Asset-liability mismatch occurs when the durations or cash flows of assets and liabilities fail to align, exposing financial institutions to risks like liquidity shortages or interest rate fluctuations. Managing this mismatch is crucial for maintaining financial stability and ensuring that obligations can be met without distress. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can identify and mitigate asset-liability mismatches effectively.
Table of Comparison
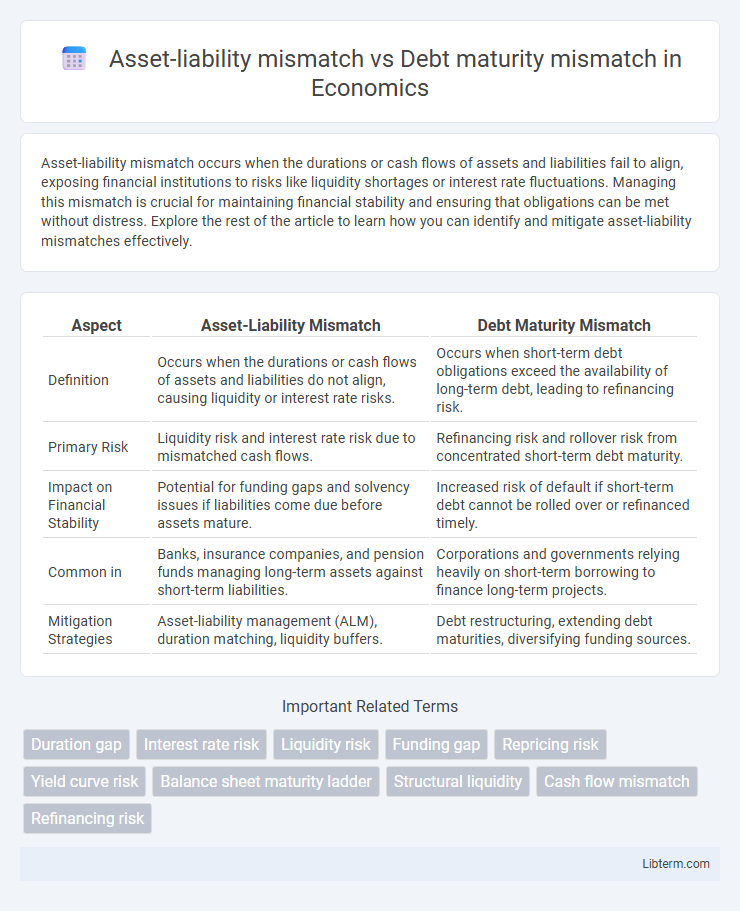
| Aspect | Asset-Liability Mismatch | Debt Maturity Mismatch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Occurs when the durations or cash flows of assets and liabilities do not align, causing liquidity or interest rate risks. | Occurs when short-term debt obligations exceed the availability of long-term debt, leading to refinancing risk. |
| Primary Risk | Liquidity risk and interest rate risk due to mismatched cash flows. | Refinancing risk and rollover risk from concentrated short-term debt maturity. |
| Impact on Financial Stability | Potential for funding gaps and solvency issues if liabilities come due before assets mature. | Increased risk of default if short-term debt cannot be rolled over or refinanced timely. |
| Common in | Banks, insurance companies, and pension funds managing long-term assets against short-term liabilities. | Corporations and governments relying heavily on short-term borrowing to finance long-term projects. |
| Mitigation Strategies | Asset-liability management (ALM), duration matching, liquidity buffers. | Debt restructuring, extending debt maturities, diversifying funding sources. |
Understanding Asset-Liability Mismatch
Asset-liability mismatch occurs when the durations and cash flows of a company's assets do not align with its liabilities, creating liquidity risks and potential solvency issues. Understanding asset-liability mismatch involves analyzing the timing differences between asset inflows and liability outflows to ensure the firm can meet its obligations without distress. This contrasts with debt maturity mismatch, which specifically refers to the misalignment of the maturity dates of debts, emphasizing the importance of synchronizing asset cash flows with liability schedules for effective financial management.
What Is Debt Maturity Mismatch?
Debt maturity mismatch occurs when a company's liabilities have shorter maturities than the assets generating the cash flow to repay them, creating liquidity risk. This mismatch forces the firm to refinance debts frequently, exposing it to market fluctuations and interest rate changes. Asset-liability mismatch, while broader, involves timing differences between asset inflows and liability outflows, but debt maturity mismatch specifically addresses the timing gap in debt obligations.
Key Differences Between Asset-Liability and Debt Maturity Mismatches
Asset-liability mismatch occurs when the durations or interest rates of a company's assets and liabilities are not aligned, leading to liquidity or interest rate risk, while debt maturity mismatch specifically refers to the misalignment between the timing of debt repayments and cash inflows. Asset-liability mismatches impact overall financial stability by affecting the firm's ability to meet long-term obligations, whereas debt maturity mismatches can trigger refinancing risks and short-term liquidity crises. Understanding these distinctions is critical for effective risk management, as asset-liability mismatch encompasses broader balance sheet risks, while debt maturity mismatch focuses on debt structure and repayment schedules.
Causes of Asset-Liability Mismatches in Finance
Asset-liability mismatch occurs when the maturities or cash flows of assets and liabilities do not align, often due to differences in interest rates, liquidity needs, or duration preferences. Causes include interest rate volatility affecting fixed and variable income streams, regulatory constraints that limit asset allocation, and behavioral factors like premature withdrawals or unexpected liabilities. In contrast, debt maturity mismatch specifically centers on the timing gap between debt obligations and the available refinancing or asset liquidation options.
Impact of Debt Maturity Mismatch on Liquidity Risks
Debt maturity mismatch occurs when an institution's short-term liabilities exceed the maturities of its long-term assets, increasing liquidity risks due to potential refinancing difficulties. This mismatch can lead to cash flow shortfalls, forcing forced asset sales or expensive borrowing to meet obligations. Unlike asset-liability mismatch, which broadly affects balance sheet stability, debt maturity mismatch specifically heightens the risk of liquidity crises during market stress.
Real-World Examples of Mismatches in Banking
Asset-liability mismatch occurs when banks hold long-term loans funded by short-term deposits, exposing them to liquidity risks if depositors withdraw funds unexpectedly. Debt maturity mismatch arises when a bank's liabilities mature before its assets, causing refinancing challenges during tight credit conditions. For example, the 2008 financial crisis highlighted how Lehman Brothers faced severe distress due to short-term borrowing to finance long-term assets, exemplifying both asset-liability and debt maturity mismatches.
Consequences for Financial Stability
Asset-liability mismatch occurs when financial institutions hold assets and liabilities with differing durations, creating liquidity risk and potential solvency issues during market stress. Debt maturity mismatch refers to the reliance on short-term debt to finance long-term assets, increasing rollover risk and vulnerability to sudden funding shortages. Both mismatches undermine financial stability by amplifying systemic risk, triggering fire sales, and causing contagion effects across banking and credit markets.
Strategies to Manage Asset-Liability Mismatches
Effective strategies to manage asset-liability mismatches include duration matching, where assets and liabilities are aligned to similar maturities to minimize interest rate risk and liquidity gaps. Cash flow matching ensures that asset inflows coincide with liability outflows, reducing the need for emergency funding. Employing hedging techniques such as interest rate swaps and diversifying asset portfolios further stabilizes financial positions against market fluctuations and debt maturity mismatches.
Risk Mitigation Techniques for Debt Maturity Mismatches
Debt maturity mismatch risk arises when an institution's short-term liabilities exceed its short-term assets, leading to refinancing and liquidity challenges. Effective risk mitigation techniques include staggered debt maturities to avoid large lump-sum repayments, maintaining adequate liquidity reserves and committed credit lines to meet obligations, and implementing interest rate swaps or derivatives to manage refinancing costs. Regular stress testing and scenario analysis further enhance resilience against adverse market conditions impacting debt rollover capacity.
Regulatory Perspectives and Compliance Standards
Asset-liability mismatch and debt maturity mismatch present distinct regulatory challenges, with asset-liability mismatch primarily scrutinized under Basel III liquidity coverage ratio (LCR) and net stable funding ratio (NSFR) to ensure adequate liquidity buffers. Debt maturity mismatch is closely monitored through compliance standards such as IFRS 7 and disclosures under the SEC's risk factor requirements, compelling firms to manage refinancing risks and align debt profiles with operational cash flows. Regulatory bodies emphasize stress testing and dynamic risk assessment frameworks to mitigate systemic risks arising from both mismatches.
Asset-liability mismatch Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com