboration
Collaboration leverages complementary strengths and shared resources to drive innovation and accelerate market entry, enhancing competitive positioning without the high costs associated with acquisitions. Strategic partnerships enable access to new technologies, customer bases, and expertise, fostering agility and reducing risks compared to outright ownership transfers. This approach supports sustainable growth by aligning goals and capabilities while preserving operational flexibility and minimizing integration challenges.
Strategic Benefits of Acquisition
Acquisition offers companies immediate access to new markets, technologies, and customer bases, accelerating growth and competitive advantage far beyond organic expansion. It enables full control over acquired resources and intellectual property, ensuring integration aligns closely with strategic objectives and operational efficiency. Furthermore, acquisitions can eliminate competition and create economies of scale, driving higher profitability and market share dominance.
Risks and Challenges in Collaboration
Collaboration involves shared decision-making and resource allocation, which can lead to conflicts over control, goals, and intellectual property rights. Misaligned expectations and cultural differences between partners increase the risk of communication breakdowns and project delays. Ensuring trust and compatibility requires rigorous due diligence and ongoing relationship management to mitigate these collaboration challenges.
Potential Pitfalls of Acquisition
Acquisitions often pose significant risks such as cultural clashes between companies, which can lead to employee dissatisfaction and decreased productivity. Financial burdens from acquisition costs and unforeseen liabilities may strain the acquiring company's resources and impact its overall stability. Integration challenges, including incompatible systems and processes, frequently result in operational disruptions and delayed realization of anticipated synergies.
When to Choose Collaboration Over Acquisition
Choose collaboration over acquisition when market uncertainty demands flexibility and rapid innovation without full integration risks. Collaboration allows sharing resources, expertise, and market access while maintaining operational independence and minimizing financial exposure. Opt for collaboration to test synergies and build strategic partnerships before committing to costly acquisitions.
When Acquisition Makes Strategic Sense
Acquisition makes strategic sense when rapid market expansion, control over key assets, or elimination of competition is critical to business goals. It enables companies to integrate valuable intellectual property, talent, or technologies swiftly, accelerating innovation and scaling operations. High capital availability and clear alignment with long-term objectives further justify the acquisition route over collaboration.
Real-World Examples: Collaboration vs Acquisition
Collaboration between companies, such as the strategic alliance between Starbucks and Nestle, allows both parties to leverage strengths while sharing risks without full ownership transfer. In contrast, acquisitions like Amazon's purchase of Whole Foods provide immediate market entry and control but involve higher capital investment and integration challenges. Real-world cases demonstrate collaboration's flexibility in innovation and market testing, while acquisitions offer definitive expansion and resource consolidation.
Future Trends in Business Partnerships and Mergers
Future trends in business partnerships emphasize strategic collaboration leveraging digital platforms, AI integration, and sustainability goals to drive innovation and agility. Acquisitions will increasingly target tech-driven startups and ESG-compliant firms to accelerate market expansion and competitive advantage. Hybrid models combining collaboration with selective acquisitions are expected to dominate, optimizing resource sharing while maintaining growth through targeted buyouts.
Collaboration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com