The Walmart Effect describes how the presence of Walmart stores significantly influences local economies, often lowering prices but also impacting small businesses and wages in surrounding areas. This phenomenon reshapes retail landscapes by driving efficiency and competitive pricing, yet it raises concerns about market monopolization and community impact. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the Walmart Effect could affect your local economy and consumer choices.
Table of Comparison
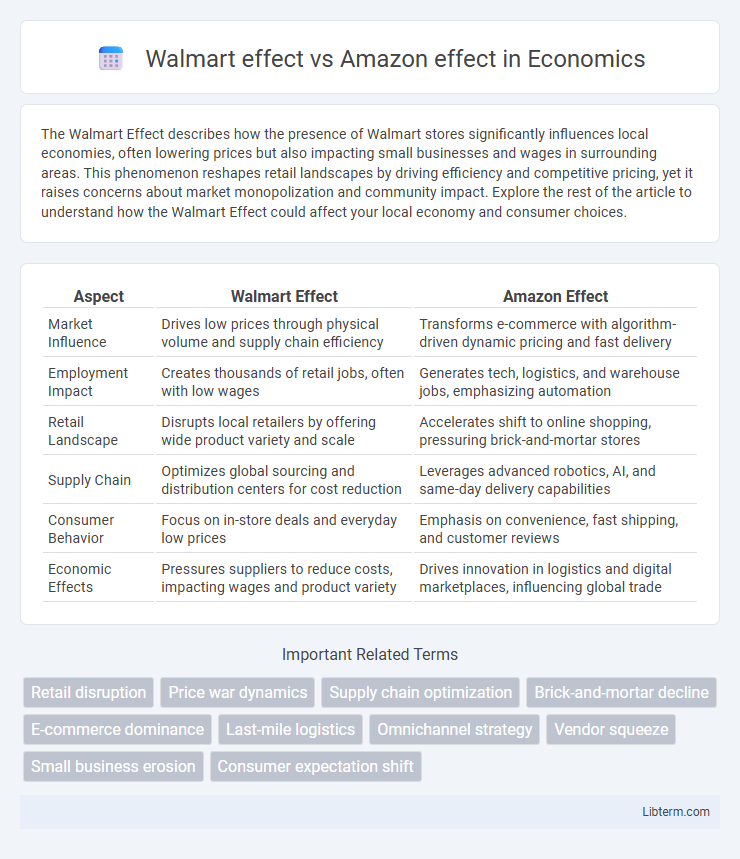
| Aspect | Walmart Effect | Amazon Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Market Influence | Drives low prices through physical volume and supply chain efficiency | Transforms e-commerce with algorithm-driven dynamic pricing and fast delivery |
| Employment Impact | Creates thousands of retail jobs, often with low wages | Generates tech, logistics, and warehouse jobs, emphasizing automation |
| Retail Landscape | Disrupts local retailers by offering wide product variety and scale | Accelerates shift to online shopping, pressuring brick-and-mortar stores |
| Supply Chain | Optimizes global sourcing and distribution centers for cost reduction | Leverages advanced robotics, AI, and same-day delivery capabilities |
| Consumer Behavior | Focus on in-store deals and everyday low prices | Emphasis on convenience, fast shipping, and customer reviews |
| Economic Effects | Pressures suppliers to reduce costs, impacting wages and product variety | Drives innovation in logistics and digital marketplaces, influencing global trade |
Understanding the Walmart Effect
The Walmart Effect refers to the significant economic impact Walmart has on local economies by lowering prices through economies of scale, which often pressures smaller retailers to reduce costs or exit the market. This effect drives supply chain efficiencies and influences consumer behavior by emphasizing low-cost goods and wide product availability. Understanding the Walmart Effect involves analyzing its role in reshaping retail landscapes, labor markets, and regional economic development.
Defining the Amazon Effect
The Amazon Effect refers to the transformative impact of Amazon's e-commerce platform on consumer behavior, retail strategies, and supply chain dynamics, driving convenience, rapid delivery, and vast product selection. Unlike the Walmart Effect, which emphasizes large-scale physical retail stores and economies of scale to lower prices, the Amazon Effect centers on digital innovation, personalized shopping experiences, and seamless omnichannel integration. This shift has accelerated the growth of online marketplaces, disrupted traditional brick-and-mortar models, and reshaped global retail ecosystems.
Price Competition: Offline vs Online
Walmart's effect on price competition centers on its ability to leverage vast physical store networks to drive down prices through economies of scale and aggressive in-store promotions. In contrast, Amazon's effect emphasizes dynamic pricing algorithms and extensive online data analytics, enabling real-time price adjustments and competitor price matching across millions of products. This shift from offline to online pricing strategies intensifies competition, pushing retailers to adopt more sophisticated, technology-driven pricing models to maintain market share.
Impact on Small Businesses
The Walmart effect often leads to small businesses struggling with lower prices and reduced market share due to Walmart's extensive supply chain and bulk purchasing power. The Amazon effect further intensifies these challenges by enabling small businesses to compete globally but also increasing pressure from massive online marketplaces with vast product selections and fast delivery options. Both retail giants force small businesses to innovate in niche markets, improve customer experience, or specialize to survive in an evolving retail landscape.
Changes in Consumer Behavior
The Walmart effect has historically driven consumer behavior toward prioritizing low prices and bulk purchasing, reshaping expectations for affordability and convenience in physical retail environments. In contrast, the Amazon effect amplifies consumer demand for rapid delivery, personalized recommendations, and seamless online shopping experiences, accelerating the shift to e-commerce dominance. These shifts highlight evolving preferences for speed, variety, and digital accessibility in purchasing habits.
Supply Chain Innovations
The Walmart effect revolutionized supply chain innovations by pioneering cross-docking logistics and real-time inventory management, significantly reducing costs and improving efficiency for suppliers and retailers. In contrast, the Amazon effect emphasized advanced automation technologies, including robotics and AI-driven demand forecasting, facilitating rapid delivery and personalized customer experiences. Both phenomena reshaped global supply chains but diverged in technological implementation and consumer engagement strategies.
Labor Market Implications
The Walmart effect on the labor market typically involves wage suppression and reduced employment quality due to aggressive cost-cutting and demand for low-skilled labor, impacting local retail jobs. Conversely, the Amazon effect promotes increased demand for warehousing, logistics, and tech-related roles, often offering higher wages but also raising concerns about job automation and workforce surveillance. Both retail giants reshape labor markets differently, with Walmart influencing traditional retail employment structures and Amazon driving digitization and gig economy growth.
Retail Store Footprint vs Digital Domination
Walmart's retail store footprint, with over 4,700 locations in the U.S., drives significant in-person customer traffic and local economic impact, emphasizing physical accessibility and convenience. Amazon's digital domination leverages over 300 million active users worldwide, prioritizing vast online product selection, personalized shopping experiences, and rapid delivery services. The Walmart effect bolsters community-based retail ecosystems, while the Amazon effect transforms consumer behavior through digital innovation and e-commerce scalability.
Community and Economic Impact
The Walmart effect often leads to the revitalization of local economies through job creation but risks undermining small businesses and depressing wages within communities. The Amazon effect accelerates economic shifts by boosting e-commerce growth and consumer convenience, yet it contributes to the decline of traditional retail jobs and challenges local tax bases. Both retail giants significantly reshape community economic landscapes by influencing employment patterns, local business sustainability, and municipal revenue streams.
Future Trends in Retail Transformation
Walmart effect drives retail transformation through supply chain efficiency and expansive physical presence, while Amazon effect emphasizes digital innovation and personalized customer experience. Future trends include hybrid models combining omnichannel strategies, leveraging AI for inventory management, and enhanced last-mile delivery systems to meet evolving consumer demands. Integration of advanced analytics and automation will further differentiate competitive positioning in the retail landscape.
Walmart effect Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com