Commodity money refers to money that has intrinsic value, such as gold, silver, or other valuable materials used historically as a medium of exchange. Unlike fiat money, commodity money's worth is based on the substance it is made from, providing natural value and stability in trade. Discover how commodity money shaped economic systems and why understanding it can enhance your financial knowledge in the full article.
Table of Comparison
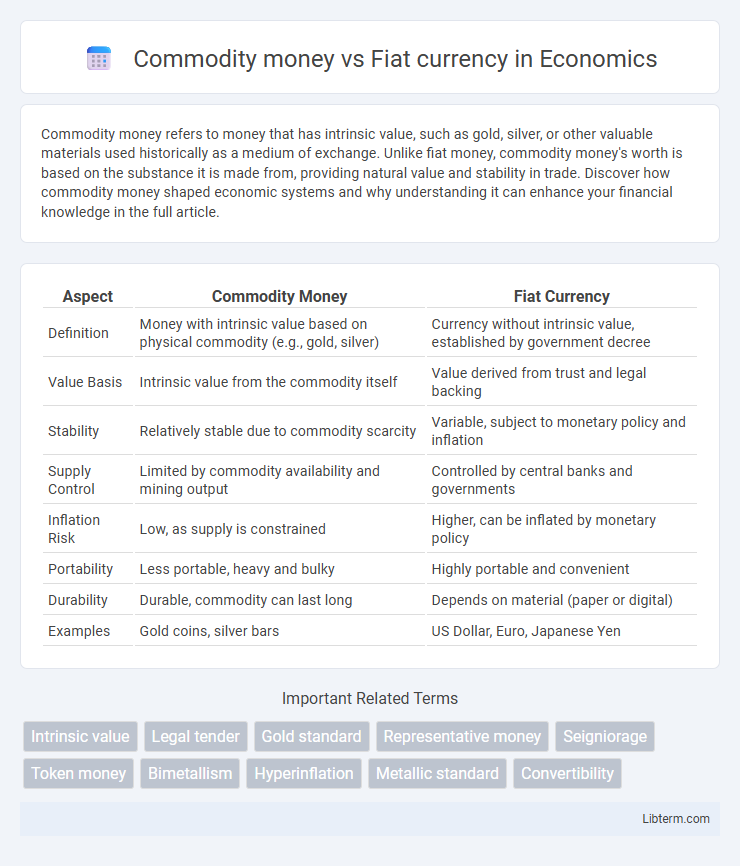
| Aspect | Commodity Money | Fiat Currency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Money with intrinsic value based on physical commodity (e.g., gold, silver) | Currency without intrinsic value, established by government decree |
| Value Basis | Intrinsic value from the commodity itself | Value derived from trust and legal backing |
| Stability | Relatively stable due to commodity scarcity | Variable, subject to monetary policy and inflation |
| Supply Control | Limited by commodity availability and mining output | Controlled by central banks and governments |
| Inflation Risk | Low, as supply is constrained | Higher, can be inflated by monetary policy |
| Portability | Less portable, heavy and bulky | Highly portable and convenient |
| Durability | Durable, commodity can last long | Depends on material (paper or digital) |
| Examples | Gold coins, silver bars | US Dollar, Euro, Japanese Yen |
Introduction to Commodity Money and Fiat Currency
Commodity money derives its value from the intrinsic worth of the material, such as gold or silver, used as currency throughout history. Fiat currency, unlike commodity money, holds value solely based on government regulation and trust, lacking intrinsic value but functioning as legal tender. Understanding the fundamental differences between the tangible assets backing commodity money and the trust-based system of fiat currency is crucial in economic studies.
Historical Evolution of Money Systems
Commodity money, used for millennia, derived its value from physical items like gold, silver, or grain, directly linked to intrinsic worth and widespread acceptability. Transitioning to fiat currency, governments began issuing paper money backed by legal decrees rather than physical commodities, enabling greater flexibility in monetary policy and economic regulation. This historical evolution reflects a shift from tangible asset-based systems to trust-based economies, facilitating modern financial complexity and global trade expansion.
Key Characteristics of Commodity Money
Commodity money derives its value from the intrinsic worth of the material it is made from, such as gold, silver, or precious metals. It is durable, divisible, and has a universally accepted value due to its physical properties and scarcity. Unlike fiat currency, commodity money maintains value independent of government backing or decree.
Key Characteristics of Fiat Currency
Fiat currency is government-issued money that has no intrinsic value and is not backed by a physical commodity, relying instead on public trust and legal decree. It is characterized by its ability to serve as a legal tender for all debts, its controllability through monetary policy by central banks, and its flexibility to accommodate economic fluctuations without the constraints of commodity reserves. Unlike commodity money, fiat currency facilitates modern economic systems by enabling inflation management, interest rate adjustments, and seamless transaction efficiency.
Advantages of Commodity Money
Commodity money offers intrinsic value due to its physical properties, such as gold or silver, which enhances trust and stability in economic transactions. Its limited supply helps prevent inflation, maintaining purchasing power over time compared to fiat currency. Unlike fiat money, commodity money is less susceptible to government manipulation, providing a reliable store of value.
Advantages of Fiat Currency
Fiat currency offers advantages such as greater flexibility in monetary policy, allowing central banks to control inflation and stabilize the economy effectively. Unlike commodity money, fiat currency is not limited by physical reserves, enabling governments to respond swiftly to financial crises and economic fluctuations. Its widespread acceptance and ease of use facilitate smoother transactions and support modern economic growth.
Limitations and Risks of Commodity Money
Commodity money faces significant limitations such as lack of portability and divisibility, making large-scale transactions cumbersome and impractical. Its value depends on the intrinsic worth of the commodity, exposing economies to price volatility and resource scarcity, which can destabilize markets. Storage and security costs also create inefficiencies compared to modern fiat currency systems that rely on government backing and legal tender status.
Limitations and Risks of Fiat Currency
Fiat currency faces limitations such as susceptibility to inflation and loss of purchasing power due to excessive money printing without intrinsic value backing. Centralized control by governments or central banks increases the risk of policy mismanagement, which can lead to hyperinflation or economic instability. Unlike commodity money, fiat currency lacks inherent value, making it vulnerable to loss of trust and currency devaluation in times of economic crisis.
Impact on Inflation and Economic Stability
Commodity money, backed by physical assets like gold or silver, tends to limit inflation due to its intrinsic value and fixed supply, promoting long-term economic stability. Fiat currency, issued by governments without intrinsic value, allows greater flexibility in monetary policy but risks higher inflation and economic volatility if not managed prudently. Central banks must balance money supply control and inflation targeting to maintain economic stability in fiat systems.
Future Perspectives: Commodity Money vs Fiat Currency
Future perspectives on commodity money versus fiat currency highlight the increasing importance of digital assets and blockchain technology in shaping monetary systems. Commodity money retains intrinsic value tied to physical resources like gold or silver, offering stability during economic uncertainty, while fiat currency depends on government trust and monetary policy flexibility for economic growth. Emerging trends suggest a hybrid approach combining digital fiat currencies with commodity-backed reserves could enhance financial security and inflation resistance in evolving global markets.
Commodity money Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com