Radical innovation transforms entire industries by introducing groundbreaking technologies or business models that disrupt existing markets and create new value. These innovations often require significant investment and carry high risks but can lead to substantial competitive advantages and long-term growth. Explore the rest of this article to discover how you can harness radical innovation for your organization's success.
Table of Comparison
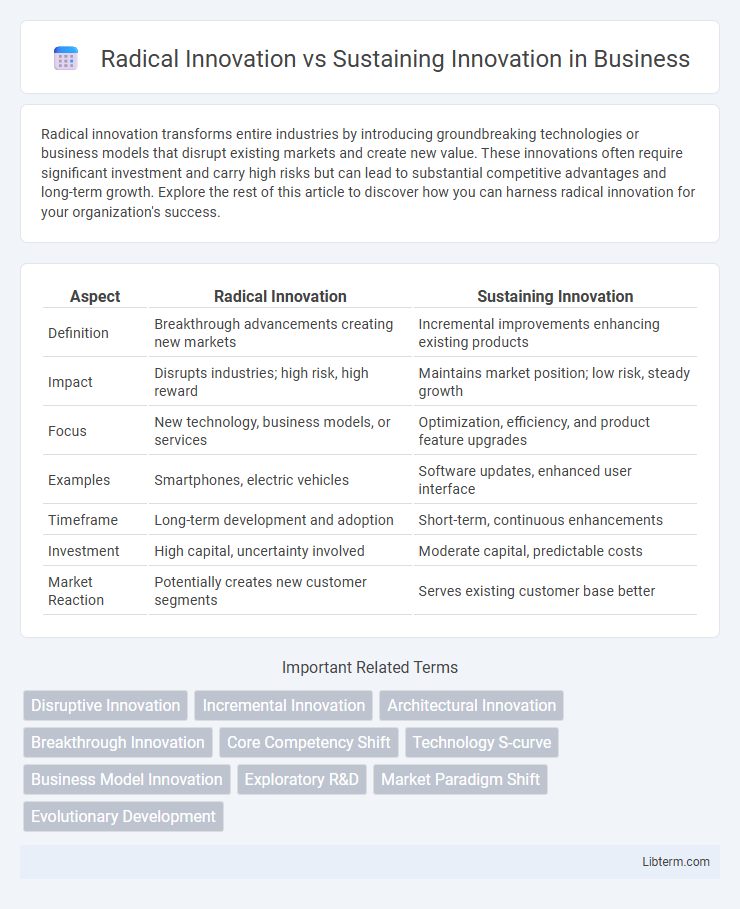
| Aspect | Radical Innovation | Sustaining Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Breakthrough advancements creating new markets | Incremental improvements enhancing existing products |
| Impact | Disrupts industries; high risk, high reward | Maintains market position; low risk, steady growth |
| Focus | New technology, business models, or services | Optimization, efficiency, and product feature upgrades |
| Examples | Smartphones, electric vehicles | Software updates, enhanced user interface |
| Timeframe | Long-term development and adoption | Short-term, continuous enhancements |
| Investment | High capital, uncertainty involved | Moderate capital, predictable costs |
| Market Reaction | Potentially creates new customer segments | Serves existing customer base better |
Introduction to Radical and Sustaining Innovation
Radical innovation introduces groundbreaking products or technologies that redefine markets and create new demand, often involving high risk and significant investment. Sustaining innovation enhances existing products or processes, targeting incremental improvements to meet evolving customer needs within established markets. Both innovation types are crucial for long-term competitiveness, balancing disruptive breakthroughs with continuous refinement.
Defining Radical Innovation
Radical innovation refers to breakthroughs that fundamentally change existing markets or create entirely new ones by introducing unprecedented products, services, or processes. It often involves high risk and significant technological advancements, disrupting industry norms and setting new standards. Unlike sustaining innovation, which incrementally improves current offerings, radical innovation drives transformational change and long-term competitive advantage.
Understanding Sustaining Innovation
Sustaining innovation involves incremental improvements to existing products, services, or processes aimed at enhancing performance and meeting current customer needs. It prioritizes optimizing established business models and sustaining competitive advantage without disrupting market dynamics. Companies focusing on sustaining innovation typically invest in refining technology and improving efficiency to maintain steady growth.
Key Differences Between Radical and Sustaining Innovation
Radical innovation introduces breakthrough technologies or business models that create new markets and disrupt existing industries, characterized by high risk and uncertainty. Sustaining innovation focuses on incremental improvements to existing products or processes, enhancing performance to maintain competitive advantage within established markets. Key differences include the scale of impact, with radical innovation driving transformational change, while sustaining innovation targets steady growth and efficiency optimization.
Benefits of Radical Innovation
Radical innovation drives transformative change by introducing groundbreaking technologies or business models that create entirely new markets and reshape industries. It enables organizations to achieve significant competitive advantages and long-term growth through disruptive advancements. By challenging the status quo, radical innovation fosters breakthroughs that sustain economic development and open unprecedented opportunities for value creation.
Advantages of Sustaining Innovation
Sustaining innovation drives incremental improvements that enhance existing products and services, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. It reduces market risks by building on proven technologies and established business models, ensuring steady revenue growth. Companies benefit from sustaining innovation by reinforcing their competitive position while efficiently utilizing current resources and capabilities.
Challenges in Implementing Radical Innovation
Implementing radical innovation faces challenges such as high uncertainty, significant resource allocation, and resistance to change within organizations. The need to disrupt existing business models and cultivate a culture that embraces risk and experimentation often hampers progress. Overcoming these obstacles requires strategic leadership, flexible processes, and commitment to long-term vision beyond short-term performance metrics.
When to Choose Sustaining Over Radical Innovation
Organizations should choose sustaining innovation when the goal is to enhance existing products or services to meet current customer needs and maintain market position. Sustaining innovation is ideal for incremental improvements that improve efficiency, performance, or user experience without disrupting existing business models. Opting for sustaining innovation reduces risk compared to radical innovation, which involves developing entirely new technologies or markets.
Industry Examples: Radical vs Sustaining Innovation
Tesla's introduction of electric vehicles exemplifies radical innovation by reshaping the automotive industry's focus on sustainable energy and autonomous driving technology. In contrast, Toyota's continuous improvement of hybrid engines represents sustaining innovation, enhancing existing vehicle efficiency and reliability without drastically altering market dynamics. Pharmaceutical companies like Moderna demonstrated radical innovation through mRNA vaccine technology, while Pfizer's subsequent booster doses illustrate sustaining innovation by refining and extending vaccine effectiveness.
Balancing Radical and Sustaining Innovation for Business Growth
Balancing radical innovation and sustaining innovation is crucial for long-term business growth, as radical innovation drives breakthrough products that create new markets, while sustaining innovation enhances existing offerings to maintain competitive advantage. Companies that allocate resources effectively between exploratory radical projects and incremental improvements can adapt to market disruptions and meet evolving customer needs. Implementing an innovation portfolio management strategy allows businesses to optimize investments, reduce risks, and maximize returns across both innovation types.
Radical Innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com