Debt refinancing can significantly lower your monthly payments and reduce overall interest costs by replacing existing debt with a new loan at better terms. It's essential to compare rates and fees carefully to ensure the refinancing option truly benefits your financial situation. Discover how refinancing works and if it's the right choice for you by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
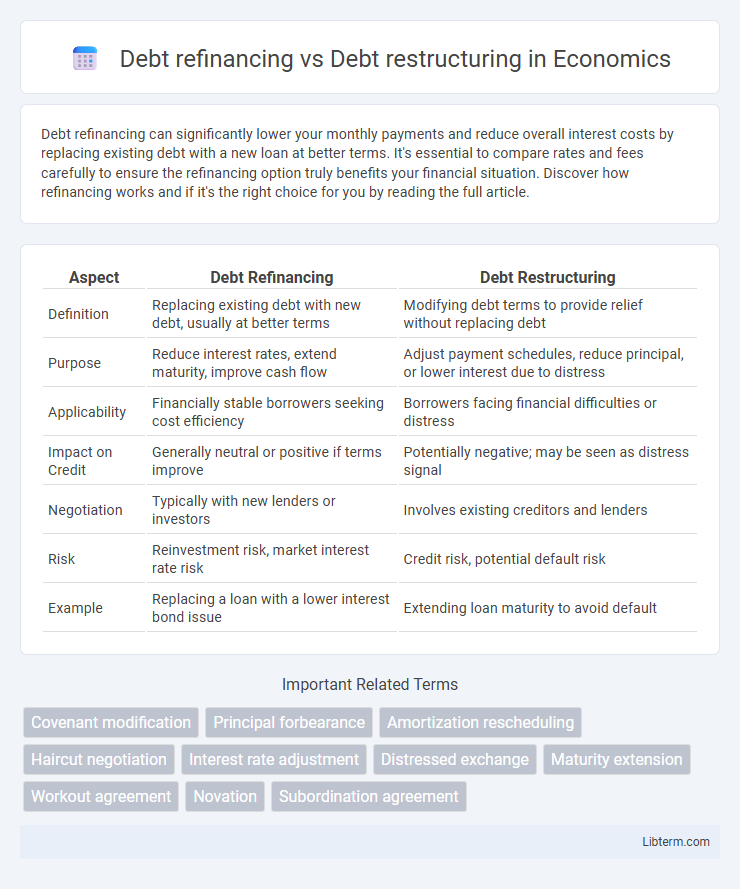
| Aspect | Debt Refinancing | Debt Restructuring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Replacing existing debt with new debt, usually at better terms | Modifying debt terms to provide relief without replacing debt |
| Purpose | Reduce interest rates, extend maturity, improve cash flow | Adjust payment schedules, reduce principal, or lower interest due to distress |
| Applicability | Financially stable borrowers seeking cost efficiency | Borrowers facing financial difficulties or distress |
| Impact on Credit | Generally neutral or positive if terms improve | Potentially negative; may be seen as distress signal |
| Negotiation | Typically with new lenders or investors | Involves existing creditors and lenders |
| Risk | Reinvestment risk, market interest rate risk | Credit risk, potential default risk |
| Example | Replacing a loan with a lower interest bond issue | Extending loan maturity to avoid default |
Introduction to Debt Refinancing and Debt Restructuring
Debt refinancing involves replacing an existing debt with a new loan, typically to secure better interest rates, extend repayment terms, or improve cash flow. Debt restructuring, by contrast, entails modifying the terms of existing debt agreements, such as reducing interest rates, extending payment schedules, or negotiating partial debt forgiveness to avoid default or bankruptcy. Both strategies aim to enhance a company's financial stability but differ in approach, with refinancing focusing on obtaining new financing and restructuring concentrating on adjusting current obligations.
Defining Debt Refinancing
Debt refinancing involves replacing an existing debt obligation with a new loan, typically to secure better terms such as lower interest rates or extended repayment periods. Unlike debt restructuring, which may include negotiating changes to the debt terms due to financial distress, refinancing aims to optimize the debt profile without changing the original loan conditions fundamentally. This financial strategy helps borrowers improve cash flow management and reduce overall borrowing costs.
Defining Debt Restructuring
Debt restructuring involves modifying the terms of existing debt agreements to provide relief to borrowers facing financial hardship, often by reducing interest rates, extending maturities, or altering payment schedules. In contrast, debt refinancing replaces old debt with new debt, typically to secure better interest rates or terms without changing the overall debt structure. Debt restructuring is a strategic financial tool used by companies or governments to avoid default and improve liquidity while maintaining creditor relationships.
Key Differences Between Refinancing and Restructuring
Debt refinancing involves replacing an existing debt with a new loan, typically to secure better interest rates or extend the repayment period, while debt restructuring entails negotiating modified terms with creditors to avoid default, which may include reduced interest rates, extended deadlines, or principal forgiveness. Refinancing aims to improve loan conditions by obtaining new credit on more favorable terms, whereas restructuring focuses on adjusting current debt obligations to enhance repayment feasibility. Key differences lie in refinancing initiating new debt to pay off old debt, whereas restructuring alters the terms of the existing debt without necessarily acquiring new funds.
Benefits of Debt Refinancing
Debt refinancing offers significant benefits such as lowering interest rates, reducing monthly payments, and improving cash flow, which can enhance overall financial stability for businesses and individuals. By replacing existing debt with new loans at more favorable terms, refinancing can extend repayment periods and free up capital for other investments or operational needs. This approach often results in cost savings and increased flexibility compared to debt restructuring, which typically involves renegotiating debt terms due to financial distress.
Benefits of Debt Restructuring
Debt restructuring improves cash flow by reducing monthly debt payments and extending loan terms, making it easier for companies to manage financial obligations. It enhances creditworthiness, allowing businesses to restore or maintain access to new financing opportunities. Compared to debt refinancing, restructuring addresses both the principal and interest terms, providing comprehensive relief tailored to a company's specific financial challenges.
Risks and Limitations of Each Approach
Debt refinancing carries risks such as increased interest rates, longer debt maturity, and potential loss of collateral, which can amplify financial strain if market conditions worsen. Debt restructuring entails limitations including possible damage to credit ratings, strained lender relationships, and the risk of insolvency if negotiations fail or debt terms remain unsustainable. Both approaches require careful assessment of cash flow capacity and long-term financial stability to avoid exacerbating liquidity challenges.
When to Choose Refinancing versus Restructuring
Debt refinancing is ideal when interest rates are lower or better terms are available, allowing borrowers to replace existing debt with new obligations to reduce costs or extend timelines. Debt restructuring suits situations where a borrower faces financial distress and cannot meet current debt obligations, aiming to negotiate reduced payments or altered terms to avoid default or bankruptcy. Choosing refinancing depends on market conditions and creditworthiness, while restructuring focuses on financial recovery and preserving business viability.
Impact on Credit Score and Financial Health
Debt refinancing typically involves replacing existing debt with new loans at better terms, which can lower interest rates and monthly payments, potentially improving credit scores if payments are made on time. Debt restructuring, often pursued during financial distress, may include negotiated changes like reduced interest rates or extended terms that can temporarily lower credit scores due to missed or modified payment agreements. While refinancing aims to enhance financial health by optimizing debt conditions, restructuring focuses on avoiding default and stabilizing finances, with varied short-term effects on creditworthiness but potential long-term benefits if managed correctly.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Debt Management Solution
Choosing between debt refinancing and debt restructuring depends on the borrower's financial health and long-term goals. Debt refinancing suits those seeking lower interest rates or extended payment terms without altering original loan conditions. Debt restructuring benefits entities needing modified repayment plans or reduced obligations to avoid default and restore financial stability.
Debt refinancing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com