A hybrid strategy combines multiple approaches to maximize efficiency and flexibility in business operations, blending traditional methods with innovative digital solutions. This approach allows organizations to adapt quickly to changing market demands while leveraging their existing strengths. Discover how adopting a hybrid strategy can transform Your business by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
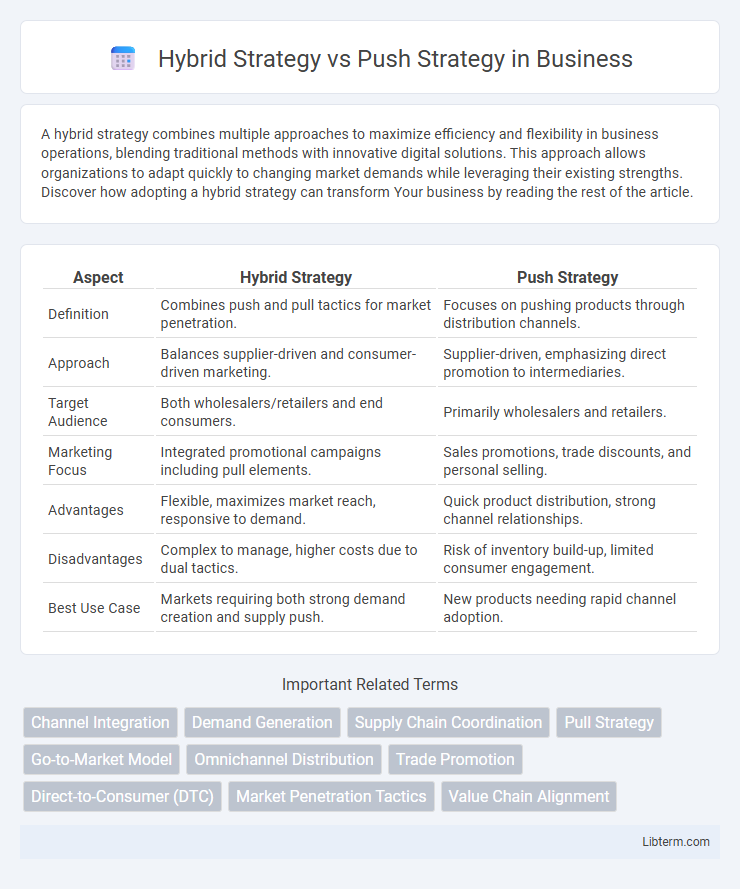
| Aspect | Hybrid Strategy | Push Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines push and pull tactics for market penetration. | Focuses on pushing products through distribution channels. |
| Approach | Balances supplier-driven and consumer-driven marketing. | Supplier-driven, emphasizing direct promotion to intermediaries. |
| Target Audience | Both wholesalers/retailers and end consumers. | Primarily wholesalers and retailers. |
| Marketing Focus | Integrated promotional campaigns including pull elements. | Sales promotions, trade discounts, and personal selling. |
| Advantages | Flexible, maximizes market reach, responsive to demand. | Quick product distribution, strong channel relationships. |
| Disadvantages | Complex to manage, higher costs due to dual tactics. | Risk of inventory build-up, limited consumer engagement. |
| Best Use Case | Markets requiring both strong demand creation and supply push. | New products needing rapid channel adoption. |
Introduction to Hybrid and Push Strategies
Hybrid strategy combines elements of push and pull approaches to optimize supply chain management, balancing inventory costs with customer demand responsiveness. Push strategy relies on forecast-driven production and distribution, aiming to maximize efficiency by anticipating market needs in advance. Both strategies impact inventory control, customer satisfaction, and operational flexibility in distinct ways.
Defining the Hybrid Strategy
The Hybrid Strategy combines elements of both push and pull marketing approaches to optimize product promotion and customer engagement. By integrating proactive selling tactics with demand-driven advertising, it balances supplier-driven supply chain efforts and consumer-driven market responses. This strategy enhances flexibility and responsiveness across distribution channels, improving overall market reach and customer satisfaction.
Understanding the Push Strategy
Push strategy emphasizes promoting products by pushing them through distribution channels to end consumers, often relying on trade promotions, personal selling, and direct marketing to retailers and wholesalers. This approach boosts product availability and visibility on shelves, driving immediate sales and inventory turnover. Effective push strategies require strong relationships with channel partners and precise demand forecasting to avoid stockouts or overstock situations.
Key Differences Between Hybrid and Push Strategies
Hybrid strategy combines elements of both push and pull marketing approaches, leveraging direct promotions to distributors while simultaneously targeting end consumers through advertising and engagement. Push strategy primarily focuses on driving products through the supply chain by incentivizing intermediaries such as wholesalers and retailers to stock and promote the product. The key difference lies in hybrid strategy's balanced use of upstream and downstream tactics, whereas push strategy concentrates mainly on supply chain stimulation.
Advantages of Hybrid Strategy
The hybrid strategy combines the strengths of both push and pull marketing approaches, enabling businesses to effectively target multiple stages of the customer journey and increase overall market reach. This approach enhances flexibility in adapting to changing consumer behaviors and optimizes resource allocation by balancing demand generation with supply chain efficiency. Companies employing a hybrid strategy often experience improved sales performance, stronger brand loyalty, and greater competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Benefits of Push Strategy
A Push Strategy effectively drives product availability by actively promoting goods to distributors and retailers, ensuring consistent shelf presence and reducing stockouts. This approach accelerates inventory turnover and enhances supply chain efficiency by anticipating demand and securing retailer commitment. Companies gain stronger control over product distribution, leading to increased market penetration and faster introduction of new products.
Use Cases for Hybrid Strategy
The hybrid strategy combines elements of both push and pull marketing, making it ideal for businesses targeting diverse customer segments with varying purchase behaviors. It is particularly effective for companies launching new products that require direct outreach to early adopters while simultaneously building strong brand awareness through content marketing. Retailers and technology firms use hybrid strategies to balance aggressive sales tactics with relationship-building efforts, maximizing customer acquisition and retention.
When to Choose Push Strategy
Choose a push strategy when launching new products or entering competitive markets to secure shelf space and supplier commitment early. This approach works best in industries with complex supply chains or when targeting intermediaries like retailers and wholesalers who can influence customer purchases. Businesses aiming to create immediate demand and generate quick sales often rely on push tactics to drive product availability and visibility.
Challenges of Implementing Each Strategy
Implementing a hybrid strategy often presents challenges such as the complexity of coordinating multiple channels and aligning marketing and sales efforts to avoid conflicts and ensure consistent messaging. Push strategies can struggle with high upfront costs and the difficulty of maintaining dealer or retailer motivation over time, often requiring continuous incentives. Both strategies demand robust data management systems to monitor performance and adapt quickly to market feedback.
Deciding the Best Fit for Your Business
Evaluating the best fit between a hybrid strategy and a push strategy requires analyzing your business goals, target market, and product lifecycle stage. A hybrid strategy combines proactive product promotion with responsive customer engagement, optimizing reach and adaptability for dynamic markets. In contrast, push strategy emphasizes aggressive distribution and sales efforts, suited for launching new products or clearing inventory efficiently.
Hybrid Strategy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com