Penetration pricing sets a low initial price to quickly attract customers and gain market share, often challenging established competitors. This strategy can boost sales volume rapidly but requires careful cost management to ensure profitability. Discover how penetration pricing can impact Your business growth and when to implement it effectively by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
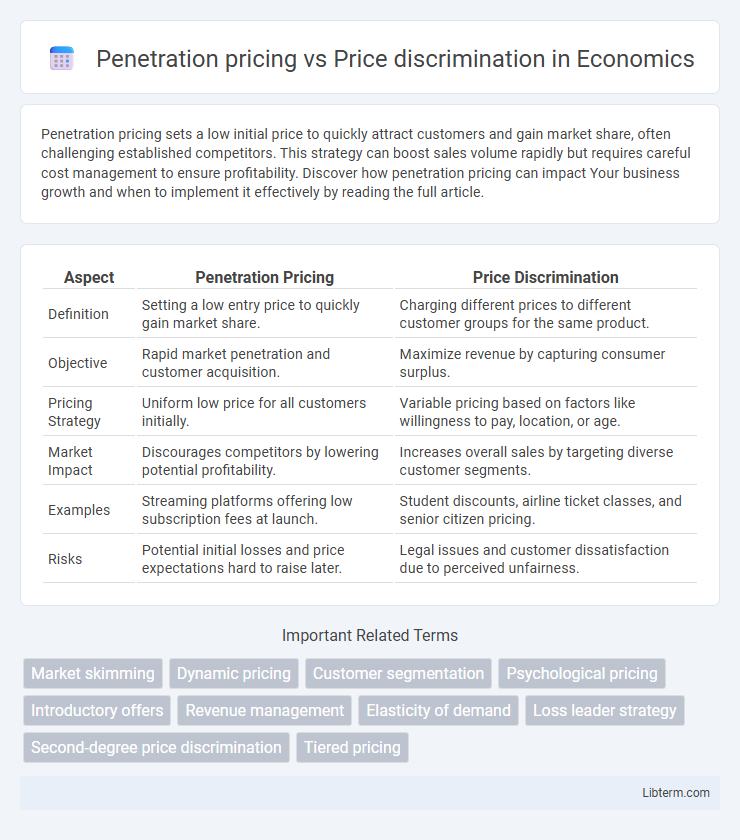
| Aspect | Penetration Pricing | Price Discrimination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Setting a low entry price to quickly gain market share. | Charging different prices to different customer groups for the same product. |
| Objective | Rapid market penetration and customer acquisition. | Maximize revenue by capturing consumer surplus. |
| Pricing Strategy | Uniform low price for all customers initially. | Variable pricing based on factors like willingness to pay, location, or age. |
| Market Impact | Discourages competitors by lowering potential profitability. | Increases overall sales by targeting diverse customer segments. |
| Examples | Streaming platforms offering low subscription fees at launch. | Student discounts, airline ticket classes, and senior citizen pricing. |
| Risks | Potential initial losses and price expectations hard to raise later. | Legal issues and customer dissatisfaction due to perceived unfairness. |
Introduction to Penetration Pricing and Price Discrimination
Penetration pricing involves setting a low initial price to quickly attract customers and gain market share, often used during product launches or in competitive markets. Price discrimination refers to charging different prices to different consumer groups based on factors such as willingness to pay, location, or purchase volume, maximizing revenue for the seller. Both strategies aim to optimize pricing but differ in application: penetration pricing targets market entry and growth, while price discrimination leverages customer segmentation for profit maximization.
Definition of Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing is a marketing strategy where a company sets a low initial price to quickly attract customers and gain market share. Unlike price discrimination, which involves charging different prices to different consumer groups based on their willingness to pay, penetration pricing focuses on entering the market aggressively with a uniform low price. This approach aims to discourage competitors and establish a strong customer base before gradually increasing prices.
Definition of Price Discrimination
Price discrimination refers to the strategy of charging different prices to different customers for the same product or service based on factors such as willingness to pay, purchase location, or buyer characteristics. This approach maximizes revenue by capturing consumer surplus and varies from penetration pricing, which involves setting a low initial price to gain market share rapidly. Price discrimination is classified into three types: first-degree (personalized pricing), second-degree (quantity-based pricing), and third-degree (group-based pricing).
Key Differences Between Penetration Pricing and Price Discrimination
Penetration pricing involves setting a low initial price to quickly attract customers and gain market share, while price discrimination charges different prices to different customer segments based on their willingness to pay. Penetration pricing aims at market entry and volume growth, whereas price discrimination seeks profit maximization by extracting consumer surplus. The key difference lies in penetration pricing's uniform low price strategy versus price discrimination's differentiated pricing approach tailored to diverse consumer groups.
Advantages of Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing offers the advantage of rapidly attracting a large customer base by setting low initial prices, which can lead to increased market share and brand recognition. This strategy helps deter potential competitors from entering the market due to reduced profit margins. Businesses benefit from economies of scale as higher sales volumes lower production costs over time, enhancing long-term profitability.
Benefits of Price Discrimination
Price discrimination enables businesses to maximize revenue by charging different prices based on customer segments' willingness to pay, leading to higher overall profitability compared to uniform pricing strategies like penetration pricing. It allows firms to capture consumer surplus, optimize market coverage, and improve resource allocation efficiency by tailoring prices for distinct groups. This pricing tactic benefits companies by increasing sales volume, enhancing competitive advantage, and funding innovation through improved cash flow streams.
Drawbacks and Risks of Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing risks include initial low margins that may lead to financial strain, making it difficult for companies to cover costs or generate profits early on. This strategy can create customer expectations for consistently low prices, complicating future price increases and reducing perceived value. Competitors might quickly match or undercut prices, triggering price wars that harm industry profitability and market stability.
Challenges Associated With Price Discrimination
Price discrimination faces challenges such as legal restrictions, customer backlash, and complex implementation requirements, making it difficult to segment markets effectively and maintain fairness. Unlike penetration pricing, which sets low initial prices to capture market share quickly, price discrimination demands detailed consumer data and the ability to prevent resale between segments. Firms must carefully navigate regulatory environments and ethical concerns to avoid penalties and reputational damage while maximizing profits.
Strategic Applications in Modern Markets
Penetration pricing involves setting an initial low price to rapidly gain market share and deter competitors, making it highly effective in launching new products within highly competitive markets. Price discrimination, by contrast, uses varied pricing strategies based on customer segments, purchase location, or timing to maximize revenue and consumer surplus, commonly seen in industries like airlines and digital services. Both strategies strategically optimize market positioning and profitability by leveraging consumer behavior and competitive dynamics in modern economies.
Choosing the Right Pricing Strategy for Your Business
Choosing the right pricing strategy involves understanding your market demand and customer segments; penetration pricing aggressively sets a low initial price to quickly gain market share, ideal for new product launches in competitive industries. Price discrimination tailors prices based on customer segments or purchase conditions, maximizing revenue by capturing consumer surplus in markets with varied willingness to pay. Businesses must analyze cost structures, customer behavior, and long-term goals to determine whether rapid market entry or differentiated pricing delivers optimal profitability and growth.
Penetration pricing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com