Joint ventures combine the strengths and resources of two or more businesses to achieve common goals while sharing risks and profits. This strategic partnership enables companies to enter new markets, access advanced technologies, and increase competitive advantage efficiently. Discover how a joint venture can transform your business opportunities in the detailed insights ahead.
Table of Comparison
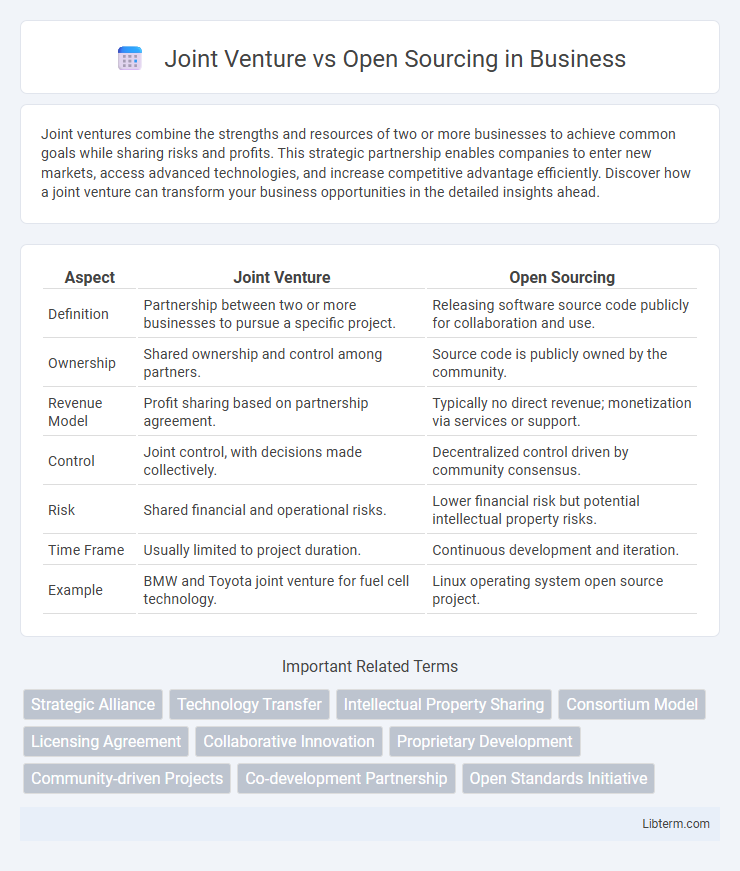
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Open Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between two or more businesses to pursue a specific project. | Releasing software source code publicly for collaboration and use. |
| Ownership | Shared ownership and control among partners. | Source code is publicly owned by the community. |
| Revenue Model | Profit sharing based on partnership agreement. | Typically no direct revenue; monetization via services or support. |
| Control | Joint control, with decisions made collectively. | Decentralized control driven by community consensus. |
| Risk | Shared financial and operational risks. | Lower financial risk but potential intellectual property risks. |
| Time Frame | Usually limited to project duration. | Continuous development and iteration. |
| Example | BMW and Toyota joint venture for fuel cell technology. | Linux operating system open source project. |
Introduction to Joint Ventures and Open Sourcing
Joint ventures involve two or more companies pooling resources to achieve a specific business goal while sharing risks and rewards, creating a legally binding partnership that fosters collaboration and strategic growth. Open sourcing refers to making software source code publicly accessible, enabling community-driven development, transparency, and innovation without exclusive ownership. Both approaches facilitate cooperation but differ fundamentally in structure, control, and intellectual property management.
Defining Joint Venture: Key Characteristics
A joint venture is a strategic alliance where two or more parties create a new, legally independent entity to achieve specific business objectives, sharing resources, risks, and profits. Key characteristics include joint ownership, mutual contribution of capital and expertise, and shared management control, often formalized through contractual agreements. Unlike open sourcing, which promotes transparent collaboration with publicly accessible code, joint ventures emphasize confidential cooperation and mutual benefit within a defined partnership structure.
Understanding Open Sourcing: Core Principles
Open sourcing revolves around making software source code freely available for modification, distribution, and collaboration, fostering innovation within a community-driven environment. Core principles include transparency, collaborative development, and the promotion of shared ownership, enabling rapid iteration and widespread adoption. Unlike joint ventures that rely on contractual partnerships, open sourcing empowers diverse contributors to jointly improve and evolve the software without centralized control.
Strategic Objectives: Joint Venture vs Open Sourcing
Joint ventures prioritize strategic objectives such as shared risk, resource pooling, and market expansion through collaborative control and mutual investment. Open sourcing focuses on maximizing innovation, community-driven development, and widespread adoption by releasing source code or technology for free use and modification. While joint ventures aim to achieve competitive advantage and revenue growth through partnership, open sourcing seeks to drive ecosystem growth and accelerated innovation via transparency and collective contribution.
Ownership and Control Differences
Joint ventures involve shared ownership and control between partnering entities, where both parties contribute resources and collaboratively manage operations, often formalized through contractual agreements. Open sourcing grants public ownership of software code, allowing anyone to use, modify, and distribute it freely, but original creators relinquish exclusive control over its development and governance. The key difference lies in joint ventures maintaining restricted, negotiated control among specific partners, while open sourcing promotes decentralized, community-driven stewardship.
Collaboration Models and Structures
Joint ventures create formal legal partnerships between companies, sharing ownership, risks, and profits through clearly defined agreements. Open sourcing relies on decentralized collaboration, allowing diverse contributors to develop and improve software in a transparent environment without exclusive ownership. While joint ventures emphasize structured governance and controlled resource allocation, open sourcing fosters community-driven innovation with flexible participation and rapid iteration.
Intellectual Property Considerations
Joint ventures allow companies to share intellectual property rights while maintaining control over proprietary technology, often through detailed legal agreements defining IP ownership and usage. Open sourcing relinquishes exclusive IP control by making code or technology publicly accessible, fostering collaboration but limiting rights to commercialize or restrict modifications. Intellectual property considerations in joint ventures emphasize protection and monetization, whereas open sourcing prioritizes transparency and community-driven innovation.
Risk Management and Liability
Joint ventures involve shared risk management and liability among partners, requiring detailed contractual agreements to allocate responsibilities and mitigate potential financial and legal exposures. Open sourcing distributes risk by allowing a diverse community to identify and fix vulnerabilities but can introduce uncertainties around intellectual property and compliance liabilities. Effective risk management in joint ventures relies on precise governance structures, while open sourcing demands robust license management and community engagement to minimize liability.
Financial Implications and Revenue Sharing
Joint ventures typically involve shared financial investment, risk, and revenue generation based on predetermined equity stakes, leading to profit distribution proportional to ownership percentages. Open sourcing eliminates direct revenue from licensing but can reduce development costs and generate indirect financial benefits through increased adoption, community contributions, and complementary service sales. Revenue sharing in joint ventures is contractually defined, whereas open source models rely on alternative monetization strategies such as support, customization, and ancillary products.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Evaluate
Choosing between a joint venture and open sourcing depends on factors such as control over intellectual property, collaboration goals, and resource allocation. Joint ventures offer shared ownership and direct influence on project direction, ideal for strategic partnerships requiring confidentiality and aligned business objectives. Open sourcing facilitates broader community innovation and rapid development but requires willingness to share code openly and potentially relinquish exclusive rights.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com