Covered interest arbitrage exploits differences in interest rates between two countries while using forward contracts to eliminate exchange rate risk, allowing investors to lock in guaranteed returns. This strategy involves borrowing in a currency with a lower interest rate, converting it to a currency with a higher interest rate, and simultaneously entering into a forward contract to convert funds back at a predetermined rate. Discover how covered interest arbitrage can optimize Your investment strategies and mitigate risks by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
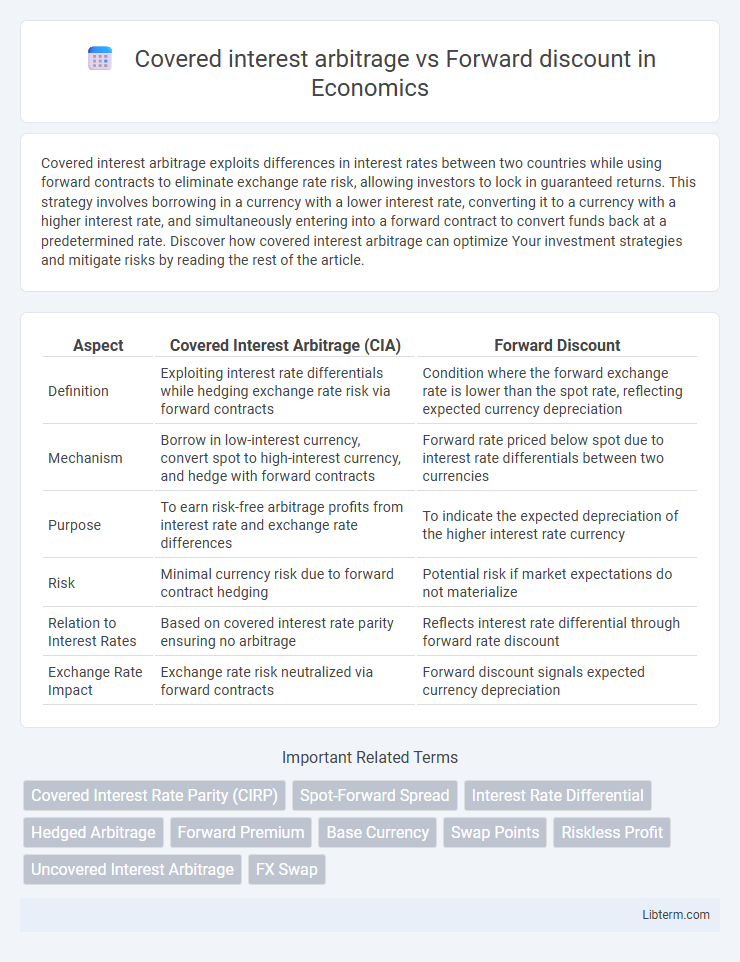
| Aspect | Covered Interest Arbitrage (CIA) | Forward Discount |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting interest rate differentials while hedging exchange rate risk via forward contracts | Condition where the forward exchange rate is lower than the spot rate, reflecting expected currency depreciation |
| Mechanism | Borrow in low-interest currency, convert spot to high-interest currency, and hedge with forward contracts | Forward rate priced below spot due to interest rate differentials between two currencies |
| Purpose | To earn risk-free arbitrage profits from interest rate and exchange rate differences | To indicate the expected depreciation of the higher interest rate currency |
| Risk | Minimal currency risk due to forward contract hedging | Potential risk if market expectations do not materialize |
| Relation to Interest Rates | Based on covered interest rate parity ensuring no arbitrage | Reflects interest rate differential through forward rate discount |
| Exchange Rate Impact | Exchange rate risk neutralized via forward contracts | Forward discount signals expected currency depreciation |
Introduction to Covered Interest Arbitrage
Covered interest arbitrage exploits differences between spot and forward exchange rates to secure risk-free profits by simultaneously investing in interest-bearing instruments across different currencies. This strategy involves borrowing in a low-interest-rate currency, converting it to a high-interest-rate currency, and using a forward contract to hedge exchange rate risk, effectively locking in returns. The forward discount reflects the market's expectation of currency depreciation, guiding traders in executing arbitrage that aligns with interest rate differentials and forward rates.
Understanding Forward Discount in Forex
Forward discount in forex occurs when the forward exchange rate is lower than the spot exchange rate, reflecting market expectations of currency depreciation. Covered interest arbitrage exploits discrepancies between interest rate differentials and forward exchange rate premiums or discounts to achieve risk-free profits. Understanding forward discount helps traders anticipate currency movements and assess the cost or benefit of hedging foreign exchange risk.
Core Principles of Covered Interest Arbitrage
Covered interest arbitrage exploits differences between spot exchange rates, forward exchange rates, and interest rates across countries, enabling risk-free profits through simultaneous currency borrowing and lending. The core principle involves using the forward exchange rate to hedge against exchange rate risk while capitalizing on interest rate differentials, ensuring no arbitrage opportunities when Covered Interest Parity (CIP) holds. This mechanism enforces equilibrium in international financial markets by aligning forward discounts or premiums with interest rate differentials between two currencies.
Calculating Forward Discount and Premium
Calculating forward discount or premium involves comparing the forward exchange rate to the spot exchange rate, expressed as a percentage of the spot rate over a specific time period. The forward discount occurs when the forward rate is lower than the spot rate, indicating a currency is expected to depreciate, while a forward premium arises when the forward rate exceeds the spot rate, signaling expected appreciation. In covered interest arbitrage, investors exploit the difference between interest rate differentials and the forward discount or premium to earn risk-free profits by simultaneously investing in foreign and domestic interest-bearing instruments.
Relationship Between Covered Interest Arbitrage and Forward Rates
Covered interest arbitrage exploits discrepancies between interest rate differentials and forward exchange rates to achieve riskless profits by simultaneously borrowing in a low-interest currency and investing in a high-interest currency while using forward contracts to hedge exchange rate risk. The forward discount or premium reflects the difference in interest rates between two countries, aligning forward exchange rates with interest rate differentials according to the interest rate parity condition. When covered interest arbitrage is possible, it drives the forward rate toward equilibrium, ensuring no arbitrage opportunities persist and maintaining consistency between forward rates and interest rate differentials.
Arbitrage Opportunities: When Do They Arise?
Arbitrage opportunities in covered interest arbitrage arise when the interest rate differential between two countries deviates from the forward discount or premium implied by the foreign exchange market, allowing traders to lock in risk-free profits. Specifically, if the forward exchange rate does not fully offset the interest rate differential, discrepancies create conditions for arbitrage between spot and forward currency markets. Efficient markets quickly adjust forward rates to eliminate these opportunities, maintaining the principle of interest rate parity.
Risk Factors: Hedging with Forward Contracts
Covered interest arbitrage involves exploiting interest rate differentials while simultaneously hedging currency risk through forward contracts, mitigating exposure to exchange rate fluctuations. The effectiveness of forward contracts in hedging depends on the accuracy of forward discount or premium, which reflects market expectations of future spot rates. Risks arise from basis risk if the forward rate deviates unexpectedly from spot rate movements and from potential default or liquidity issues in forward contract counterparties.
Practical Examples: Covered Interest Arbitrage in Action
Covered interest arbitrage involves capitalizing on interest rate differentials between two countries by simultaneously borrowing in a currency with a lower interest rate and investing in a currency with a higher rate while using forward contracts to hedge exchange rate risk. For example, if the U.S. interest rate is 2% and the Eurozone's is 5%, an investor could borrow USD, convert to EUR, invest at 5%, and lock in the forward contract rate to avoid currency risk, ensuring a riskless profit when the returns are converted back to USD. This contrasts with the forward discount, which reflects the expected depreciation of a currency based on interest rate parity but does not guarantee arbitrage profits without actual execution of covered interest arbitrage strategies.
Market Efficiency and Interest Rate Parity
Covered interest arbitrage ensures market efficiency by exploiting discrepancies between spot and forward exchange rates, aligning returns and preventing arbitrage opportunities. The forward discount reflects the interest rate differential between two countries, supporting the interest rate parity (IRP) condition that mandates equalized returns on risk-adjusted investments. Deviations from IRP trigger covered interest arbitrage, driving the forward rate to adjust until the market reaches equilibrium and maintains efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Covered Interest Arbitrage and Forward Discount
Covered interest arbitrage offers a risk-free strategy by exploiting interest rate differentials while using forward contracts to hedge exchange rate risk, ensuring guaranteed returns. Forward discount reflects market expectations of currency depreciation but carries exchange rate risk if not paired with interest arbitrage. Selecting between covered interest arbitrage and forward discount depends on an investor's risk tolerance and market outlook, with arbitrage favored for risk-averse investors seeking certainty and forward discount suitable for those willing to accept currency risk for potential gains.
Covered interest arbitrage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com