Specialization enhances efficiency and expertise by allowing individuals or organizations to focus on a specific area, leading to higher quality outcomes and competitive advantage. Developing deep knowledge in one field enables faster problem-solving and innovation tailored to unique challenges. Discover how specialization can transform Your professional growth and success by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
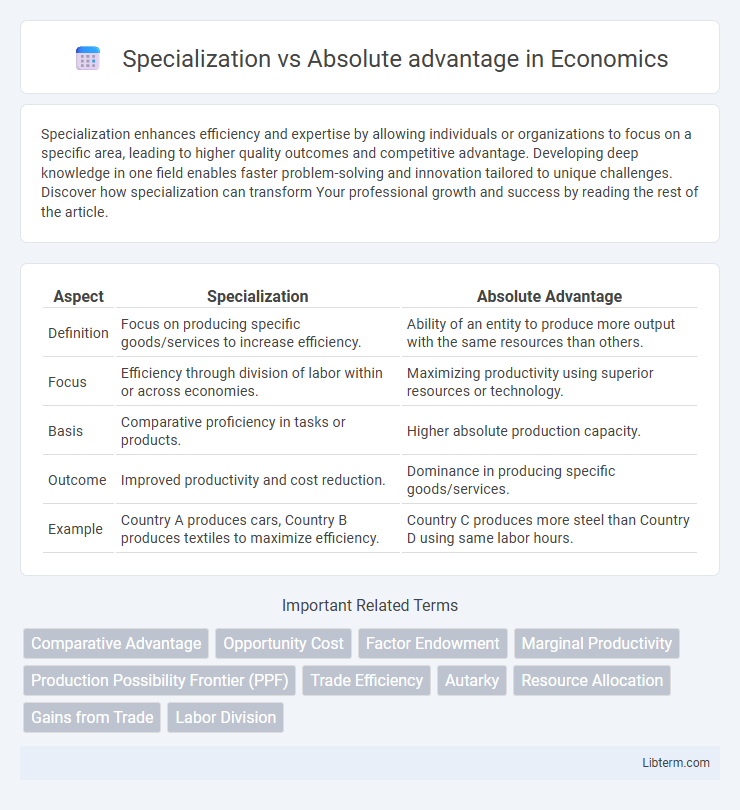
| Aspect | Specialization | Absolute Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on producing specific goods/services to increase efficiency. | Ability of an entity to produce more output with the same resources than others. |
| Focus | Efficiency through division of labor within or across economies. | Maximizing productivity using superior resources or technology. |
| Basis | Comparative proficiency in tasks or products. | Higher absolute production capacity. |
| Outcome | Improved productivity and cost reduction. | Dominance in producing specific goods/services. |
| Example | Country A produces cars, Country B produces textiles to maximize efficiency. | Country C produces more steel than Country D using same labor hours. |
Understanding Specialization and Absolute Advantage
Specialization involves focusing resources and efforts on producing a limited range of goods or services to increase efficiency and expertise. Absolute advantage refers to the ability of an individual, firm, or country to produce a good or service more efficiently than others, using fewer inputs or resources. Understanding specialization and absolute advantage helps optimize production processes and maximize economic gains by leveraging comparative strengths.
Key Differences Between Specialization and Absolute Advantage
Specialization refers to the concentration of resources and efforts on a particular task or production to increase efficiency, while absolute advantage occurs when a country or individual can produce a good using fewer resources than others. Specialization enhances productivity through focused skills and economies of scale, whereas absolute advantage emphasizes the direct comparison of resource efficiency in producing goods. The key difference lies in specialization being a strategy for efficiency gains, whereas absolute advantage measures the inherent production efficiency relative to competitors.
How Specialization Boosts Productivity
Specialization boosts productivity by allowing workers or countries to focus on tasks where they have the highest efficiency, leveraging their skills and resources optimally. This division of labor enhances output quality and speed, fostering economies of scale and innovation in specific fields. Unlike absolute advantage, which emphasizes the ability to produce more overall, specialization maximizes comparative benefits, enabling trade and mutual growth.
The Role of Absolute Advantage in Global Trade
Absolute advantage plays a crucial role in global trade by enabling countries to produce goods more efficiently than others, reducing production costs and maximizing output. When a nation specializes in products where it holds an absolute advantage, global resource allocation becomes more efficient, promoting higher overall economic welfare. This efficiency fosters increased trade volumes and stronger international economic integration.
Economic Benefits of Specialization
Specialization enhances productivity by allowing individuals or countries to focus on tasks where they have the highest efficiency, leading to increased total output and resource utilization. This economic benefit boosts trade opportunities, enabling entities to exchange goods or services at lower costs compared to self-sufficiency. Specialization reduces production time and expenses, fostering economies of scale and promoting overall economic growth.
Impacts of Absolute Advantage on Resource Allocation
Absolute advantage enables countries to allocate resources more efficiently by producing goods with lower input costs compared to others, increasing overall productivity. This efficiency leads to optimized resource distribution, reducing waste and maximizing output in sectors where a nation excels. Consequently, absolute advantage drives economic growth by allowing nations to specialize based on their inherent production strengths, enhancing global trade benefits.
Real-World Examples: Specialization vs Absolute Advantage
China's specialization in electronics manufacturing capitalizes on efficient labor and supply chain integration, demonstrating its absolute advantage in producing smartphones at scale. Germany's focus on high-precision engineering and automotive technology exemplifies specialization that leverages skilled craftsmanship and innovation. These real-world cases highlight how countries optimize production by either absolute advantage or targeted specialization to boost global trade competitiveness.
Challenges and Limitations of Specialization
Specialization often leads to increased efficiency and productivity but faces challenges such as over-dependence on specific industries, which can cause economic vulnerability during market shifts or disruptions. Limited flexibility restricts the ability to adapt to changing consumer demands, resulting in potential unemployment or underutilization of skills in the workforce. Furthermore, excessive specialization may hinder innovation and reduce overall economic diversity, making regions or countries less resilient to global economic fluctuations.
Absolute Advantage in the Modern Economy
Absolute advantage in the modern economy refers to a country's ability to produce goods or services more efficiently than others, using fewer resources or less time. This concept drives international trade by enabling nations to focus on industries where they have the highest productivity, thus maximizing output and economic growth. Emphasizing absolute advantage helps businesses and governments allocate resources optimally, fostering competitive advantage in global markets.
Choosing Between Specialization and Absolute Advantage
Choosing between specialization and absolute advantage requires analyzing productivity and resource allocation efficiency. Specialization maximizes output by focusing on tasks where opportunity costs are lowest, while absolute advantage emphasizes producing goods with the highest absolute productivity. Decision-makers balance these concepts by evaluating comparative efficiency and the potential gains from trade to optimize overall economic performance.
Specialization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com