Bid price represents the highest amount a buyer is willing to pay for an asset at a given time, playing a crucial role in financial markets and trading. Understanding bid price helps you make informed decisions about when to buy or sell stocks, commodities, or currencies for optimal gains. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your grasp of how bid price impacts your investment strategies.
Table of Comparison
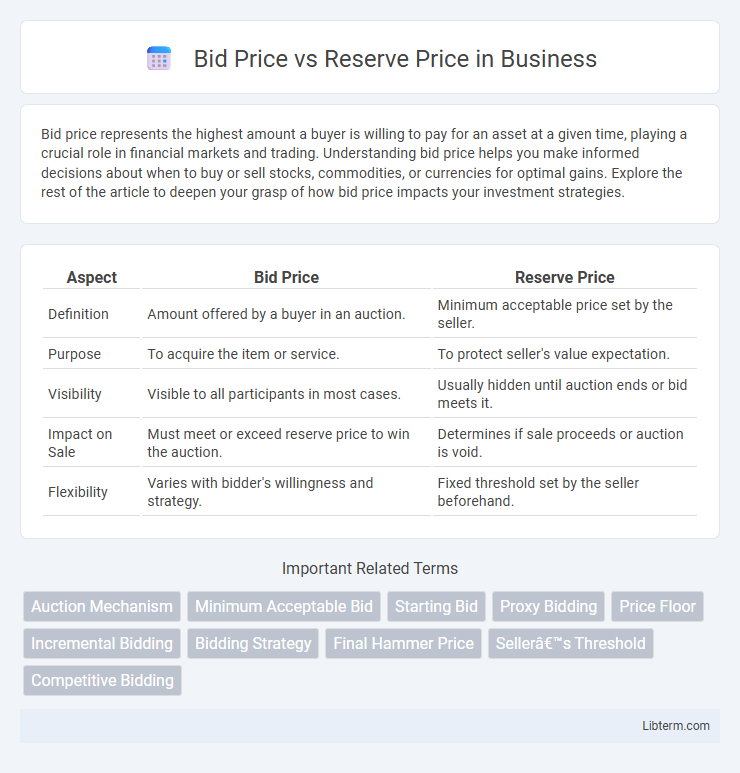
| Aspect | Bid Price | Reserve Price |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Amount offered by a buyer in an auction. | Minimum acceptable price set by the seller. |
| Purpose | To acquire the item or service. | To protect seller's value expectation. |
| Visibility | Visible to all participants in most cases. | Usually hidden until auction ends or bid meets it. |
| Impact on Sale | Must meet or exceed reserve price to win the auction. | Determines if sale proceeds or auction is void. |
| Flexibility | Varies with bidder's willingness and strategy. | Fixed threshold set by the seller beforehand. |
Understanding Bid Price and Reserve Price
Bid price represents the highest amount a buyer is willing to pay for an item during an auction, reflecting market demand and buyer interest. Reserve price is the minimum price set by the seller that must be met for the sale to proceed, protecting the seller's valuation and investment. Understanding the relationship between bid price and reserve price helps in assessing auction dynamics and setting realistic expectations for buyers and sellers.
Key Differences Between Bid Price and Reserve Price
The bid price is the actual amount a buyer offers in an auction, reflecting their willingness to pay, while the reserve price is the minimum amount a seller is willing to accept, often kept confidential until bidding ends. The key difference lies in their roles: the bid price is a public figure that fluctuates during the auction, whereas the reserve price ensures the seller's minimum acceptable value is met to avoid selling below cost. Understanding these distinctions helps buyers strategize their bids and sellers protect their asset's value.
How Bid Price Works in Auctions
Bid price in auctions represents the amount a participant offers to pay for an item, driving the competitive process to determine the final sale value. The auctioneer evaluates each bid against the reserve price, which is the minimum acceptable threshold set by the seller to ensure the item is not sold below a certain value. If the bid price meets or exceeds the reserve price, the item is sold to the highest bidder, ensuring fair market value is achieved while protecting the seller's interests.
The Role of Reserve Price in Auction Strategy
Reserve price serves as a critical benchmark in auction strategy, acting as the minimum acceptable bid set by the seller to protect the item's value. It influences bidding behavior by deterring low bids and ensuring the auction does not conclude below the seller's valuation threshold. Understanding the interaction between bid price and reserve price helps bidders gauge their bidding limits and strategize accordingly to maximize win probability without overpaying.
Importance of Setting an Appropriate Reserve Price
Setting an appropriate reserve price is critical in auctions to protect the seller from accepting bids below the item's market value. A well-calibrated reserve price ensures a balance between attracting competitive bids and safeguarding the asset's worth, preventing undervalued sales. Misjudging the reserve price can lead to either no sale or missed profit opportunities, impacting overall auction success.
Impact of Reserve Price on Auction Outcomes
The reserve price acts as a threshold that must be met for an auction item to be sold, directly influencing bidding behavior and final sale prices. A higher reserve price can discourage bidders, potentially leading to unsold items, while a lower reserve price encourages more participation but may result in lower revenues. Setting an optimal reserve price balances attracting competitive bids and ensuring the seller's minimum acceptable value is met, thereby maximizing auction efficiency and outcomes.
Factors Influencing Bid Price in Auctions
Bid price in auctions is influenced by factors such as bidder demand, item rarity, market conditions, and perceived value, which collectively drive competitive bidding behavior. The reserve price sets the minimum acceptable amount, impacting bidder strategy and willingness to participate. Economic trends, auction type, and bidder budget constraints also play critical roles in shaping the final bid price.
Reserve Price: Risks and Benefits for Sellers
The reserve price acts as a hidden minimum threshold that safeguards sellers from underselling their items, ensuring they achieve a desired value during auctions. Setting the reserve price too high can deter potential bidders and reduce auction participation, increasing the risk of no sale. However, an appropriately set reserve price balances protection with attracting competitive bids, maximizing the seller's revenue potential while minimizing the risk of unsold inventory.
Common Mistakes When Setting Reserve Price
Setting a reserve price too high often discourages bidders, leading to low auction participation and missed sales opportunities. Another common mistake is failing to align the reserve price with current market value, resulting in unrealistic expectations and prolonged auctions. Sellers sometimes overlook competitive analysis, causing the reserve price to be set without considering similar items' performance and demand.
Tips for Optimizing Bid Price and Reserve Price
Optimizing bid price and reserve price involves analyzing market trends, competitor pricing, and demand elasticity to set competitive yet profitable thresholds. Use data-driven tools to track auction dynamics and adjust reserve prices to avoid undervaluing products while attracting serious bidders. Continuously test different price points and monitor bidder behavior to find the optimal balance that maximizes sales conversions and revenue.
Bid Price Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com