The maturity period refers to the length of time until a financial instrument, such as a bond or a fixed deposit, reaches its full term and the principal amount is repaid to the investor. Understanding the maturity period is crucial for managing investment risks and aligning your financial goals with the appropriate investment horizon. Explore the rest of the article to learn how maturity periods impact your investment strategy and returns.
Table of Comparison
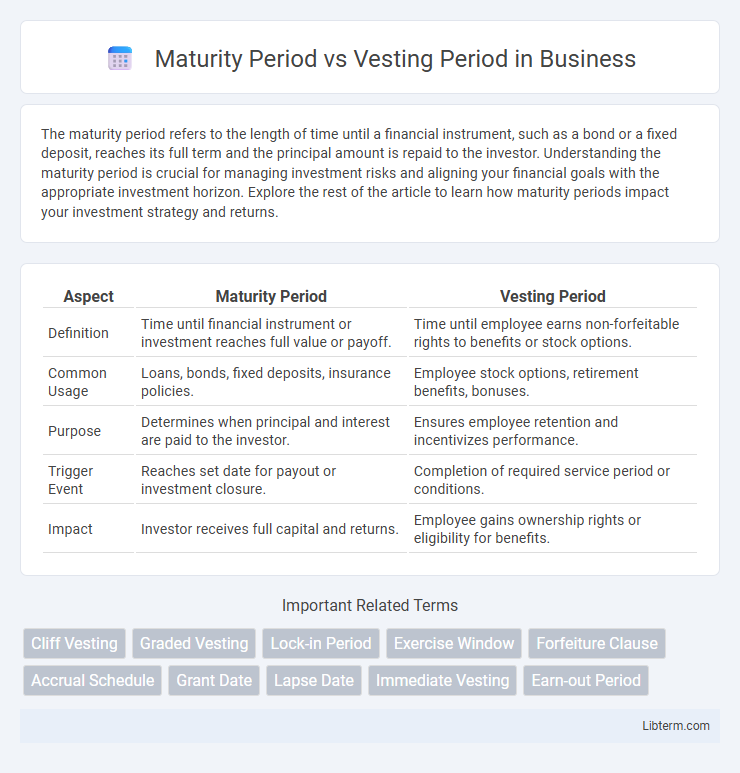
| Aspect | Maturity Period | Vesting Period |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Time until financial instrument or investment reaches full value or payoff. | Time until employee earns non-forfeitable rights to benefits or stock options. |
| Common Usage | Loans, bonds, fixed deposits, insurance policies. | Employee stock options, retirement benefits, bonuses. |
| Purpose | Determines when principal and interest are paid to the investor. | Ensures employee retention and incentivizes performance. |
| Trigger Event | Reaches set date for payout or investment closure. | Completion of required service period or conditions. |
| Impact | Investor receives full capital and returns. | Employee gains ownership rights or eligibility for benefits. |
Understanding Maturity Period and Vesting Period
The maturity period refers to the time duration until a financial instrument, such as a bond or fixed deposit, reaches its full value and the principal amount is repaid to the investor. The vesting period is the time frame during which an employee earns the right to receive benefits, like stock options or retirement plans, contingent on continued service. Understanding the differences between maturity and vesting periods is crucial for investors and employees to manage their financial planning and benefits effectively.
Key Differences Between Maturity and Vesting Periods
The maturity period is the time span until a financial instrument, like a bond or fixed deposit, reaches its full term and pays out principal and interest, while the vesting period refers to the time an employee must work before gaining ownership rights to employer-provided benefits such as stock options or retirement plans. Maturity periods are primarily related to investment timelines and returns, whereas vesting periods are linked to employment benefits and employee retention incentives. Understanding these differences is crucial for managing investment strategies and employee compensation plans effectively.
Importance of Maturity Period in Financial Planning
The maturity period is crucial in financial planning as it determines the exact timeline when an investment or financial instrument will be fully payable, allowing investors to strategically align their funds with long-term financial goals. Unlike the vesting period, which relates to rights accumulation, the maturity period guarantees access to principal and returns, ensuring liquidity and helping in precise cash flow management. Proper understanding of the maturity period aids in risk assessment, timing of reinvestment, and achieving targeted financial milestones efficiently.
Vesting Period: Definition and Significance
The vesting period is the length of time an employee must work at a company before gaining full ownership of employer-granted benefits, such as stock options or retirement contributions. This period ensures employee retention by incentivizing long-term commitment and aligns employee interests with company performance. Understanding the vesting schedule is crucial for maximizing compensation benefits and planning financial decisions effectively.
How Maturity Period Affects Investment Returns
The maturity period directly impacts investment returns by determining the duration over which the principal amount earns interest or appreciates in value, with longer maturity periods typically yielding higher returns due to compounded growth. Investments held until maturity usually avoid market volatility risks, ensuring investors receive the full expected returns, unlike those withdrawn prematurely. Understanding the maturity period helps investors align their financial goals with optimal investment horizons, maximizing total returns after factoring in potential reinvestment opportunities.
Impact of Vesting Period in Employee Benefits
The vesting period directly impacts employee benefits by determining the time frame employees must remain with a company before gaining non-forfeitable rights to retirement or stock options. Unlike the maturity period, which defines when benefits are payable, the vesting period incentivizes employee retention and aligns workforce stability with organizational growth. A longer vesting period can enhance loyalty but may also affect employee motivation and turnover rates.
Legal Implications of Maturity and Vesting Periods
Maturity periods define the timeframe in which a financial instrument or investment becomes payable or fully settles, affecting the enforceability of related legal contracts and obligations. Vesting periods determine when an individual gains legal entitlement to asset ownership or benefits, with implications for employment agreements and equity plans enforceability. Understanding these periods is crucial for ensuring compliance with contract law and minimizing disputes over ownership rights and payment claims.
Common Examples of Maturity and Vesting Periods
Maturity periods commonly range from 1 to 30 years in fixed deposits, government bonds, and life insurance policies, reflecting the time until an investment reaches full value. Vesting periods typically span 3 to 5 years in employee stock options, retirement plans like 401(k)s, and pension schemes, marking when ownership rights are fully granted. Understanding these standard durations helps investors and employees plan for liquidity events and long-term financial goals effectively.
Factors Influencing Maturity and Vesting Timelines
Maturity period and vesting period are influenced by factors such as the type of financial instrument or employee benefit plan, legal and regulatory frameworks, and company policies. Market conditions, including interest rates and economic stability, also affect the maturity timeline, while employee performance, tenure, and contractual agreements impact the vesting schedule. Understanding these variables is crucial for accurately predicting when assets or benefits become accessible.
Choosing the Right Period for Financial Goals
Choosing the right maturity period or vesting period depends on your specific financial goals and timeline for liquidity needs. Maturity periods determine when investment principal and interest are returned, ideal for fixed-term savings targets, while vesting periods control when ownership rights in employee stock options or retirement benefits fully transfer, aligning with long-term employment or retirement planning. Evaluating risk tolerance, cash flow requirements, and tax implications ensures optimal alignment between these periods and your financial strategy.
Maturity Period Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com