SAFE and venture debt are innovative financing tools designed to fuel startup growth without immediately diluting ownership. Venture debt provides your company with capital that complements equity funding while preserving valuation and control. Explore the article to understand how these options can strategically support your startup's financial health.
Table of Comparison
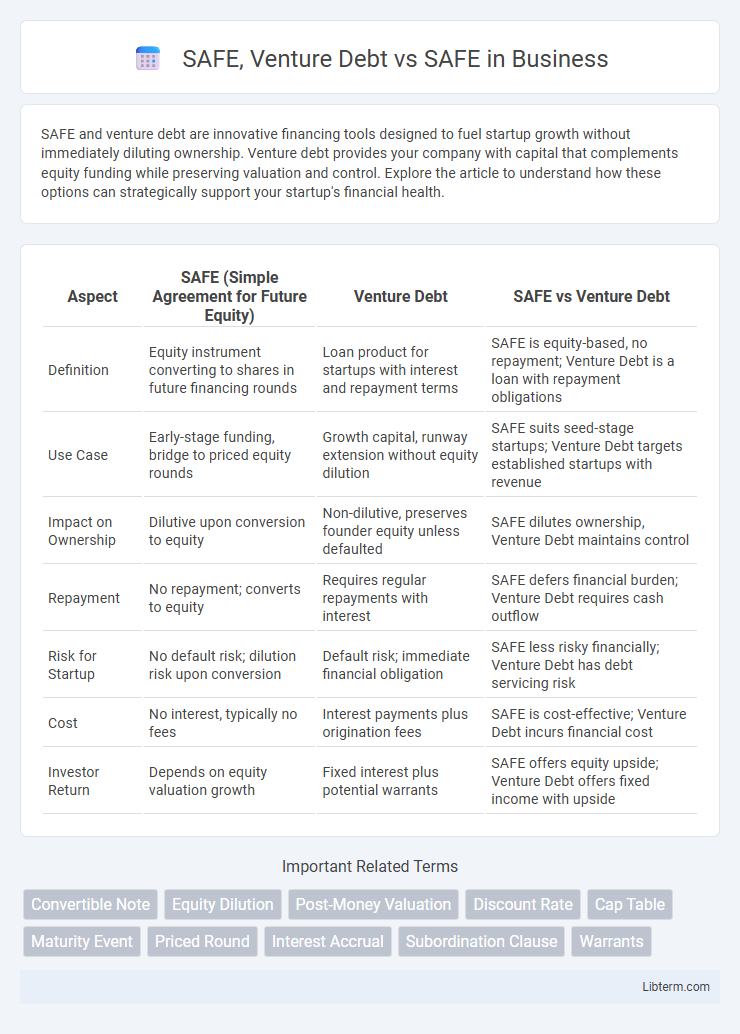
| Aspect | SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity) | Venture Debt | SAFE vs Venture Debt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Equity instrument converting to shares in future financing rounds | Loan product for startups with interest and repayment terms | SAFE is equity-based, no repayment; Venture Debt is a loan with repayment obligations |
| Use Case | Early-stage funding, bridge to priced equity rounds | Growth capital, runway extension without equity dilution | SAFE suits seed-stage startups; Venture Debt targets established startups with revenue |
| Impact on Ownership | Dilutive upon conversion to equity | Non-dilutive, preserves founder equity unless defaulted | SAFE dilutes ownership, Venture Debt maintains control |
| Repayment | No repayment; converts to equity | Requires regular repayments with interest | SAFE defers financial burden; Venture Debt requires cash outflow |
| Risk for Startup | No default risk; dilution risk upon conversion | Default risk; immediate financial obligation | SAFE less risky financially; Venture Debt has debt servicing risk |
| Cost | No interest, typically no fees | Interest payments plus origination fees | SAFE is cost-effective; Venture Debt incurs financial cost |
| Investor Return | Depends on equity valuation growth | Fixed interest plus potential warrants | SAFE offers equity upside; Venture Debt offers fixed income with upside |
Introduction to SAFE and Venture Debt
SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity) is an investment contract allowing startups to raise capital without immediate equity dilution, converting to shares during future funding rounds. Venture debt provides startups with loans complemented by warrants, offering non-dilutive capital that extends runway while minimizing equity loss. Comparing SAFE and venture debt highlights differences in funding structure, risk exposure, and repayment obligations critical for strategic capital planning.
Understanding SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity)
SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity) is an investment contract allowing investors to convert their investment into equity at a future financing event without determining a valuation upfront. Unlike traditional venture debt, SAFE does not require repayment or interest, providing flexibility and reducing financial risk for startups. SAFE agreements typically include valuation caps and discount rates to protect investor interests during equity conversion.
What Is Venture Debt?
Venture debt is a specialized type of loan provided to startup companies that have already raised equity financing but want to avoid further dilution. Unlike SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity), which converts into equity during future financing rounds, venture debt offers capital with a fixed repayment schedule and interest, typically secured by the company's assets or warrant coverage. This form of debt allows startups to extend their runway and fund growth initiatives without immediately sacrificing ownership stakes.
Key Differences Between SAFE and Venture Debt
SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity) is an equity instrument allowing investors to convert their investment into shares during future funding rounds without immediate debt obligations or interest accrual. Venture debt is a loan provided to startups that requires repayment with interest, often coupled with warrants for equity participation, creating a debt liability on the company's balance sheet. Key differences include SAFE's conversion into equity without repayment pressure, while venture debt mandates scheduled repayments and interest, impacting cash flow and financial risk.
Advantages of Using SAFE for Startups
SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity) offers startups a streamlined fundraising method with lower legal costs and faster execution compared to traditional venture debt or equity financing. Unlike venture debt, SAFE agreements do not require monthly repayments or interest, reducing immediate financial pressure on early-stage companies. This flexible structure allows startups to secure capital without diluting ownership prematurely or incurring debt obligations, facilitating growth and investor alignment.
Benefits of Choosing Venture Debt
Venture debt provides startups with non-dilutive capital, allowing founders to maintain greater equity ownership compared to SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity) instruments. This financing option offers flexible repayment terms and can extend operating runway without immediate valuation pressure, which is critical for companies seeking growth without dilution. Venture debt also complements equity rounds by bridging funding gaps and improving a startup's financial runway while preserving investor equity stakes.
Risks and Drawbacks of SAFE Agreements
SAFE agreements present risks such as valuation cap disagreements, potential dilution for founders, and uncertainty in conversion terms during subsequent funding rounds. Unlike venture debt, SAFEs do not provide repayment obligations or fixed interest, increasing investor risk if the startup fails to raise further capital. The lack of a maturity date in SAFEs can leave investors waiting indefinitely without guaranteed returns or control mechanisms.
Potential Pitfalls of Venture Debt Financing
Venture debt financing often entails higher interest rates and warrants that can dilute equity, making it a costly option compared to SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity) which avoids immediate dilution. Unlike SAFE notes that convert into equity during future funding rounds, venture debt requires fixed repayment schedules regardless of startup success, increasing financial strain and risk of insolvency. Startups must also consider restrictive covenants commonly imposed in venture debt agreements, which can limit operational flexibility and hinder growth.
When to Choose SAFE vs Venture Debt
SAFE (Simple Agreement for Future Equity) is ideal for early-stage startups seeking quick, flexible funding without immediate valuation or debt obligations. Venture debt suits companies with established revenue and traction looking to extend runway without diluting equity significantly. Choose SAFE when prioritizing speed and simplicity, and opt for venture debt to leverage growth capital while minimizing shareholder dilution.
Conclusion: Deciding the Best Funding Option
Choosing between SAFE and venture debt depends on startup goals, risk tolerance, and growth stage. SAFE offers equity conversion without immediate repayment, ideal for early-stage companies prioritizing long-term value. Venture debt requires scheduled repayment with interest, suitable for startups seeking capital without equity dilution but with predictable revenue streams.
SAFE, Venture Debt Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com