Behavioral economics explores how psychological, social, and emotional factors influence economic decision-making, challenging the traditional assumption of rational behavior. This field reveals patterns like biases and heuristics that shape choices in real-life contexts. Discover how these insights can impact Your financial decisions by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
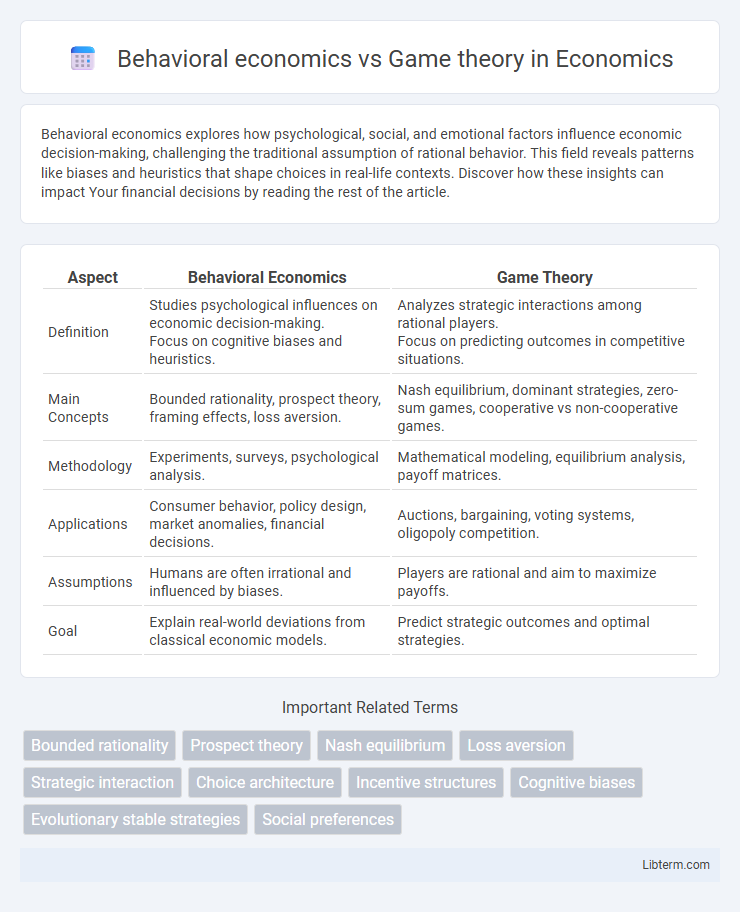
| Aspect | Behavioral Economics | Game Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Studies psychological influences on economic decision-making. Focus on cognitive biases and heuristics. |
Analyzes strategic interactions among rational players. Focus on predicting outcomes in competitive situations. |
| Main Concepts | Bounded rationality, prospect theory, framing effects, loss aversion. | Nash equilibrium, dominant strategies, zero-sum games, cooperative vs non-cooperative games. |
| Methodology | Experiments, surveys, psychological analysis. | Mathematical modeling, equilibrium analysis, payoff matrices. |
| Applications | Consumer behavior, policy design, market anomalies, financial decisions. | Auctions, bargaining, voting systems, oligopoly competition. |
| Assumptions | Humans are often irrational and influenced by biases. | Players are rational and aim to maximize payoffs. |
| Goal | Explain real-world deviations from classical economic models. | Predict strategic outcomes and optimal strategies. |
Introduction to Behavioral Economics and Game Theory
Behavioral economics studies how psychological, cognitive, and emotional factors influence economic decision-making, challenging the traditional assumption of rationality. Game theory analyzes strategic interactions where individuals or groups make decisions that affect one another's outcomes, emphasizing mathematical models of competition and cooperation. Both fields intersect by incorporating human behavior complexities and strategic considerations to better predict real-world economic and social choices.
Core Principles of Behavioral Economics
Behavioral economics integrates insights from psychology to explain how cognitive biases, heuristics, and emotions influence economic decision-making, deviating from the traditional assumption of fully rational agents in game theory. Core principles include bounded rationality, loss aversion, and mental accounting, which highlight that individuals often make decisions based on simplified models and emotional responses rather than purely logical calculations. These factors challenge the predictive accuracy of classical game theory by emphasizing realistic human behavior in strategic interactions.
Fundamental Concepts in Game Theory
Game theory studies strategic interactions where players choose actions to maximize their payoffs, focusing on concepts such as Nash equilibrium, dominant strategies, and backward induction. Behavioral economics incorporates psychological insights into decision-making, highlighting deviations from rationality predicted by game theory models. Fundamental concepts in game theory provide the analytical framework to predict outcomes in competitive and cooperative scenarios by modeling players' incentives and expectations.
Comparing Assumptions: Rationality and Decision-Making
Behavioral economics challenges the traditional assumption of complete rationality by incorporating psychological insights into decision-making, recognizing that individuals often act irrationally due to biases and heuristics. Game theory assumes rational agents who strategically anticipate others' actions to maximize their own payoffs in competitive or cooperative settings. The comparison highlights that while game theory models ideal rational decisions in interdependent situations, behavioral economics accounts for bounded rationality and imperfect decision processes observed in real-world behavior.
Real-World Applications of Behavioral Economics
Behavioral economics influences real-world decisions by integrating psychological insights into economic models, improving policies in areas like retirement savings and health choices. It addresses irrational behaviors, helping design nudges that promote beneficial outcomes without restricting freedom. This contrasts with game theory's strategic interaction models, which are more focused on competitive scenarios and equilibrium analysis.
Strategic Interactions in Game Theory
Game theory analyzes strategic interactions where individuals or groups make decisions that consider the potential choices of others, modeling behavior in competitive and cooperative environments. It emphasizes equilibrium outcomes, such as Nash equilibrium, where no player benefits from unilaterally changing their strategy. Behavioral economics incorporates psychological insights into economic decision-making but often relies on traditional game theory frameworks to study how real-world biases affect strategic behavior.
Psychological Influences in Economic Choices
Behavioral economics examines how psychological factors such as cognitive biases, emotions, and heuristics impact individual economic decisions, often leading to deviations from traditional rational choice models. Game theory analyzes strategic interactions where individuals anticipate others' choices, incorporating psychological elements like trust and reciprocity to predict outcomes in competitive and cooperative environments. Both fields emphasize the significance of mental processes in economic behavior, but behavioral economics centers on individual decision-making errors while game theory focuses on interactive decision dynamics.
Key Differences Between Behavioral Economics and Game Theory
Behavioral economics primarily examines how psychological factors and cognitive biases influence individual decision-making, often deviating from traditional rational models. Game theory analyzes strategic interactions among rational agents, focusing on predicting outcomes in competitive or cooperative scenarios through payoff matrices and equilibrium concepts such as Nash equilibrium. The key difference lies in behavioral economics incorporating real human behavior and irrationality, while game theory assumes rationality and strategic reasoning in multi-agent environments.
Overlapping and Complementary Insights
Behavioral economics and game theory intersect in analyzing decision-making processes under uncertainty by incorporating psychological factors and strategic interactions. Both fields emphasize the importance of understanding how individuals deviate from purely rational choices, with behavioral economics highlighting cognitive biases and game theory modeling strategic interdependencies among agents. Combining these insights enhances predictions of real-world outcomes in markets, negotiations, and public policy by considering both individual behavioral quirks and interactive decision contexts.
Future Directions and Research in Economic Decision Science
Future research in economic decision science emphasizes integrating behavioral economics' insights on cognitive biases and emotions with game theory's strategic interaction models to better predict real-world decision-making. Advances in experimental methods and machine learning facilitate the exploration of how social norms and bounded rationality influence strategic behavior in dynamic environments. Emerging studies focus on applying these integrated frameworks to areas such as climate change negotiations, digital market platforms, and collective risk management to enhance policy design and strategic decision-making outcomes.
Behavioral economics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com