Economic dynamism drives innovation, growth, and competitiveness within markets, fostering an environment where businesses can thrive and adapt to changing conditions. Regions with high economic dynamism often experience increased job creation, higher productivity, and improved living standards. Explore the rest of this article to understand how economic dynamism can impact Your community and opportunities.
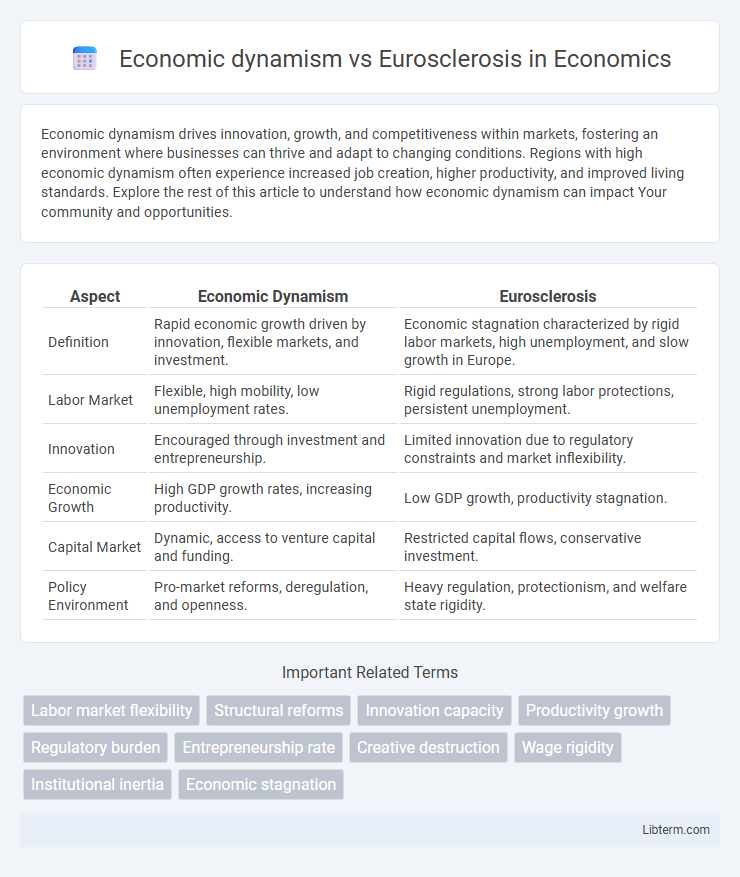
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Economic Dynamism | Eurosclerosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid economic growth driven by innovation, flexible markets, and investment. | Economic stagnation characterized by rigid labor markets, high unemployment, and slow growth in Europe. |
| Labor Market | Flexible, high mobility, low unemployment rates. | Rigid regulations, strong labor protections, persistent unemployment. |
| Innovation | Encouraged through investment and entrepreneurship. | Limited innovation due to regulatory constraints and market inflexibility. |
| Economic Growth | High GDP growth rates, increasing productivity. | Low GDP growth, productivity stagnation. |
| Capital Market | Dynamic, access to venture capital and funding. | Restricted capital flows, conservative investment. |
| Policy Environment | Pro-market reforms, deregulation, and openness. | Heavy regulation, protectionism, and welfare state rigidity. |
Understanding Economic Dynamism: Definition and Drivers
Economic dynamism refers to the capacity of an economy to foster innovation, adapt to technological changes, and encourage entrepreneurial activities, resulting in sustained growth and productivity improvements. Key drivers include flexible labor markets, robust investment in research and development, efficient allocation of capital, and supportive regulatory frameworks. These elements contrast sharply with eurosclerosis, a term describing stagnation characterized by rigid labor laws, excessive bureaucracy, and low innovation rates that hinder economic adaptability and competitiveness.
Eurosclerosis: Origins and Key Characteristics
Eurosclerosis refers to the economic stagnation experienced by several European countries during the 1970s and 1980s, characterized by high unemployment, rigid labor markets, and slow job creation. This phenomenon originated from excessive government intervention, inflexible labor regulations, and strong welfare systems that discouraged entrepreneurship and labor mobility. Key characteristics include persistent structural unemployment, sluggish productivity growth, and resistance to economic reforms essential for fostering dynamic market conditions.
Historical Perspectives on European Economic Stagnation
European economic stagnation in the mid-20th century is often attributed to Eurosclerosis, characterized by rigid labor markets, excessive regulation, and protectionist policies that stifled innovation and growth. In contrast, economic dynamism during this period was observed in economies embracing market liberalization, technological advancement, and flexible labor practices, leading to higher productivity and competitiveness. Historical analyses highlight that policy inflexibility and institutional inertia were central to Europe's slower economic progress compared to more dynamic economies like the United States.
Comparing Growth Rates: Dynamic vs. Sclerotic Economies
Dynamic economies exhibit higher average GDP growth rates, often exceeding 3-4% annually, driven by robust innovation, flexible labor markets, and competitive regulatory environments. In contrast, sclerotic economies, characterized by rigid institutions, excessive bureaucracy, and labor market inflexibility, frequently experience stagnating growth rates below 1-2%, impeding long-term economic expansion. Empirical data from the European Union highlight the divergence in productivity gains and employment generation between vibrant economies like Germany and the sluggish, sclerotic ones in parts of Southern and Eastern Europe.
Labor Market Flexibility and Innovation
Labor market flexibility significantly enhances economic dynamism by enabling rapid adjustment to market changes, fostering innovation through easier hiring and firing, and promoting skill reallocation. Eurosclerosis, characterized by rigid labor regulations and high employment protection, inhibits innovation by limiting entrepreneurs' ability to adapt workforce structures and slows down economic responsiveness. Empirical studies reveal that countries with flexible labor markets tend to exhibit higher rates of technological adoption and innovation-driven growth compared to economies constrained by rigid employment laws.
Regulatory Burdens in the European Context
Regulatory burdens in the European context have significantly contributed to eurosclerosis, impeding economic dynamism by stifling innovation and entrepreneurship. Complex compliance requirements, high administrative costs, and fragmented regulatory frameworks across EU member states create barriers to market entry and cross-border trade. Streamlining regulations and enhancing regulatory harmonization are essential to fostering a more competitive and dynamic European economy.
Entrepreneurship and Business Creation
Economic dynamism, characterized by high rates of entrepreneurship and business creation, drives innovation, job growth, and market adaptability. Eurosclerosis, marked by rigid regulations and labor market inefficiencies in some European countries, stifles new business formation and limits economic flexibility. Encouraging startup ecosystems and reducing bureaucratic barriers are essential to counteracting eurosclerotic effects and fostering sustainable economic growth.
The Role of Social Policies in Economic Performance
Social policies significantly influence economic dynamism by shaping labor market flexibility and workforce adaptability, vital metrics in countering Eurosclerosis--a term describing sluggish economic growth due to rigid welfare systems. Countries implementing efficient social safety nets alongside active labor market policies tend to balance protection with incentives for employment, thereby enhancing productivity and innovation. Empirical data from OECD member states highlight that moderate social expenditures coupled with targeted retraining programs correlate with stronger GDP growth and lower unemployment rates, underscoring the role of social policies in sustaining economic vitality.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Cautionary Tales
Case studies on economic dynamism versus Eurosclerosis reveal stark contrasts in regional performance across Europe, with countries like Germany and Sweden exemplifying success through adaptable labor markets and innovation-driven growth. Conversely, southern European nations such as Greece and Italy illustrate the challenges of Eurosclerosis, characterized by rigid regulations and stagnant economic reforms that hinder competitiveness. These examples underscore the importance of structural flexibility and policy reform in fostering sustainable economic vitality within the European Union.
Policy Solutions for Revitalizing European Economies
Policy solutions for revitalizing European economies focus on enhancing economic dynamism by promoting labor market flexibility, fostering innovation through increased R&D investments, and reducing regulatory burdens that contribute to Eurosclerosis. Structural reforms targeting inefficient public sectors and strengthening small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) stimulate job creation and productivity growth. Investment in digital infrastructure and education equips the workforce for future industries, counteracting stagnation and improving competitiveness in the global market.
Economic dynamism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com