Non-circumvention agreements protect parties from being bypassed in business transactions, ensuring fair dealings and safeguarding valuable contacts. These agreements prevent unauthorized parties from directly engaging with your clients or partners, preserving trust and business integrity. Explore the rest of this article to understand how non-circumvention clauses can secure your interests effectively.
Table of Comparison
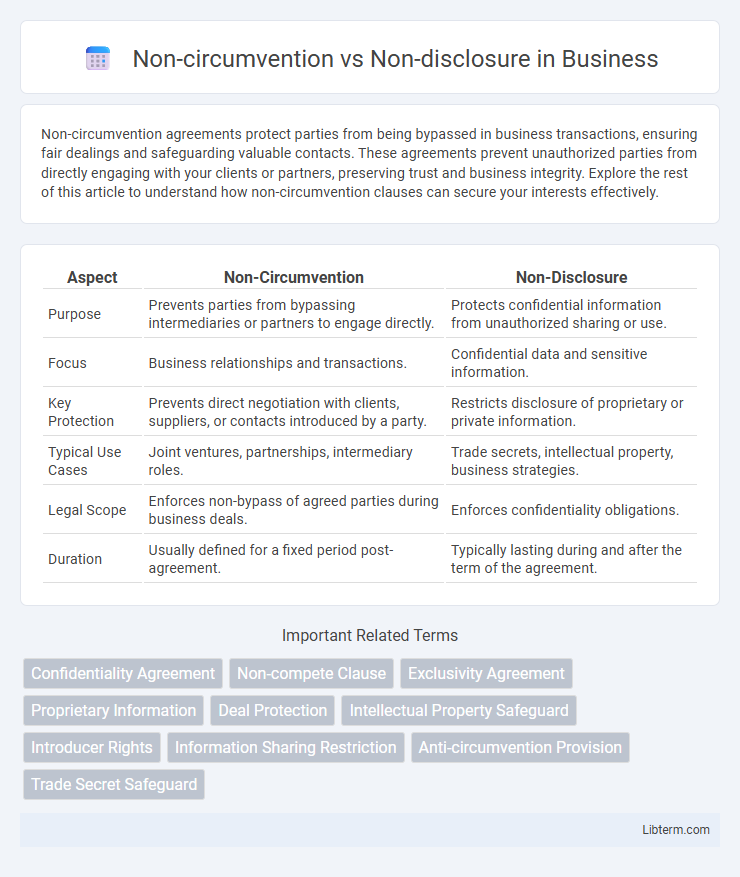
| Aspect | Non-Circumvention | Non-Disclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents parties from bypassing intermediaries or partners to engage directly. | Protects confidential information from unauthorized sharing or use. |
| Focus | Business relationships and transactions. | Confidential data and sensitive information. |
| Key Protection | Prevents direct negotiation with clients, suppliers, or contacts introduced by a party. | Restricts disclosure of proprietary or private information. |
| Typical Use Cases | Joint ventures, partnerships, intermediary roles. | Trade secrets, intellectual property, business strategies. |
| Legal Scope | Enforces non-bypass of agreed parties during business deals. | Enforces confidentiality obligations. |
| Duration | Usually defined for a fixed period post-agreement. | Typically lasting during and after the term of the agreement. |
Understanding Non-Circumvention Agreements: Definition and Purpose
Non-circumvention agreements protect parties from being bypassed in business transactions, ensuring intermediaries receive due commissions or benefits. These contracts prevent one party from directly contacting or dealing with another party introduced by the intermediary without permission. The primary purpose is to maintain trust and safeguard business relationships by legally prohibiting unfair circumvention and unauthorized dealings.
What is a Non-Disclosure Agreement? Key Elements Explained
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a legal contract designed to protect confidential information shared between parties, preventing unauthorized disclosure to third parties. Key elements include the definition of confidential information, the obligations of the receiving party to maintain secrecy, the duration of confidentiality, and the exclusions specifying what information is not covered. Unlike Non-Circumvention agreements, which prevent parties from bypassing intermediaries in business deals, NDAs focus exclusively on safeguarding sensitive information.
Core Differences Between Non-Circumvention and Non-Disclosure
Non-circumvention agreements prevent parties from bypassing intermediaries to engage directly with clients or contacts, ensuring protection of business relationships and commissions. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) focus on protecting confidential information from being shared or used without authorization. The core difference lies in non-circumvention safeguarding transactional integrity, while non-disclosure protects sensitive information confidentiality.
When to Use a Non-Circumvention Agreement
A Non-Circumvention Agreement is essential when parties want to protect business relationships and contacts from being bypassed during negotiations or transactions, ensuring intermediaries receive due credit and compensation. Use this agreement in scenarios involving third-party introductions to safeguard against direct dealings that exclude the introducer. It is particularly relevant in industries like real estate, finance, and international trade where maintaining trust and exclusivity is crucial.
Situations Ideal for Non-Disclosure Agreements
Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are ideal for situations involving the protection of sensitive information such as trade secrets, business strategies, or proprietary data during negotiations or partnerships. They legally restrict parties from sharing confidential details with unauthorized third parties, ensuring information security. NDAs are commonly used in contexts like mergers and acquisitions, product development, and collaborations requiring secrecy.
Legal Enforceability: Non-Circumvention vs. Non-Disclosure
Non-circumvention agreements primarily prevent parties from bypassing intermediaries to engage directly with clients or partners, ensuring legal enforceability by clearly outlining prohibited actions and remedies. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) focus on protecting confidential information, relying on specific definitions of proprietary data and obligations not to disclose or misuse it, which courts enforce through injunctive relief or damages. Legal enforceability of both depends on precise language, jurisdictional standards, and the demonstration of actual harm or potential breach in contractual obligations.
Protecting Business Interests with Non-Circumvention Clauses
Non-circumvention clauses are essential in protecting business interests by preventing parties from bypassing intermediaries or partners to engage directly with clients, suppliers, or vendors, thereby securing the original business relationships and financial benefits. While non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) focus on safeguarding confidential information, non-circumvention agreements specifically deter unauthorized dealings that could undermine negotiated partnerships. Incorporating non-circumvention clauses ensures trust and fairness in transactions, minimizing risks of lost revenue and maintaining the integrity of strategic alliances.
Data Protection and Confidentiality in Non-Disclosure Agreements
Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) primarily focus on data protection and confidentiality by legally binding parties to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. Non-circumvention agreements prevent parties from bypassing each other to directly engage with clients or partners, but they do not inherently address data confidentiality or privacy. In practice, combining NDAs with non-circumvention clauses ensures both protection of confidential data and prevention of unauthorized business dealings, enhancing overall security in collaborative environments.
Common Pitfalls in Drafting Non-Circumvention and Non-Disclosure
Common pitfalls in drafting Non-Circumvention and Non-Disclosure agreements include vague definitions of protected parties and information, which can lead to enforcement challenges. Failing to specify the duration of obligations or the scope of permitted disclosures often results in ambiguity and potential loopholes. Overlooking jurisdictional differences in confidentiality laws and the lack of clear remedies for breaches can undermine the effectiveness of these agreements.
Best Practices for Using Non-Circumvention and Non-Disclosure Agreements
Non-circumvention agreements prevent parties from bypassing intermediaries, ensuring protection of business contacts and deal structures, while non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) secure confidential information shared during negotiations. Best practices include clearly defining the scope, duration, and obligations within both agreements to avoid ambiguities, coupled with consistent enforcement and legal review to align with jurisdictional requirements. Combining NC and NDA provisions into a single, well-drafted contract enhances trust and mitigates risks in collaborative ventures and complex transactions.
Non-circumvention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com