A horizontal merger involves the combination of two companies operating in the same industry, aiming to increase market share and reduce competition. This strategic move often results in enhanced economies of scale and a stronger competitive position. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a horizontal merger can impact Your business landscape.
Table of Comparison
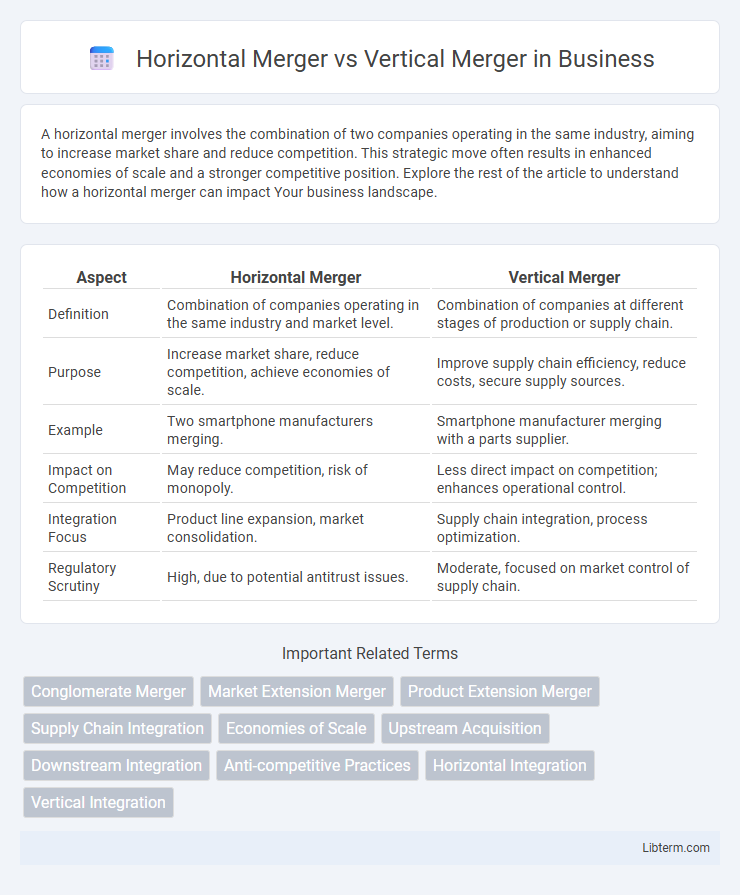
| Aspect | Horizontal Merger | Vertical Merger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of companies operating in the same industry and market level. | Combination of companies at different stages of production or supply chain. |
| Purpose | Increase market share, reduce competition, achieve economies of scale. | Improve supply chain efficiency, reduce costs, secure supply sources. |
| Example | Two smartphone manufacturers merging. | Smartphone manufacturer merging with a parts supplier. |
| Impact on Competition | May reduce competition, risk of monopoly. | Less direct impact on competition; enhances operational control. |
| Integration Focus | Product line expansion, market consolidation. | Supply chain integration, process optimization. |
| Regulatory Scrutiny | High, due to potential antitrust issues. | Moderate, focused on market control of supply chain. |
Introduction to Horizontal and Vertical Mergers
Horizontal mergers occur between companies operating within the same industry and market level, aiming to consolidate market share and reduce competition. Vertical mergers involve firms at different stages of the supply chain, designed to enhance operational efficiency and control over the production process. Both merger types strategically reshape business structures to improve market positioning and streamline operations.
Definitions: What is a Horizontal Merger?
A horizontal merger occurs when two companies operating in the same industry and at the same stage of production combine to increase market share and reduce competition. This type of merger aims to achieve economies of scale, enhance product offerings, and strengthen market positioning. Companies pursuing horizontal mergers often seek to consolidate resources and streamline operations within a specific sector.
Definitions: What is a Vertical Merger?
A vertical merger occurs when two companies operating at different stages within the same industry supply chain combine, such as a manufacturer merging with a supplier or distributor. This type of merger aims to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance control over the production process. Vertical mergers contrast with horizontal mergers, which involve companies competing in the same market segment or industry level.
Key Differences Between Horizontal and Vertical Mergers
Horizontal mergers combine companies operating in the same industry and at the same stage of production, aiming to increase market share and reduce competition. Vertical mergers unite firms at different stages of the supply chain, enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring better control over production processes. Key differences include the merger's impact on market competition, integration of supply chains, and the nature of synergies achieved.
Strategic Motivations Behind Horizontal Mergers
Horizontal mergers primarily aim to increase market share by combining companies within the same industry and at the same production stage, enabling economies of scale and reducing competition. Strategic motivations include enhancing product offerings, expanding customer base, and achieving cost synergies through consolidated operations. These mergers often seek to fortify market positioning and improve bargaining power with suppliers and distributors.
Strategic Motivations Behind Vertical Mergers
Vertical mergers aim to enhance supply chain efficiency by integrating companies operating at different stages of production, reducing transaction costs and improving coordination. Strategic motivations include securing access to critical inputs, ensuring reliable distribution channels, and gaining greater control over the production process to increase market competitiveness. Companies pursue vertical mergers to achieve cost savings, improve quality control, and foster innovation by closely aligning upstream and downstream operations.
Advantages of Horizontal Mergers
Horizontal mergers enhance market share by combining companies within the same industry, leading to increased economies of scale and cost efficiencies. They enable stronger competitive positioning through expanded product lines and customer bases, which can result in higher revenue growth. Furthermore, horizontal mergers often reduce duplication of efforts and streamline operations, boosting overall profitability and market influence.
Advantages of Vertical Mergers
Vertical mergers enhance supply chain efficiency by integrating different stages of production, reducing costs associated with transaction fees and delays. They improve control over inputs and distribution channels, ensuring consistent quality and timely delivery. Enhanced coordination also fosters innovation and competitive advantage through streamlined operations and better resource allocation.
Risks and Challenges in Horizontal vs Vertical Mergers
Horizontal mergers face risks such as regulatory scrutiny for potential monopolistic behavior, integration complexities between similar business units, and market overlap causing internal competition. Vertical mergers encounter challenges including coordinating different stages of the supply chain, potential antitrust concerns related to foreclosure of competitors, and complexities in managing diverse operational processes. Both merger types risk cultural clashes, integration delays, and unforeseen financial burdens impacting overall synergy realization.
Real-World Examples of Horizontal and Vertical Mergers
The horizontal merger between Disney and 21st Century Fox in 2019 combined two major entertainment companies, expanding Disney's content library and market reach. In contrast, the vertical merger of Amazon acquiring Whole Foods in 2017 integrated Amazon's e-commerce platform with a physical grocery chain, enhancing supply chain efficiency and customer access. These mergers illustrate how horizontal mergers concentrate market share within the same industry, while vertical mergers align complementary stages of production or distribution.
Horizontal Merger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com