Human capital accumulation involves investing in education, skills, and health to enhance the productivity and economic value of individuals. This process drives innovation, improves job performance, and boosts overall economic growth by equipping your workforce with necessary competencies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how strategic human capital development can transform your organization's success.
Table of Comparison
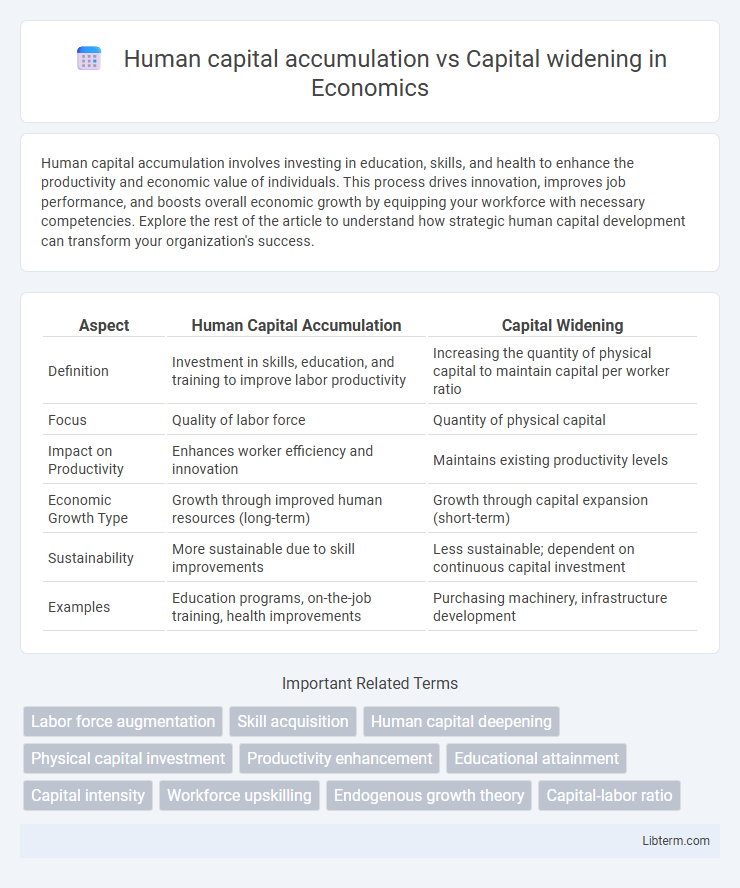
| Aspect | Human Capital Accumulation | Capital Widening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in skills, education, and training to improve labor productivity | Increasing the quantity of physical capital to maintain capital per worker ratio |
| Focus | Quality of labor force | Quantity of physical capital |
| Impact on Productivity | Enhances worker efficiency and innovation | Maintains existing productivity levels |
| Economic Growth Type | Growth through improved human resources (long-term) | Growth through capital expansion (short-term) |
| Sustainability | More sustainable due to skill improvements | Less sustainable; dependent on continuous capital investment |
| Examples | Education programs, on-the-job training, health improvements | Purchasing machinery, infrastructure development |
Introduction to Human Capital Accumulation and Capital Widening
Human capital accumulation involves enhancing the skills, knowledge, and competencies of the workforce through education and training, leading to increased productivity and innovation. Capital widening refers to expanding the amount of physical capital per worker, such as machinery and infrastructure, to maintain or improve output levels as the labor force grows. While capital widening supports quantitative growth, human capital accumulation drives qualitative improvements essential for sustainable economic development.
Defining Human Capital Accumulation
Human capital accumulation refers to the process of increasing the skills, knowledge, and experience possessed by an individual or workforce through education, training, and health improvements. This investment enhances productivity and innovation, driving long-term economic growth. Unlike capital widening, which expands the quantity of capital assets, human capital accumulation focuses on improving the quality and effectiveness of labor inputs.
Understanding Capital Widening
Capital widening refers to increasing the quantity of capital per worker to maintain the existing level of capital intensity as the labor force grows, ensuring productivity remains stable. Unlike human capital accumulation, which enhances workers' skills and knowledge, capital widening focuses on expanding physical capital stock proportionally with labor. This approach sustains economic growth by preventing dilution of capital but does not inherently improve labor productivity or technological progress.
Key Differences Between Human Capital Accumulation and Capital Widening
Human capital accumulation involves enhancing the skills, knowledge, and experience of the workforce, leading to increased productivity and innovation. In contrast, capital widening refers to expanding the quantity of capital inputs, such as machinery and infrastructure, without necessarily improving their quality or efficiency. The key difference lies in human capital accumulation emphasizing qualitative improvements in labor, while capital widening focuses on quantitative increases in physical capital stock.
The Role of Education and Training in Human Capital Accumulation
Education and training are critical drivers of human capital accumulation, enhancing workers' skills, productivity, and innovation capabilities. Unlike capital widening, which increases the quantity of capital per worker, human capital accumulation improves the quality of labor through knowledge, expertise, and adaptability. Investments in vocational training, higher education, and continuous skill development foster economic growth by creating a more competent and efficient workforce.
Investment in Physical Assets: Capital Widening Explained
Investment in physical assets under capital widening involves expanding the quantity of existing capital to support a growing workforce, maintaining the capital-to-labor ratio. Human capital accumulation emphasizes enhancing workers' skills and knowledge, boosting productivity without necessarily increasing physical asset volumes. Capital widening ensures economic growth by distributing more machinery, infrastructure, and equipment across labor inputs, rather than improving the quality of labor itself.
Impacts on Economic Growth: Human Capital vs. Capital Widening
Human capital accumulation drives economic growth by enhancing workforce skills, innovation, and productivity, leading to sustainable increases in output and living standards. Capital widening, which expands the quantity of physical capital per worker, boosts growth by enabling more extensive production but faces diminishing returns over time. Studies reveal that long-term growth heavily depends on human capital development, as it fosters technological progress and adaptability beyond mere capital accumulation.
Policy Approaches for Enhancing Human Capital Accumulation
Policy approaches for enhancing human capital accumulation emphasize investments in education, vocational training, and lifelong learning programs to improve workforce skills and productivity. Targeted funding for early childhood development and health care ensures a strong foundation for cognitive and physical growth, which directly impacts labor market outcomes. Governments also promote access to technology and digital literacy to adapt the workforce to evolving economic demands, fostering innovation and competitiveness.
Challenges and Limitations in Capital Widening
Capital widening, which involves increasing the quantity of physical capital per worker, faces significant challenges including diminishing returns to scale and limited productivity growth when simply expanding machinery or infrastructure. The approach often struggles with inefficiencies such as underutilized resources and increased maintenance costs that do not necessarily translate into proportional output gains. Unlike human capital accumulation, which enhances workers' skills and innovation capacity, capital widening alone may fail to sustain long-term economic growth due to technological stagnation and an inability to adapt to evolving market demands.
Future Trends: Balancing Human Capital and Capital Widening for Sustainable Growth
Future trends emphasize integrating human capital accumulation with capital widening to drive sustainable economic growth. Investment in education, skills training, and health enhances workforce productivity, while expanding physical capital infrastructure supports this skilled labor force. Strategic policies aim to harmonize technological adoption and workforce development to maintain long-term competitiveness and inclusive growth.
Human capital accumulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com