Advertising elasticity measures how changes in advertising expenditure influence sales or demand, revealing the effectiveness of marketing investments. Understanding this concept helps you optimize your advertising budget for maximum return on investment. Explore the article to learn how to calculate advertising elasticity and apply it to your business strategy.
Table of Comparison
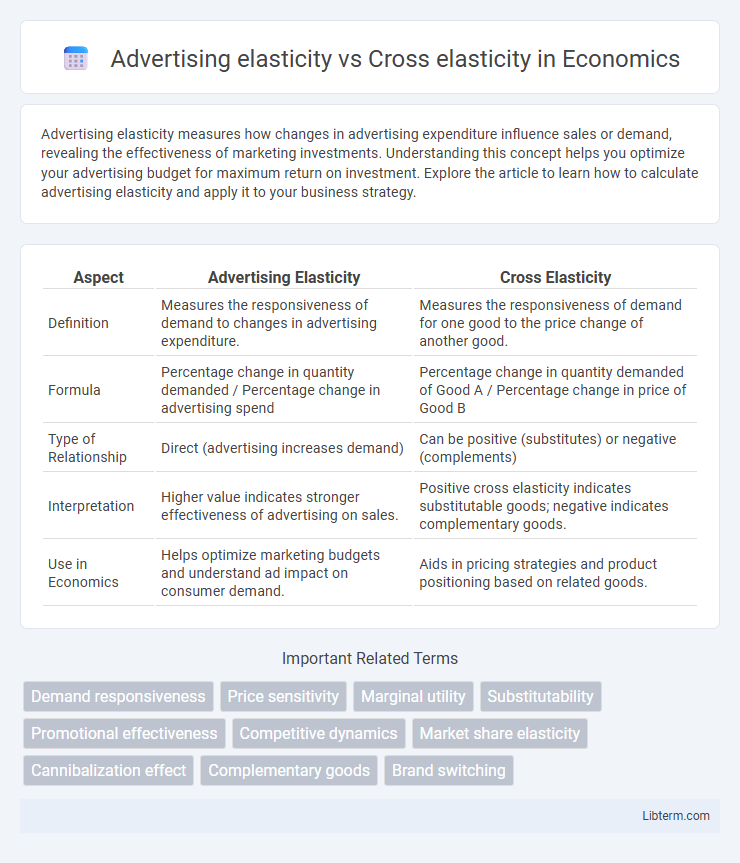
| Aspect | Advertising Elasticity | Cross Elasticity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures the responsiveness of demand to changes in advertising expenditure. | Measures the responsiveness of demand for one good to the price change of another good. |
| Formula | Percentage change in quantity demanded / Percentage change in advertising spend | Percentage change in quantity demanded of Good A / Percentage change in price of Good B |
| Type of Relationship | Direct (advertising increases demand) | Can be positive (substitutes) or negative (complements) |
| Interpretation | Higher value indicates stronger effectiveness of advertising on sales. | Positive cross elasticity indicates substitutable goods; negative indicates complementary goods. |
| Use in Economics | Helps optimize marketing budgets and understand ad impact on consumer demand. | Aids in pricing strategies and product positioning based on related goods. |
Introduction to Advertising Elasticity and Cross Elasticity
Advertising elasticity measures the responsiveness of product demand to changes in advertising expenditure, indicating how effectively advertising influences sales volume. Cross elasticity of demand assesses how the quantity demanded of one product reacts to price changes of another product, highlighting substitute or complementary relationships. Understanding both elasticities helps businesses optimize marketing strategies and pricing decisions to maximize revenue and market share.
Defining Advertising Elasticity of Demand
Advertising elasticity of demand measures the percentage change in product demand resulting from a one percent change in advertising expenditure, indicating the effectiveness of marketing efforts on sales. Cross elasticity of demand quantifies how the quantity demanded of one product responds to price changes of another product, reflecting substitute or complementary relationships. Understanding advertising elasticity helps businesses optimize advertising budgets by linking promotional activities directly to demand fluctuations.
Understanding Cross Elasticity of Demand
Understanding cross elasticity of demand involves measuring the responsiveness of the quantity demanded for one product when the price of a related product changes, providing insights into substitute and complementary goods. Advertising elasticity quantifies the impact of advertising expenditure on the demand for a specific product, indicating how promotional efforts influence sales volume. Distinguishing cross elasticity helps businesses optimize pricing strategies and marketing budgets by identifying interdependencies between products in competitive markets.
Key Differences Between Advertising and Cross Elasticity
Advertising elasticity measures the responsiveness of product demand to changes in advertising expenditure, reflecting the direct impact of marketing efforts on sales volume. Cross elasticity of demand quantifies how the demand for one product changes in response to price changes of a related product, indicating substitutability or complementarity between goods. Key differences include that advertising elasticity captures promotional influence on a single product's demand, while cross elasticity reveals interdependence between different products' demands based on price variations.
Factors Influencing Advertising Elasticity
Advertising elasticity measures the responsiveness of sales to changes in advertising expenditure, heavily influenced by factors such as brand strength, product differentiation, and market saturation. High advertising elasticity is often observed in highly competitive markets with numerous substitutes, where consumer attention and preferences can shift quickly. Consumer demographics, media mix effectiveness, and product life cycle stage also significantly affect the magnitude of advertising elasticity.
Factors Affecting Cross Elasticity
Cross elasticity of demand measures how the quantity demanded of one product responds to price changes of a related product, influenced by factors such as the degree of substitutability, the closeness of the relationship between products, and consumer preferences. Brand loyalty and the availability of alternative products also significantly impact cross elasticity, with stronger loyalty reducing sensitivity to competitor price changes. Advertising elasticity, on the other hand, quantifies the responsiveness of demand to changes in advertising expenditure, primarily driven by the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and market saturation levels.
Measuring Advertising Elasticity: Methods and Metrics
Measuring advertising elasticity involves quantifying how changes in advertising spend affect sales volume, typically using methods like regression analysis to estimate the percentage change in sales resulting from a one percent change in advertising expenditure. Common metrics include the Advertising Elasticity of Demand (AED), which captures direct responsiveness, and holdout experiments that isolate advertising effects by comparing exposed and control groups. Cross elasticity differs by assessing how changes in advertising for one product influence the demand for a substitute or complementary product, often analyzed through cross-price elasticity models adapted for promotional impact.
Practical Examples of Cross Elasticity in Markets
Cross elasticity of demand measures how the quantity demanded of one product changes in response to the price change of another, essential in analyzing substitute and complementary goods. For example, when the price of coffee rises, the demand for tea, a substitute, typically increases, while a price hike in printers may reduce demand for complementary ink cartridges. Understanding cross elasticity helps marketers adjust pricing strategies to optimize revenue by anticipating shifts in consumer preferences across related products.
Strategic Implications for Marketers and Advertisers
Advertising elasticity measures the responsiveness of product demand to changes in advertising expenditure, enabling marketers to allocate budgets efficiently by identifying high-impact campaigns that directly boost sales. Cross elasticity evaluates how the demand for one product changes in response to advertising shifts for another product, helping advertisers understand competitive dynamics and potential market cannibalization. Strategic implications include optimizing media mix by focusing on high advertising elasticity brands while monitoring cross elasticity effects to minimize negative competitive impacts and maximize overall market share growth.
Conclusion: Integrating Elasticity Concepts in Marketing Decisions
Advertising elasticity measures the responsiveness of product demand to changes in advertising expenditure, while cross elasticity evaluates the impact of the price change of one product on the demand for another. Integrating both concepts into marketing decisions allows businesses to optimize advertising budgets by targeting campaigns that maximize demand shifts and anticipate competitor reactions. This dual approach enhances strategic planning, improves resource allocation, and drives more effective market positioning.
Advertising elasticity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com