Input-output analysis is a quantitative economic technique that models the interdependencies between different sectors of an economy, tracing how the output of one industry becomes the input for another. This method helps reveal the flow of goods and services, enabling more accurate predictions of economic impacts and resource allocation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how input-output analysis can enhance Your economic planning and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
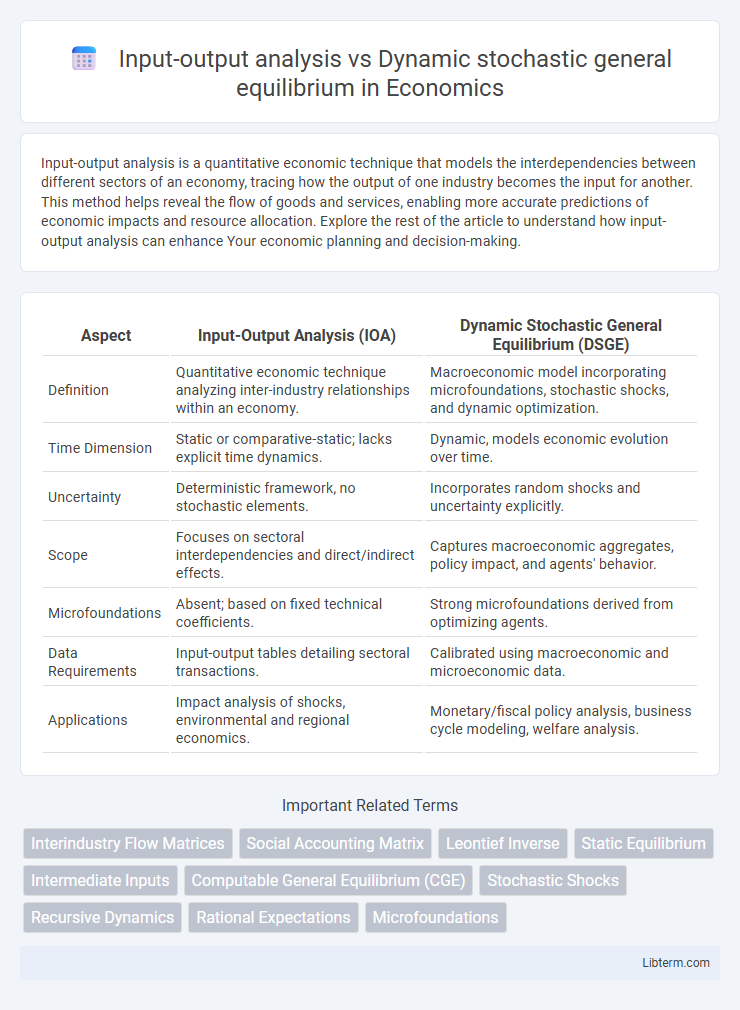
| Aspect | Input-Output Analysis (IOA) | Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Quantitative economic technique analyzing inter-industry relationships within an economy. | Macroeconomic model incorporating microfoundations, stochastic shocks, and dynamic optimization. |
| Time Dimension | Static or comparative-static; lacks explicit time dynamics. | Dynamic, models economic evolution over time. |
| Uncertainty | Deterministic framework, no stochastic elements. | Incorporates random shocks and uncertainty explicitly. |
| Scope | Focuses on sectoral interdependencies and direct/indirect effects. | Captures macroeconomic aggregates, policy impact, and agents' behavior. |
| Microfoundations | Absent; based on fixed technical coefficients. | Strong microfoundations derived from optimizing agents. |
| Data Requirements | Input-output tables detailing sectoral transactions. | Calibrated using macroeconomic and microeconomic data. |
| Applications | Impact analysis of shocks, environmental and regional economics. | Monetary/fiscal policy analysis, business cycle modeling, welfare analysis. |
Introduction to Input-Output Analysis and DSGE
Input-output analysis quantifies interindustry linkages by mapping the flow of goods and services within an economy using Leontief matrices, offering a static snapshot to evaluate sectoral dependencies and impacts of demand changes. Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) models incorporate microeconomic foundations with stochastic shocks and forward-looking agents to capture temporal economic fluctuations, policy effects, and equilibrium behavior under uncertainty. While input-output analysis excels in structural decomposition and static impact assessment, DSGE models provide a comprehensive, dynamic framework for macroeconomic policy evaluation and forecasting.
Historical Background and Development
Input-output analysis, developed by Wassily Leontief in the 1930s, provides a quantitative framework for understanding inter-industry relationships within an economy, emphasizing fixed production coefficients and linear interdependencies. Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) models emerged in the 1980s as a response to limitations in earlier macroeconomic models, integrating microeconomic foundations with stochastic shocks and forward-looking behavior to capture dynamic adjustments in economic variables. The evolution of DSGE marked a significant advancement by incorporating expectations and policy analysis, while input-output analysis remains foundational for structural economic assessments and sectoral linkages.
Fundamental Concepts of Input-Output Analysis
Input-output analysis fundamentally maps the interdependencies between industries, capturing the flow of goods and services within an economy through fixed technical coefficients in a Leontief matrix. This method emphasizes static economic relationships and sectoral output requirements, contrasting with Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) models, which incorporate time dynamics, stochastic shocks, and optimizing agents under uncertainty. The core utility of input-output analysis lies in its detailed representation of how changes in one sector propagate through the economy via direct and indirect effects, forming the foundation for empirical economic impact evaluations.
Core Principles of Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium
Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) models integrate microeconomic foundations with macroeconomic outcomes by incorporating agents' optimization behavior under uncertainty and intertemporal decision-making. Unlike Input-Output Analysis, which focuses on static inter-industry relationships, DSGE models emphasize stochastic shocks, forward-looking expectations, and equilibrium conditions across multiple markets and time periods. Core principles include rational expectations, market clearing, and the dynamic adjustment of economic variables driven by random innovations within a general equilibrium framework.
Modeling Economic Systems: IO vs DSGE Approaches
Input-output analysis models economic systems by capturing inter-industry relationships using fixed coefficients to represent production dependencies, emphasizing structural economic flows and multiplier effects. Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) models incorporate microfoundations, expectations, and stochastic shocks, offering a comprehensive framework for analyzing macroeconomic policy responses and market dynamics over time. While IO models excel in detailed sectoral interactions and static impact assessments, DSGE models provide dynamic policy evaluation under uncertainty with equilibrium conditions.
Data Requirements and Calibration
Input-output analysis requires detailed sectoral transaction tables reflecting the flow of goods and services within an economy, relying heavily on historical and static data for calibration. Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) models demand extensive microeconomic data, including preferences, technology parameters, and stochastic shock processes, requiring sophisticated calibration or Bayesian estimation techniques to match observed macroeconomic dynamics. DSGE calibration is more complex and data-intensive, often incorporating time-series data and structural estimation, while input-output analysis primarily uses aggregate, cross-sectional economic data.
Strengths and Limitations of Input-Output Models
Input-output analysis excels at capturing sectoral interdependencies through detailed transaction tables, enabling precise short-term economic impact assessments and resource flow tracing. Its main limitations include static assumptions, inability to account for price changes, and lack of behavioral responses under uncertainty, restricting effectiveness in dynamic or stochastic environments. Compared to Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) models, input-output frameworks offer clarity and granularity but fall short in modeling macroeconomic dynamics and policy shock responses.
Advantages and Weaknesses of DSGE Frameworks
Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) models offer advantages such as incorporating microeconomic foundations, allowing for the analysis of policy impacts over time under uncertainty, and capturing endogenous responses of agents within the economy. Weaknesses of DSGE frameworks include reliance on strong assumptions like rational expectations and representative agents, potential oversimplification of complex economic dynamics, and challenges in accurately calibrating parameters to real-world data. In comparison, while input-output analysis excels in detailing inter-industry relationships without relying on behavioral assumptions, it lacks the dynamic and stochastic features that DSGE models provide for macroeconomic policy evaluation.
Comparative Applications in Policy Analysis
Input-output analysis excels in mapping sectoral interdependencies and quantifying immediate economic ripple effects, making it ideal for assessing short-term policy impacts on production and employment. Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) models provide a forward-looking framework that incorporates expectations, monetary and fiscal policy shocks, and microfoundations, enabling comprehensive evaluation of medium- to long-term macroeconomic policy dynamics and welfare effects. Policymakers rely on input-output analysis for static, regional impact studies, while DSGE models inform decisions on structural reforms and stabilization policies through simulation of policy scenarios under uncertainty.
Future Directions and Integration of IO and DSGE
Future directions in economic modeling emphasize integrating Input-Output (IO) analysis with Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) models to capture sectoral interactions alongside macroeconomic fluctuations. Combining IO's detailed inter-industry linkages with DSGE's micro-founded stochastic dynamics can enhance predictive accuracy and policy simulations, especially in assessing supply chain shocks and structural transformations. Advances in computational power and data availability enable the development of hybrid models that leverage IO's granularity and DSGE's forward-looking optimization frameworks for robust scenario analysis.
Input-output analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com