Maintaining confidentiality is essential for protecting sensitive information and ensuring trust in personal and professional relationships. Your privacy safeguards not only prevent unauthorized access but also uphold ethical standards and compliance with legal requirements. Explore the rest of this article to understand how confidentiality impacts your daily interactions and strategies for enhancing it.
Table of Comparison
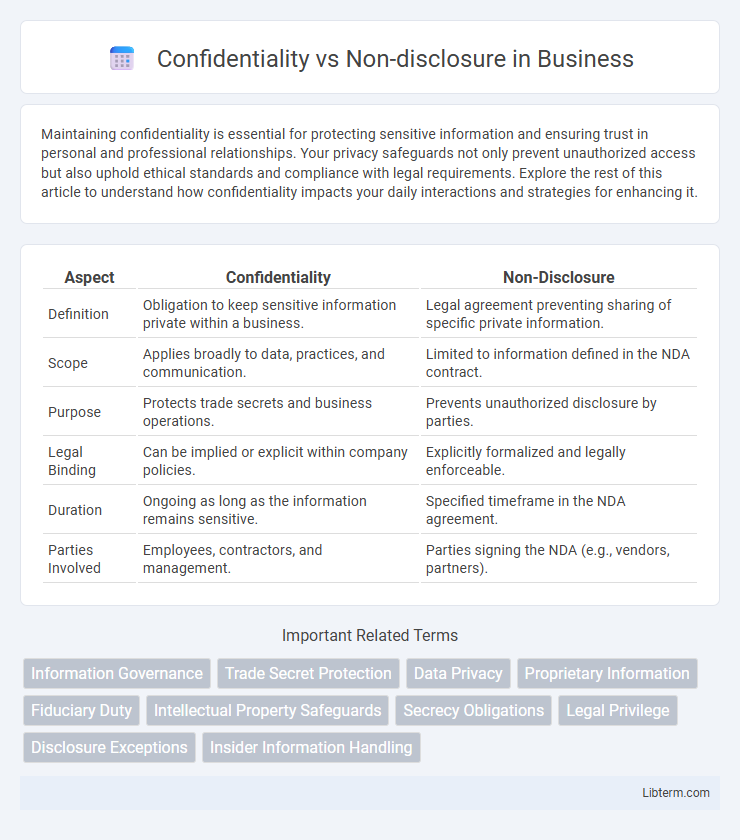
| Aspect | Confidentiality | Non-Disclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Obligation to keep sensitive information private within a business. | Legal agreement preventing sharing of specific private information. |
| Scope | Applies broadly to data, practices, and communication. | Limited to information defined in the NDA contract. |
| Purpose | Protects trade secrets and business operations. | Prevents unauthorized disclosure by parties. |
| Legal Binding | Can be implied or explicit within company policies. | Explicitly formalized and legally enforceable. |
| Duration | Ongoing as long as the information remains sensitive. | Specified timeframe in the NDA agreement. |
| Parties Involved | Employees, contractors, and management. | Parties signing the NDA (e.g., vendors, partners). |
Understanding Confidentiality: Definition and Importance
Confidentiality refers to the ethical and legal duty to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring that private data remains secure within an organization or between parties. Understanding confidentiality is crucial for maintaining trust, preventing data breaches, and complying with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Unlike non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) that are specific contracts, confidentiality encompasses broader obligations to safeguard information in various contexts such as healthcare, business, and legal fields.
What is a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)?
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a legally binding contract that establishes a confidential relationship between parties, ensuring sensitive information shared during business dealings remains protected from unauthorized disclosure. NDAs specify the types of information considered confidential, the obligations of the receiving party, and the duration of confidentiality, safeguarding trade secrets, proprietary data, and intellectual property. Unlike general confidentiality principles, NDAs provide explicit legal remedies for breaches, making them essential tools in maintaining privacy and competitive advantage in corporate environments.
Key Differences Between Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure
Confidentiality refers to the ethical or legal duty to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, applying broadly across various contexts such as healthcare, business, or law. Non-disclosure specifically involves contractual agreements, known as Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), designed to legally bind parties to not reveal certain proprietary information. The key difference lies in confidentiality being a general principle or obligation, while non-disclosure is a formalized, enforceable contract focused on preventing information leaks between specific parties.
Legal Foundations: Confidentiality vs Non-Disclosure
Confidentiality and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) both serve to protect sensitive information but differ in legal scope and application. Confidentiality obligations arise from fiduciary duties, contracts, or statutory laws ensuring information is not disclosed unlawfully, while NDAs are explicit contracts specifically designed to prevent parties from revealing proprietary or confidential information. Courts enforce NDAs based on contract principles, whereas confidentiality duties may be implied by law or professional standards, making the legal foundation of NDAs more formalized and narrowly tailored.
Use Cases: When to Choose Confidentiality or Non-Disclosure
Confidentiality agreements are ideal for ongoing business relationships where sensitive information needs sustained protection, such as partnerships or employee roles involving proprietary data. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are best suited for specific, one-time exchanges of information, like product pitches or merger negotiations, ensuring the recipient cannot disclose critical details. Selecting between confidentiality clauses and NDAs depends on factors like duration, scope of information, and the nature of the relationship involved.
Essential Clauses in Confidentiality Agreements
Essential clauses in confidentiality agreements include the definition of confidential information, detailing what must be protected to avoid ambiguity. The obligations of the receiving party are clearly outlined, specifying how information must be handled and the duration of the confidentiality period. Remedies for breach, exclusions from confidentiality, and the governing law clause ensure enforceability and clarify legal recourse in case of violations.
Drafting an Effective Non-Disclosure Agreement
Drafting an effective Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) requires precise definitions of confidential information, clear obligations for all parties, and specified duration of confidentiality. Including exclusions, permitted disclosures, and remedies for breach strengthens enforceability and clarity. Tailoring clauses to the specific nature of the business relationship ensures protection of sensitive data while minimizing ambiguity.
Common Pitfalls in Confidentiality and NDA Arrangements
Common pitfalls in confidentiality and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) include vague definitions of confidential information, lack of clear timeframes for confidentiality obligations, and insufficient scope limitations, which can lead to legal ambiguities and unenforceability. Failing to specify the parties bound by the agreement or the permitted uses of confidential information often results in unintended disclosures or misuse. Ensuring precise language and detailed provisions in NDAs is crucial to protect sensitive data effectively and avoid costly disputes.
Consequences of Breaching Confidentiality or NDAs
Breaching confidentiality or non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) can result in severe legal and financial repercussions including lawsuits, monetary damages, and injunctions to prevent further disclosure. Violations may also lead to loss of trust, damage to professional reputation, and termination of business relationships. Companies often impose strict penalties and pursue enforcement to protect proprietary information and maintain competitive advantage.
Best Practices for Protecting Sensitive Information
Confidentiality involves maintaining the privacy of sensitive information within an organization, ensuring data access is restricted to authorized individuals only. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) legally bind parties to refrain from sharing proprietary information, establishing clear guidelines for information sharing and privacy. Best practices for protecting sensitive information include implementing robust access controls, conducting regular employee training, and enforcing strict data encryption and monitoring protocols.
Confidentiality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com