Income smoothing involves using accounting techniques to level out fluctuations in a company's financial results, presenting a more consistent and stable earnings pattern. This practice can influence investor perception, credit ratings, and management's credibility by reducing volatility in reported income. Explore the article to understand how income smoothing impacts financial analysis and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
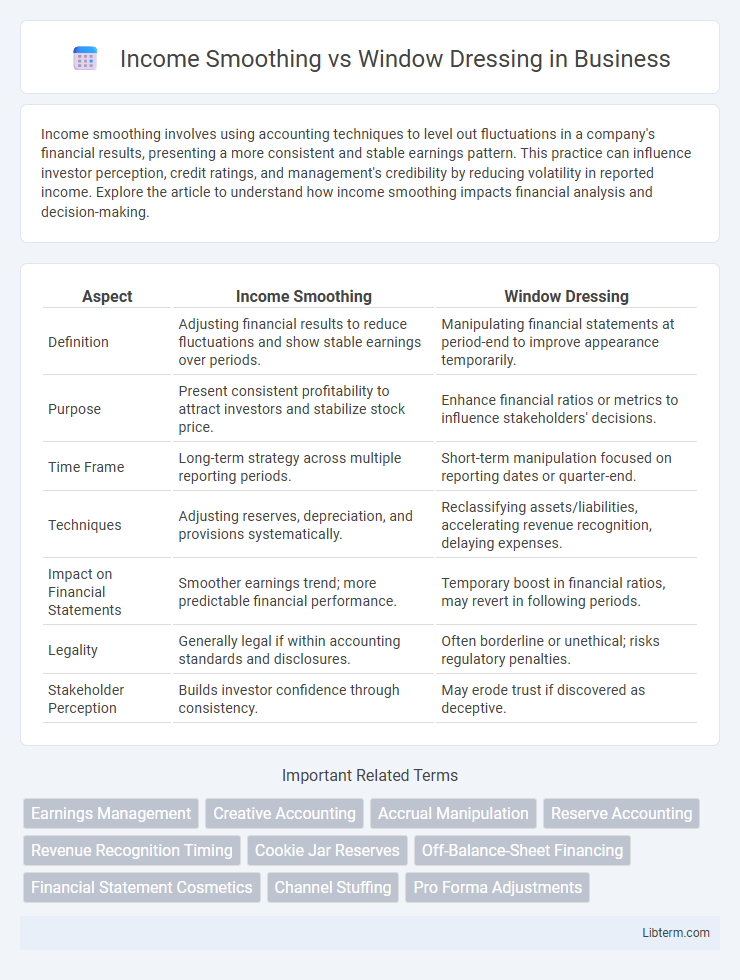
| Aspect | Income Smoothing | Window Dressing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusting financial results to reduce fluctuations and show stable earnings over periods. | Manipulating financial statements at period-end to improve appearance temporarily. |
| Purpose | Present consistent profitability to attract investors and stabilize stock price. | Enhance financial ratios or metrics to influence stakeholders' decisions. |
| Time Frame | Long-term strategy across multiple reporting periods. | Short-term manipulation focused on reporting dates or quarter-end. |
| Techniques | Adjusting reserves, depreciation, and provisions systematically. | Reclassifying assets/liabilities, accelerating revenue recognition, delaying expenses. |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Smoother earnings trend; more predictable financial performance. | Temporary boost in financial ratios, may revert in following periods. |
| Legality | Generally legal if within accounting standards and disclosures. | Often borderline or unethical; risks regulatory penalties. |
| Stakeholder Perception | Builds investor confidence through consistency. | May erode trust if discovered as deceptive. |
Introduction to Income Smoothing and Window Dressing
Income smoothing involves strategically managing financial reports to reduce fluctuations in earnings, creating a perception of stable and consistent profitability over time. Window dressing refers to manipulative practices aimed at enhancing the appearance of a company's financial statements at specific reporting periods to mislead stakeholders. Both techniques impact financial transparency and investor perception but differ in timing and methods of altering financial presentation.
Defining Income Smoothing
Income smoothing is an accounting practice aimed at reducing fluctuations in reported earnings to present a more consistent financial performance over time. It involves strategic timing of revenues and expenses to avoid significant spikes or drops in income, helping investors and stakeholders perceive stability. This differs from window dressing, which primarily focuses on improving financial statement appearances at specific reporting dates without necessarily achieving long-term income consistency.
Understanding Window Dressing
Window dressing involves strategic financial reporting practices aimed at enhancing a company's appearance in financial statements, often by manipulating short-term metrics without altering underlying economic realities. Techniques such as timing revenues or expenses, reclassifying transactions, and adjusting accruals are commonly employed to present a more favorable financial position during reporting periods. This practice differs from income smoothing, which seeks to reduce earnings volatility over time, whereas window dressing primarily targets improving financial ratios at specific reporting intervals.
Key Differences Between Income Smoothing and Window Dressing
Income smoothing involves the consistent adjustment of earnings to reduce fluctuations and present stable financial performance over multiple periods, while window dressing focuses on manipulating financial statements at period-end to create a more favorable short-term appearance. Income smoothing typically employs methods such as adjusting accruals or provisions systematically, whereas window dressing uses tactics like shifting expenses or revenues temporarily. The key difference lies in income smoothing's goal of long-term credibility versus window dressing's aim of enhancing the immediate financial snapshot.
Common Techniques Used in Income Smoothing
Income smoothing commonly involves techniques such as deferring expenses to future periods, accelerating revenues, and utilizing reserves or provisions to manage profit fluctuations. Companies may also adjust depreciation methods or manipulate discretionary accruals to create stable earnings patterns. These practices aim to present consistent financial performance, enhancing investor confidence while potentially obscuring true economic conditions.
Typical Methods of Window Dressing
Typical methods of window dressing include accelerating revenue recognition, delaying expense recording, and manipulating inventory levels to inflate financial performance at period-end. Companies may also engage in one-time transactions, such as selling assets or securing short-term loans, to artificially boost liquidity and solvency ratios. These tactics create a misleading financial picture aimed at impressing investors and creditors without reflecting the company's true operational health.
Motivations Behind Income Smoothing
Income smoothing is motivated by management's desire to present stable and predictable earnings to investors, reducing perceived risk and enhancing stock valuation. This practice involves adjusting accounting methods to minimize fluctuations in net income, thereby creating a consistent financial narrative. Unlike window dressing, which aims to improve financial statements temporarily for specific reporting periods, income smoothing focuses on long-term earnings consistency.
Reasons for Window Dressing in Financial Reporting
Window dressing in financial reporting aims to present a more favorable financial position to stakeholders by temporarily adjusting financial statements at reporting dates, often to attract investment or secure loans. Companies engage in practices like accelerating revenue recognition or deferring expenses to enhance liquidity metrics and profitability ratios, improving perceived creditworthiness and market valuation. These manipulations address short-term performance pressures from investors, regulatory requirements, and competitive benchmarks without necessarily reflecting the company's true economic condition.
Ethical Implications and Regulatory Perspectives
Income smoothing manipulates earnings to present stable financial performance, raising ethical concerns related to misleading stakeholders and compromising transparency. Window dressing involves short-term adjustments to financial statements to create a more favorable year-end appearance, often violating regulatory standards and risking legal repercussions. Regulatory frameworks like GAAP and IFRS explicitly prohibit such manipulations to ensure truthful reporting and protect investor confidence.
Detecting and Preventing Manipulative Financial Practices
Detecting and preventing manipulative financial practices such as income smoothing and window dressing requires thorough analysis of financial statements and cash flow patterns to identify inconsistencies and unusual fluctuations. Techniques like forensic accounting, ratio analysis, and audit trail examination are effective in uncovering artificial adjustments that distort true earnings or financial positions. Implementing strong internal controls, regulatory oversight, and transparent disclosure policies significantly reduce the risk of these deceptive accounting tactics.
Income Smoothing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com