Exchange rate determination depends on factors like interest rates, inflation, and economic stability, which influence currency value in global markets. Market speculation and government intervention also play critical roles in shifting exchange rates daily. Explore the full article to understand how these elements impact your international financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
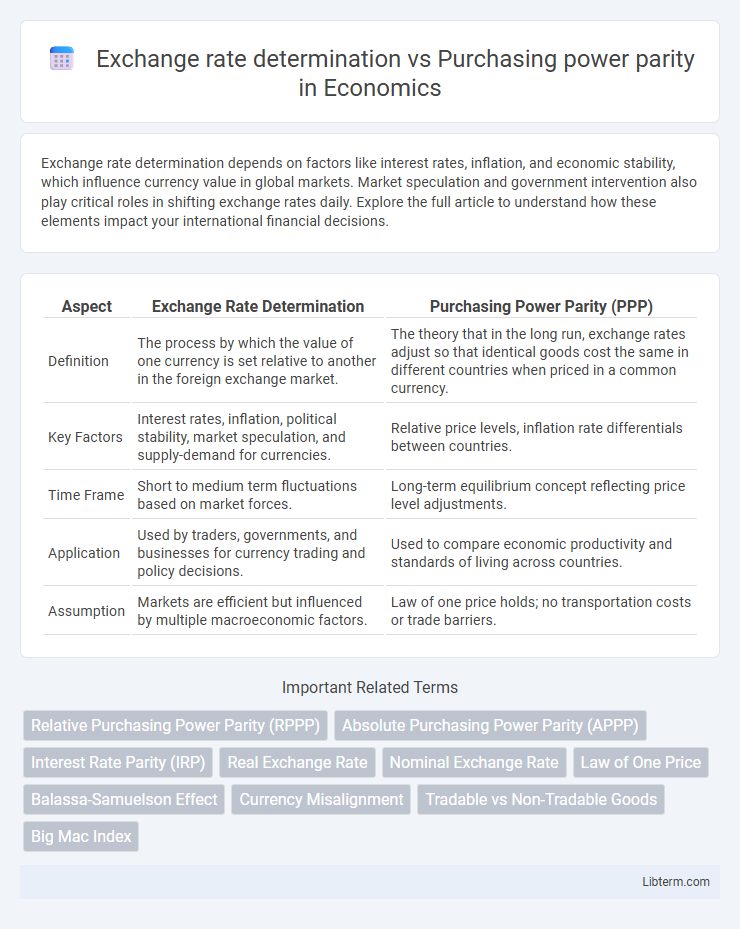
| Aspect | Exchange Rate Determination | Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process by which the value of one currency is set relative to another in the foreign exchange market. | The theory that in the long run, exchange rates adjust so that identical goods cost the same in different countries when priced in a common currency. |
| Key Factors | Interest rates, inflation, political stability, market speculation, and supply-demand for currencies. | Relative price levels, inflation rate differentials between countries. |
| Time Frame | Short to medium term fluctuations based on market forces. | Long-term equilibrium concept reflecting price level adjustments. |
| Application | Used by traders, governments, and businesses for currency trading and policy decisions. | Used to compare economic productivity and standards of living across countries. |
| Assumption | Markets are efficient but influenced by multiple macroeconomic factors. | Law of one price holds; no transportation costs or trade barriers. |
Introduction to Exchange Rate Determination
Exchange rate determination involves analyzing the factors that influence the value of one currency relative to another, such as interest rates, inflation, and trade balances. It encompasses models like the monetary approach, asset market approach, and behavioral equilibrium exchange rate, which explain currency fluctuations in both short and long term. Understanding exchange rate determination provides the foundation for comparing actual exchange rates to those predicted by purchasing power parity (PPP), which reflects price level differences across countries.
Understanding Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) explains exchange rate determination by comparing the relative price levels of a fixed basket of goods and services between two countries, aiming for equal purchasing power. PPP implies that in the long run, exchange rates adjust to offset differences in inflation rates, making imported goods cost the same across borders. Economists use PPP as a benchmark to assess whether a currency is undervalued or overvalued relative to its true economic value.
Key Theories of Exchange Rate Determination
Exchange rate determination primarily revolves around theories such as Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), Interest Rate Parity (IRP), and the Balance of Payments model. PPP theory asserts that exchange rates adjust to equalize the price levels of a basket of goods between two countries, reflecting inflation differentials. In contrast, IRP emphasizes the role of interest rate differentials in forecasting future exchange rates, while the Balance of Payments approach links currency value to trade and capital flow balances.
Absolute vs Relative Purchasing Power Parity
Absolute Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) asserts that exchange rates between two currencies are equal to the ratio of their price levels, implying identical purchasing power across countries without accounting for transportation costs or trade barriers. Relative Purchasing Power Parity, on the other hand, focuses on the rate of change in price levels or inflation rates between countries, suggesting that the percentage change in exchange rates over time mirrors the differential inflation rates. While Absolute PPP provides a theoretical anchor point for exchange rates based on price level equality, Relative PPP offers a dynamic framework explaining exchange rate fluctuations through inflation differentials.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
Exchange rates are influenced by a complex interplay of factors including interest rates, inflation, political stability, and market speculation, which cause short-term fluctuations beyond the scope of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP). While PPP emphasizes long-term equilibrium based on price level differences between countries, real exchange rate movements can deviate significantly due to capital flows, differential economic growth, and central bank interventions. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately predicting exchange rate behavior and managing international financial risks.
The Role of Inflation in PPP and Exchange Rates
Inflation plays a critical role in purchasing power parity (PPP) by influencing the relative price levels between countries, which in turn affects exchange rate adjustments to maintain parity. Higher inflation in one country relative to another typically leads to a depreciation of its currency to offset increased domestic prices and preserve purchasing power equilibrium. This inflation-driven exchange rate movement aligns with the PPP theory, which asserts that exchange rates adjust to equalize the cost of identical goods across different economies over time.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Exchange Rate Movements
Short-term exchange rate movements are influenced primarily by interest rate differentials, capital flows, and market speculation, often causing volatility that deviates from Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) predictions. In contrast, long-term exchange rate trends tend to align more closely with PPP, as price level adjustments correct disparities in purchasing power between countries over time. Understanding the distinction between these time horizons is essential for accurate currency forecasting and international investment decisions.
Limitations of Purchasing Power Parity
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) often fails to accurately determine exchange rates due to factors like transportation costs, tariffs, and non-tradable goods, which create price disparities across countries. Market imperfections, such as differing consumption patterns and government interventions, further distort PPP predictions. Consequently, short-term exchange rate fluctuations are better explained by interest rates, capital flows, and speculative activities rather than solely relying on PPP.
Empirical Evidence: Exchange Rates vs PPP
Empirical evidence often shows significant deviations between actual exchange rates and Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) predictions, particularly in the short run due to market frictions, speculative activities, and differing interest rates. Studies reveal that while PPP may serve as a reasonable long-term benchmark, exchange rates frequently exhibit volatility not explained by relative price levels alone. Cross-country analyses confirm that exchange rate determination is influenced by a combination of macroeconomic fundamentals, such as inflation differentials and trade balances, alongside PPP, but these factors explain only part of the fluctuations observed in real-world currency markets.
Practical Implications for Investors and Policymakers
Exchange rate determination relies on factors such as interest rates, capital flows, and market speculation, influencing short-term currency movements critical for investors managing portfolio risks and policymakers aiming for monetary stability. Purchasing power parity (PPP) provides a long-term benchmark for exchange rates based on relative price levels, helping investors evaluate currency misalignments and guiding policymakers in assessing inflation differentials and trade competitiveness. Understanding the divergence between market-driven exchange rates and PPP forecasts enables better hedging strategies for investors and more informed intervention policies to correct persistent currency imbalances.
Exchange rate determination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com