Offshoring involves relocating business processes or services to another country to reduce costs and access specialized skills. It can significantly improve efficiency and drive global competitiveness for companies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how offshoring can impact your business strategy.
Table of Comparison
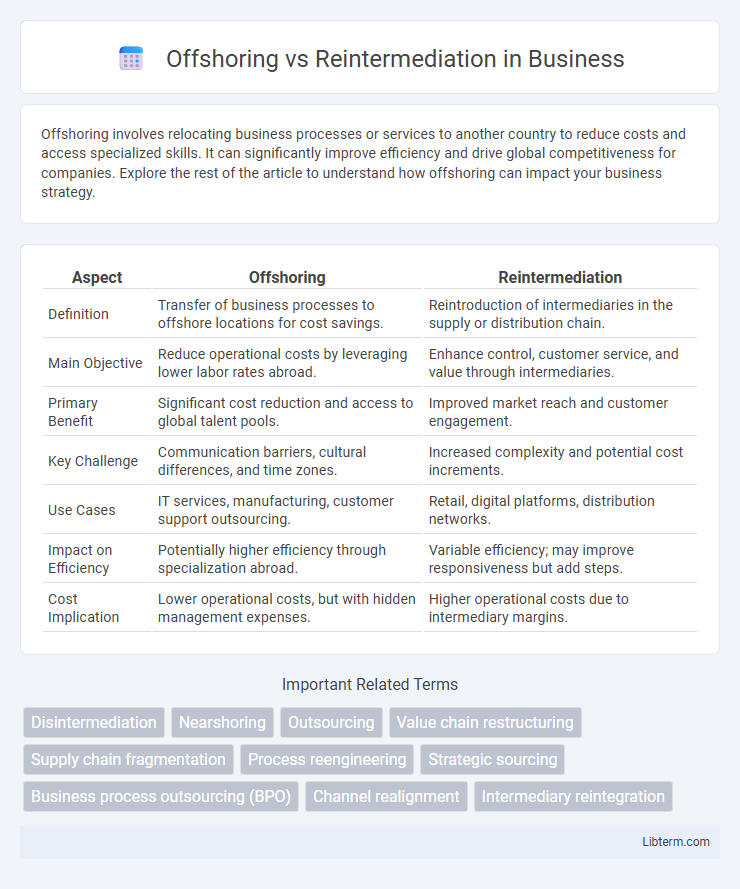
| Aspect | Offshoring | Reintermediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transfer of business processes to offshore locations for cost savings. | Reintroduction of intermediaries in the supply or distribution chain. |
| Main Objective | Reduce operational costs by leveraging lower labor rates abroad. | Enhance control, customer service, and value through intermediaries. |
| Primary Benefit | Significant cost reduction and access to global talent pools. | Improved market reach and customer engagement. |
| Key Challenge | Communication barriers, cultural differences, and time zones. | Increased complexity and potential cost increments. |
| Use Cases | IT services, manufacturing, customer support outsourcing. | Retail, digital platforms, distribution networks. |
| Impact on Efficiency | Potentially higher efficiency through specialization abroad. | Variable efficiency; may improve responsiveness but add steps. |
| Cost Implication | Lower operational costs, but with hidden management expenses. | Higher operational costs due to intermediary margins. |
Understanding Offshoring: Definition and Key Concepts
Offshoring involves relocating business processes or services to another country to leverage cost advantages, access specialized skills, or improve operational efficiency. Key concepts include labor arbitrage, where companies benefit from lower wages abroad, and the strategic choice of locations with favorable economic regulations and infrastructure. Understanding offshoring requires analyzing factors such as cultural differences, communication challenges, and geopolitical risks impacting sustainability and profitability.
What is Reintermediation? A Modern Overview
Reintermediation refers to the process of reintroducing intermediaries into a supply chain or transaction workflow, often enabled by advanced digital platforms and technologies. It contrasts with disintermediation by adding value through enhanced service delivery, improved customer engagement, and data-driven insights. Modern reintermediation leverages AI, blockchain, and IoT to optimize operations, increase transparency, and create new business models in industries such as finance, retail, and manufacturing.
Historical Context: Evolution of Offshoring and Reintermediation
Offshoring emerged prominently in the late 20th century as companies sought cost reduction by relocating manufacturing and services to countries with lower labor costs, driven by globalization and advances in communication technologies. Reintermediation arose in the early 21st century with the rise of digital platforms, restoring intermediaries in supply chains and markets that were previously bypassed by disintermediation during the internet boom. The evolution of offshoring reflects shifts in economic strategies toward global efficiency, while reintermediation highlights the adaptation of business models to new technological landscapes and consumer behaviors.
Core Benefits of Offshoring for Global Businesses
Offshoring enables global businesses to significantly reduce operational costs by leveraging lower labor expenses and economies of scale in international markets. It also provides access to a diverse talent pool with specialized skills, enhancing innovation and productivity. Moreover, offshoring supports 24/7 business operations through time zone advantages, improving customer service and accelerating project timelines.
Major Advantages of Reintermediation in Digital Markets
Reintermediation in digital markets enhances customer experience by integrating advanced intermediaries that provide personalized services, streamlined transactions, and improved trust between buyers and sellers. It allows businesses to leverage data analytics and artificial intelligence to offer tailored product recommendations and efficient support, boosting customer loyalty and retention. Furthermore, reintermediation facilitates better regulatory compliance and risk management by incorporating specialized intermediaries skilled in digital security and legal frameworks.
Risks and Challenges: Offshoring vs Reintermediation
Offshoring risks include cultural misunderstandings, data security vulnerabilities, and reliance on distant supply chains, which can lead to operational delays and increased costs. Reintermediation challenges involve managing complex new layers of intermediaries, potential loss of direct customer relationships, and difficulties ensuring consistent service quality across channels. Both strategies demand robust risk mitigation plans to address regulatory compliance, communication barriers, and fluctuating market dynamics effectively.
Economic Impact: Comparing Offshoring and Reintermediation
Offshoring shifts production and service jobs to lower-cost countries, often resulting in reduced labor costs and increased company profits but can lead to domestic job losses and wage stagnation. Reintermediation, by contrast, introduces new intermediaries or digital platforms within the supply chain, potentially creating domestic jobs and enhancing value through improved services and efficiencies. Economically, offshoring emphasizes cost reduction and global competitiveness, while reintermediation fosters innovation and job creation within local markets, impacting GDP growth differently depending on the industry and region.
Industry Case Studies: Offshoring vs Reintermediation Success Stories
Industry case studies reveal that offshoring in the manufacturing sector, such as Apple's use of Chinese factories, has driven significant cost reduction and scalability. In contrast, reintermediation success is exemplified by Amazon transforming retail through digital platforms that reestablish intermediary roles in supply chains to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. Both strategies demonstrate unique competitive advantages depending on industry dynamics, with offshoring typically optimizing cost structures and reintermediation enhancing value through technology-driven market connectivity.
Future Trends: The Convergence of Offshoring and Reintermediation
Future trends indicate a convergence of offshoring and reintermediation as businesses seek hybrid models combining cost efficiency with enhanced value-added services. Advanced technologies like AI, blockchain, and cloud computing facilitate seamless integration, enabling firms to optimize global supply chains while improving transparency and customer engagement. This convergence drives innovation in outsourcing strategies, promoting agile, scalable, and resilient operational frameworks for the evolving global market.
Strategic Decision-Making: Choosing Between Offshoring and Reintermediation
Strategic decision-making between offshoring and reintermediation involves evaluating cost efficiency, operational control, and market responsiveness. Offshoring offers access to lower labor costs and global talent pools, while reintermediation enhances customer experience through improved direct engagement and streamlined digital channels. Companies must balance scalability, risk management, and innovation potential to align the chosen approach with long-term business objectives and competitive advantage.
Offshoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com