Closed source technology protects proprietary software by restricting access to its underlying code, enhancing security and control for developers. This approach often guarantees a more stable and polished user experience, as code modifications are tightly regulated. Explore the rest of the article to understand how closed source technology can impact Your software choices and innovation strategies.
Table of Comparison
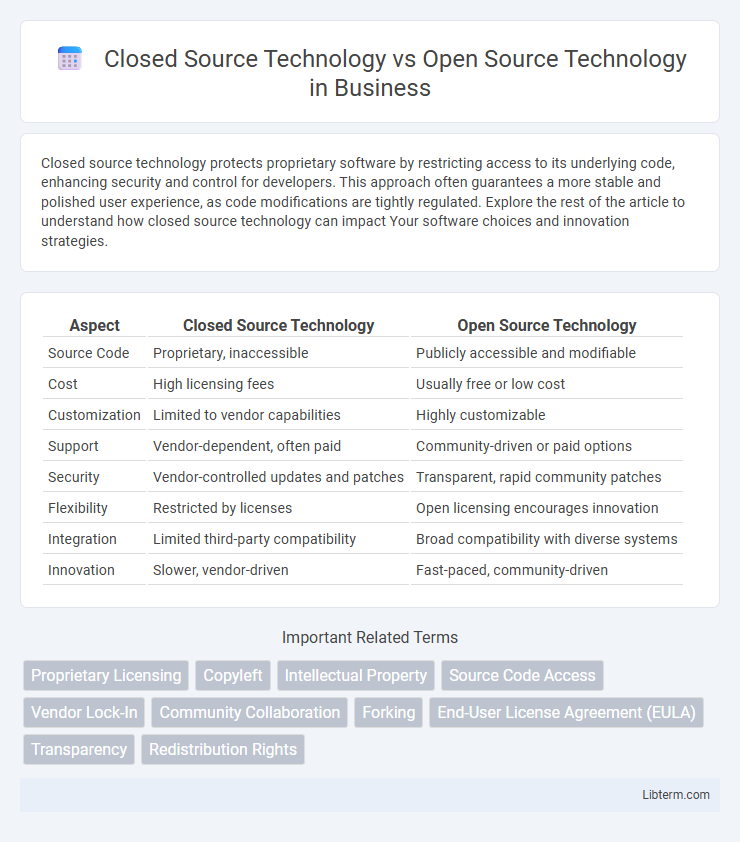
| Aspect | Closed Source Technology | Open Source Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Source Code | Proprietary, inaccessible | Publicly accessible and modifiable |
| Cost | High licensing fees | Usually free or low cost |
| Customization | Limited to vendor capabilities | Highly customizable |
| Support | Vendor-dependent, often paid | Community-driven or paid options |
| Security | Vendor-controlled updates and patches | Transparent, rapid community patches |
| Flexibility | Restricted by licenses | Open licensing encourages innovation |
| Integration | Limited third-party compatibility | Broad compatibility with diverse systems |
| Innovation | Slower, vendor-driven | Fast-paced, community-driven |
Introduction to Closed Source and Open Source Technologies
Closed source technology refers to software whose source code is not shared with the public, restricting access and modification to authorized developers only. Open source technology allows users to freely view, modify, and distribute the source code, promoting collaboration and transparency. This fundamental difference impacts software development, security, customization, and licensing models within the tech industry.
Core Differences Between Closed and Open Source
Closed source technology restricts access to its source code, allowing only the original developers to modify or distribute the software, which ensures controlled security and proprietary ownership. Open source technology provides public access to its source code, enabling collaboration, customization, and transparency while encouraging community-driven improvements. The core differences lie in accessibility, control over the software, and the collaboration model, with closed source emphasizing proprietary rights and open source promoting shared development.
Licensing and Legal Considerations
Closed source technology operates under proprietary licenses that restrict access to source code, limiting modification, distribution, and usage to the terms defined by the software vendor. Open source technology uses licenses such as GPL, MIT, or Apache, granting users the rights to freely use, modify, and distribute the software, often requiring attribution and maintaining the same license for derivatives. Legal considerations for closed source often involve strict compliance with licensing agreements and potential penalties for violations, while open source requires adherence to license obligations to avoid infringement, especially in commercial applications.
Security Aspects: Open vs Closed Source
Closed source technology limits code access, reducing exposure to unauthorized modifications but potentially obscuring vulnerabilities from public scrutiny. Open source technology allows continuous peer review, facilitating rapid identification and patching of security flaws through community collaboration. Security depends on implementation and maintenance practices rather than the source model alone.
Cost Implications and Total Cost of Ownership
Closed source technology often entails higher upfront licensing fees and ongoing subscription costs, increasing the total cost of ownership (TCO) for organizations. Open source technology reduces initial expenses by offering free or low-cost access to software, but potential costs arise from customization, support, and maintenance requirements. Evaluating TCO requires considering not only software acquisition but also long-term expenses related to integration, training, and scalability within both closed and open source environments.
Customization and Flexibility
Closed source technology offers limited customization and flexibility as the source code is proprietary, restricting users from modifying or adapting the software to specific needs. Open source technology provides extensive customization and flexibility by allowing users to access, modify, and distribute the source code freely, fostering innovation and tailored solutions. The collaborative nature of open source communities accelerates feature development and adaptability compared to the rigid structure of closed source environments.
Community Support and Development
Open Source Technology thrives on active community support, offering rapid innovation, transparency, and collaborative problem-solving from developers worldwide. Closed Source Technology relies on proprietary teams, limiting external contributions but ensuring controlled development and consistent updates. The vibrant open source communities accelerate feature improvements and security patches, while closed source depends on internal resources for maintenance and support.
Business Adoption and Industry Trends
Closed source technology remains prevalent in industries requiring strict security and control, such as finance and healthcare, enabling businesses to protect proprietary information and comply with regulations. Open source technology sees growing adoption across various sectors due to its cost-effectiveness, rapid innovation, and collaborative development model, with enterprises leveraging platforms like GitHub and Linux to accelerate digital transformation. Industry trends indicate a hybrid approach, where companies integrate open source components within proprietary systems to balance flexibility, innovation, and governance.
Examples of Popular Closed and Open Source Technologies
Closed source technology like Microsoft Windows, Adobe Photoshop, and Apple's iOS dominate industries with proprietary software controlled by companies, ensuring exclusive access to source code and licensing restrictions. In contrast, popular open source technologies such as Linux operating systems, Apache HTTP Server, and the Mozilla Firefox browser empower users with transparency, collaborative development, and customizable solutions. These open source projects benefit from vibrant communities, rapid innovation, and cost-effective deployment compared to their closed source counterparts.
Choosing the Right Technology: Key Factors to Consider
Choosing the right technology involves evaluating factors such as flexibility, security, and community support. Closed source technology offers controlled environments and proprietary support, while open source technology provides transparency, customization, and collaborative development. Assessing project requirements, budget constraints, and long-term scalability is essential for making an informed decision between these two approaches.
Closed Source Technology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com