Stakeholders play a crucial role in the success of any project or organization by influencing decisions and outcomes through their interests and contributions. Effective stakeholder management ensures alignment between project goals and expectations, fostering collaboration and minimizing conflicts. Discover how understanding your stakeholders can enhance project success in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
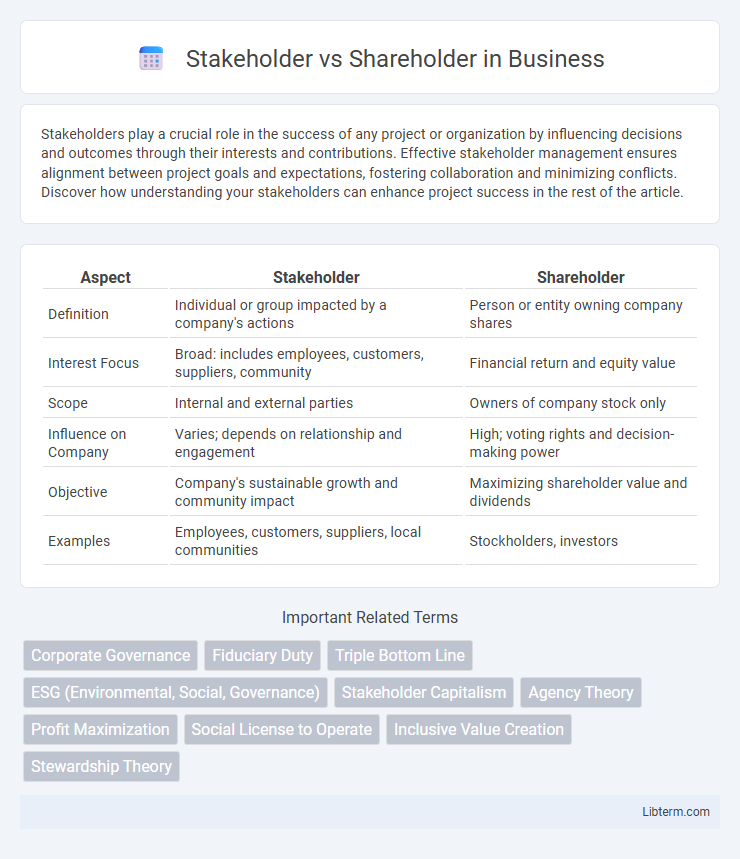
| Aspect | Stakeholder | Shareholder |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual or group impacted by a company's actions | Person or entity owning company shares |
| Interest Focus | Broad: includes employees, customers, suppliers, community | Financial return and equity value |
| Scope | Internal and external parties | Owners of company stock only |
| Influence on Company | Varies; depends on relationship and engagement | High; voting rights and decision-making power |
| Objective | Company's sustainable growth and community impact | Maximizing shareholder value and dividends |
| Examples | Employees, customers, suppliers, local communities | Stockholders, investors |
Understanding Stakeholders and Shareholders
Stakeholders encompass all individuals or groups affected by a company's operations, including employees, customers, suppliers, and the community, while shareholders specifically refer to individuals or entities owning shares in the company. Understanding stakeholders involves recognizing their diverse interests and the impact of corporate decisions on each group, whereas understanding shareholders focuses on their investment returns and influence on governance. Effective business strategies balance stakeholder engagement and shareholder value to ensure sustainable growth and long-term success.
Key Differences Between Stakeholders and Shareholders
Stakeholders encompass a broad group including employees, customers, suppliers, and the community, all affected by a company's operations, while shareholders specifically hold ownership through stock and are primarily concerned with financial returns. Shareholders have voting rights in corporate decisions, directly influencing company policy, whereas stakeholders may have indirect influence based on their relationship with the business. The key difference lies in interests: shareholders seek profit maximization, whereas stakeholders prioritize a range of outcomes such as sustainability, social impact, and long-term stability.
Roles and Interests of Shareholders
Shareholders are individuals or entities that own shares in a corporation and have a financial interest in the company's profitability and stock value. Their primary role involves voting on major corporate decisions, such as electing board members, approving mergers, and influencing dividend policies. Unlike stakeholders, whose interests may include employees, customers, and the community, shareholders mainly focus on maximizing return on investment and protecting their equity stake.
The Broader Scope of Stakeholders
Stakeholders encompass a wider group than shareholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and government entities, all of whom influence or are influenced by a company's operations. The broader scope of stakeholders highlights the importance of balancing diverse interests such as social responsibility, environmental impact, and longterm sustainability beyond mere financial returns to shareholders. Effective stakeholder management drives corporate governance strategies aimed at creating shared value and mitigating risks across multiple dimensions of business impact.
Impact on Corporate Decision-Making
Stakeholders encompass a broad range of groups including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities, whose interests significantly influence corporate decision-making by prioritizing sustainable practices and long-term value creation. Shareholders specifically focus on financial returns and stock performance, driving decisions aimed at maximizing short-term profitability and shareholder value. The balance between stakeholder and shareholder interests determines strategic priorities, risk management, and corporate governance approaches within organizations.
Stakeholder Theory vs Shareholder Theory
Stakeholder Theory emphasizes the importance of balancing the interests of all parties affected by a company's actions, including employees, customers, suppliers, and the community, promoting long-term value creation and ethical responsibility. Shareholder Theory prioritizes maximizing shareholder wealth as the primary goal, focusing on financial returns and market performance as key indicators of business success. The debate between these theories centers on whether corporate governance should address broader societal impacts or concentrate solely on shareholder profits.
Benefits of Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement fosters collaboration and drives sustainable business growth by incorporating diverse perspectives that enhance decision-making and innovation. Active involvement of stakeholders--including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities--builds trust, improves reputation, and mitigates risks through transparent communication. Companies prioritizing stakeholder engagement often experience higher customer loyalty, better regulatory compliance, and long-term value creation beyond immediate shareholder profits.
Potential Conflicts Between Stakeholders and Shareholders
Conflicts between stakeholders and shareholders often arise due to differing priorities: shareholders seek maximizing financial returns, while stakeholders prioritize long-term sustainability and social responsibility. Decision-making tensions emerge when profit-driven strategies may undermine employee welfare, environmental standards, or community interests. Balancing these competing demands requires integrating stakeholder engagement without compromising shareholder value.
Modern Corporate Responsibility Trends
Modern corporate responsibility trends emphasize the importance of stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities, alongside traditional shareholders. Companies adopting stakeholder-oriented approaches prioritize long-term value creation, sustainability, and ethical governance to meet evolving social and environmental expectations. This shift reflects a broader commitment to inclusive growth and corporate accountability beyond mere financial returns.
The Future of Stakeholder and Shareholder Relations
The future of stakeholder and shareholder relations hinges on balancing profit generation with social responsibility, emphasizing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to meet evolving market demands. Companies increasingly integrate stakeholder interests, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities, into corporate strategies to enhance long-term value and resilience. This shift promotes sustainable growth by aligning shareholder returns with broader societal goals, fostering trust and investor confidence in a rapidly changing economic landscape.
Stakeholder Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com