A purchase order is a formal document issued by a buyer to a supplier, outlining the products or services required, quantities, and agreed prices. It serves as a legally binding contract that ensures clarity and accountability between both parties involved in a transaction. Explore the rest of the article to understand how managing your purchase orders effectively can streamline your procurement process.
Table of Comparison
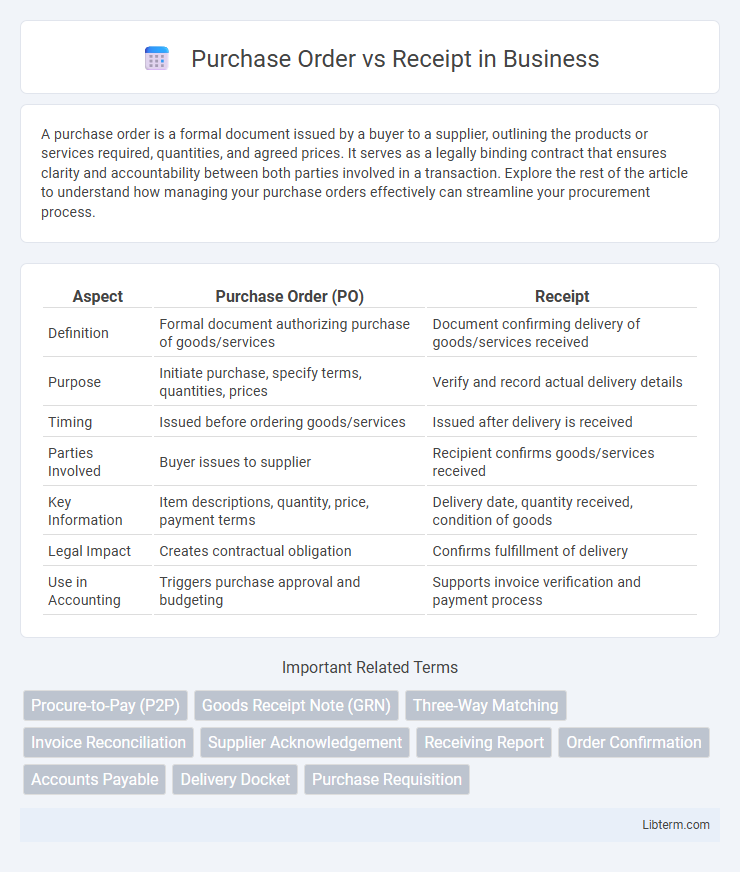
| Aspect | Purchase Order (PO) | Receipt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal document authorizing purchase of goods/services | Document confirming delivery of goods/services received |
| Purpose | Initiate purchase, specify terms, quantities, prices | Verify and record actual delivery details |
| Timing | Issued before ordering goods/services | Issued after delivery is received |
| Parties Involved | Buyer issues to supplier | Recipient confirms goods/services received |
| Key Information | Item descriptions, quantity, price, payment terms | Delivery date, quantity received, condition of goods |
| Legal Impact | Creates contractual obligation | Confirms fulfillment of delivery |
| Use in Accounting | Triggers purchase approval and budgeting | Supports invoice verification and payment process |
Understanding Purchase Orders
Purchase orders serve as formal contracts issued by buyers to suppliers, detailing the types, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services. They establish clear terms for the transaction, ensuring both parties have a mutual understanding before fulfillment begins. Proper use of purchase orders streamlines procurement workflows, reduces errors, and enhances financial accountability in supply chain management.
What Is a Receipt?
A receipt is a documented acknowledgment that goods or services have been delivered and accepted, serving as proof of transaction completion between buyer and seller. It details item descriptions, quantities, prices, delivery dates, and payment information, enabling accurate financial recordkeeping and inventory management. Receipts play a crucial role in verifying that purchased items match the purchase order, ensuring accountability in procurement processes.
Key Differences Between Purchase Orders and Receipts
Purchase orders are formal documents issued by a buyer to authorize a purchase and specify product details, quantities, and agreed prices, serving as a contractual agreement with the supplier. Receipts are issued by the seller after goods or services are delivered, confirming the transaction and payment for the order. The key difference lies in their function: purchase orders initiate and authorize procurement, while receipts verify fulfillment and record completed sales.
The Purpose of Purchase Orders in Business
Purchase orders serve as formal contracts that detail the products or services a buyer intends to purchase, establishing clear terms such as quantity, price, and delivery dates. They help businesses manage procurement efficiently by providing a documented approval process and reducing the risk of errors or misunderstandings with suppliers. This structured approach streamlines financial planning and inventory control by creating an auditable trail from purchase request to payment.
The Role of Receipts in Transaction Records
Receipts play a crucial role in transaction records by providing verifiable evidence of goods or services received, ensuring accuracy and accountability in financial audits. Unlike purchase orders, which are requests authorizing procurement, receipts confirm completion and acceptance of the transaction, facilitating inventory management and payment processing. Maintaining accurate receipt documentation supports audit trails, prevents fraud, and improves vendor relationship management.
Purchase Order Workflow Explained
The purchase order workflow begins with the buyer creating a purchase order (PO) detailing the requested products or services, quantities, and agreed prices, which is then sent to the supplier for approval. Upon acceptance, the supplier fulfills the order and generates a receipt or goods receipt note confirming delivery and condition of the items received. This receipt is matched against the original purchase order and invoice for accuracy, enabling efficient inventory management and payment processing within the procurement cycle.
How Receipts Validate Purchases
Receipts play a critical role in validating purchases by confirming that the delivered goods or services match the terms specified in the Purchase Order, such as quantity, quality, and price. This verification process helps organizations maintain accurate inventory records, ensures proper payment authorization, and supports audit compliance by providing proof of transaction completion. Validating purchases through receipts minimizes discrepancies and disputes between buyers and suppliers, enhancing procurement efficiency and financial control.
Importance of Using Both Purchase Orders and Receipts
Using both purchase orders and receipts is crucial for accurate financial management and inventory control. Purchase orders initiate and authorize purchases by outlining specific details, while receipts confirm the delivery and acceptance of goods or services, ensuring accountability and preventing fraud. Integrating these documents streamlines reconciliation processes and supports audit compliance by providing a clear, verifiable transaction trail.
Common Mistakes in PO and Receipt Management
Common mistakes in Purchase Order (PO) and Receipt management include mismatched quantities and incorrect item descriptions, leading to inventory discrepancies and payment delays. Failure to verify PO details against delivery receipts often results in duplicate payments or missed invoices. Poor communication between procurement and receiving teams exacerbates these errors, causing inefficiencies in the supply chain process.
Best Practices for Organizing Purchase Orders and Receipts
Organizing purchase orders and receipts effectively requires implementing a digital document management system that categorizes and links purchase orders directly with their corresponding receipts to ensure accuracy and traceability. Establish clear protocols for timely matching and verification to reduce discrepancies, enhance audit readiness, and streamline accounts payable processes. Regularly review and update organizational policies to maintain compliance with financial regulations and improve overall procurement efficiency.
Purchase Order Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com