The maturity period defines the time frame when an investment or financial instrument reaches its full value, allowing the principal amount to be repaid along with any accrued interest. Understanding this period is crucial for making informed decisions about when to withdraw or reinvest funds to maximize returns. Explore the rest of the article to learn how maturity periods impact your financial planning and investment strategies.
Table of Comparison
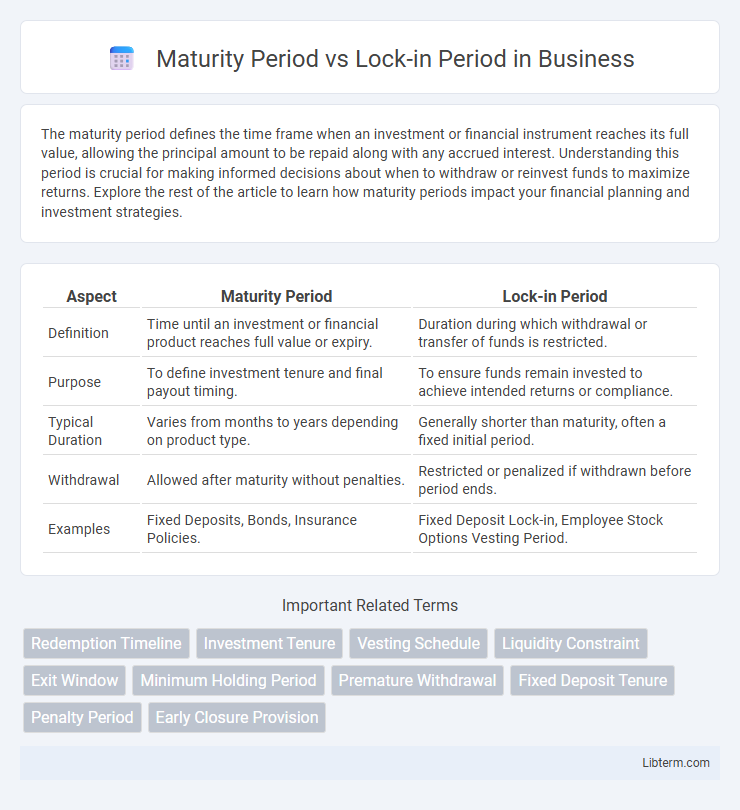
| Aspect | Maturity Period | Lock-in Period |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Time until an investment or financial product reaches full value or expiry. | Duration during which withdrawal or transfer of funds is restricted. |
| Purpose | To define investment tenure and final payout timing. | To ensure funds remain invested to achieve intended returns or compliance. |
| Typical Duration | Varies from months to years depending on product type. | Generally shorter than maturity, often a fixed initial period. |
| Withdrawal | Allowed after maturity without penalties. | Restricted or penalized if withdrawn before period ends. |
| Examples | Fixed Deposits, Bonds, Insurance Policies. | Fixed Deposit Lock-in, Employee Stock Options Vesting Period. |
Understanding Maturity Period
The maturity period refers to the duration after which a financial instrument or investment, such as a fixed deposit or bond, reaches its full term and the principal amount along with accrued interest becomes payable to the investor. Understanding the maturity period is essential for effective financial planning and liquidity management because it determines when funds will be accessible without penalties. Unlike the lock-in period, which restricts withdrawals for a specified time, the maturity period marks the endpoint at which the investment naturally concludes.
Defining Lock-in Period
The lock-in period refers to a predetermined span during which investors cannot redeem or withdraw their funds from an investment. It is a crucial feature in financial instruments like mutual funds, fixed deposits, and pension plans that ensures the capital remains invested to achieve desired returns. While the maturity period defines the total lifespan until the investment matures, the lock-in period strictly limits early access to funds, preserving investment discipline and growth potential.
Key Differences Between Maturity and Lock-in Periods
Maturity period refers to the total duration after which an investment or financial product reaches full term and the principal amount along with accrued interest becomes available to the investor. Lock-in period denotes the minimum time frame during which the investor cannot withdraw or redeem the investment, ensuring capital remains invested and prevents premature exit. The key difference lies in their function: maturity period signals the investment's lifespan, while lock-in period restricts early liquidity, often shorter than or equal to the maturity period.
Importance of Maturity Period in Investments
The maturity period in investments is crucial as it defines the timeline for when the principal and accrued returns become accessible, impacting liquidity and financial planning. Unlike the lock-in period, which restricts withdrawals to encourage long-term savings, the maturity period marks the completion of the investment cycle, ensuring investors receive full benefits. Understanding the maturity period helps investors align their investment horizon with financial goals, optimize returns, and manage risks effectively.
Role of Lock-in Period in Financial Products
The lock-in period in financial products serves as a predefined timeframe during which investors cannot withdraw their funds, ensuring disciplined investing and preventing premature redemption. This period stabilizes the investment pool, enabling fund managers to execute long-term strategies without the disruption of sudden outflows. By enforcing a lock-in period, financial products often achieve better returns compared to those without such restrictions, aligning investor goals with the product's maturity timeline.
How Maturity Period Affects Withdrawal Options
The maturity period directly influences withdrawal options by determining when the invested principal becomes accessible without penalties. During the maturity period, funds are typically locked in, restricting premature withdrawals or subjecting them to penalties and reduced returns. After the maturity period ends, investors gain full access to their funds, enabling withdrawals or reinvestment without restrictions.
Impact of Lock-in Period on Liquidity
The lock-in period directly affects liquidity by restricting investors from redeeming or selling their investments until the specified duration expires, thereby limiting access to funds despite the maturity period potentially allowing earlier redemption. During the lock-in period, assets remain illiquid, which can pose challenges for investors needing immediate cash flow or financial flexibility. Understanding the distinction between maturity and lock-in periods is crucial for assessing the timing of liquidity availability and managing investment risk accordingly.
Tax Implications: Maturity Period vs Lock-in Period
The maturity period marks the end of an investment's tenure when both principal and accrued interest become payable and taxable according to prevailing income tax laws. The lock-in period refers to a fixed timeframe during which the investment cannot be withdrawn without incurring penalties or tax consequences, often designed to encourage long-term savings. Tax implications differ as premature withdrawal during the lock-in period may attract penalties and higher tax liability, whereas at maturity, gains are typically subject to capital gains tax or income tax based on the investment type.
Choosing Investments: Considering Both Periods
Choosing investments requires careful evaluation of both maturity period and lock-in period to balance liquidity and returns. The maturity period determines when the principal amount and interest are fully payable, while the lock-in period restricts premature withdrawal, affecting investment flexibility. Understanding these timelines helps investors select options aligned with their financial goals and liquidity needs.
Tips for Managing Maturity and Lock-in Periods
Managing maturity periods and lock-in periods efficiently requires strategic financial planning and awareness of investment goals. Prioritize reviewing the terms of fixed deposits, mutual funds, or insurance policies to understand penalties or benefits associated with early withdrawals during lock-in periods. Leveraging reminders and portfolio tracking tools ensures timely actions at maturity, optimizing liquidity and minimizing losses.
Maturity Period Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com