Ambiguity seeking is a behavioral tendency where individuals prefer uncertain or unclear situations over those with well-defined outcomes. This preference often influences decision-making processes, particularly in risk management and economic choices. Explore the rest of this article to understand how ambiguity seeking impacts your judgments and strategies.
Table of Comparison
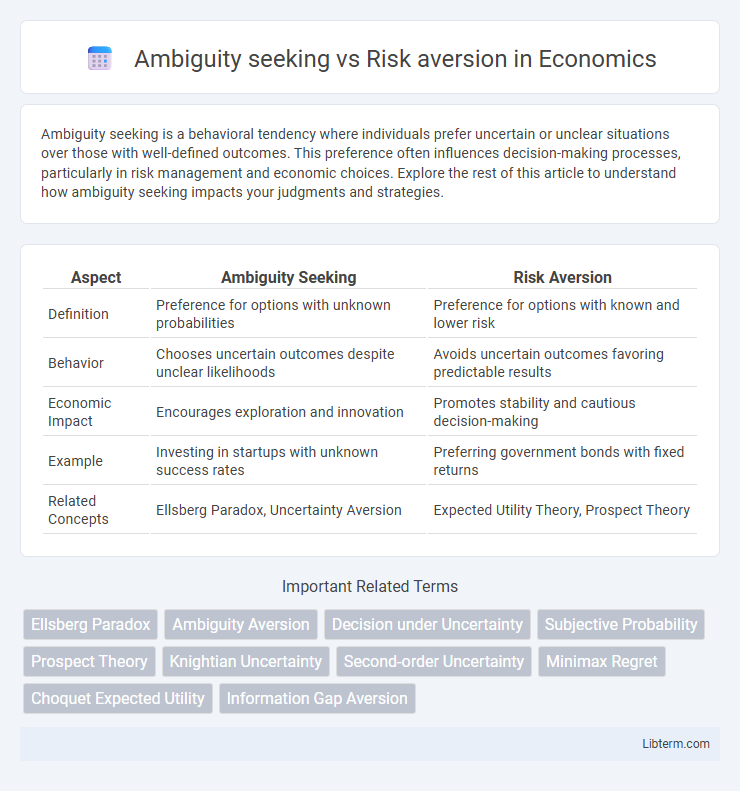
| Aspect | Ambiguity Seeking | Risk Aversion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preference for options with unknown probabilities | Preference for options with known and lower risk |
| Behavior | Chooses uncertain outcomes despite unclear likelihoods | Avoids uncertain outcomes favoring predictable results |
| Economic Impact | Encourages exploration and innovation | Promotes stability and cautious decision-making |
| Example | Investing in startups with unknown success rates | Preferring government bonds with fixed returns |
| Related Concepts | Ellsberg Paradox, Uncertainty Aversion | Expected Utility Theory, Prospect Theory |
Introduction to Ambiguity Seeking and Risk Aversion
Ambiguity seeking reflects a preference for options with unknown probabilities, contrasting sharply with risk aversion, where individuals favor choices with known risks and stable outcomes. In decision theory, ambiguity refers to situations with uncertain probabilities, while risk involves quantifiable likelihoods. Understanding these concepts is crucial for modeling behavior in finance, economics, and psychology, as they influence investment strategies and decision-making under uncertainty.
Defining Ambiguity and Risk in Decision Making
Ambiguity in decision making refers to situations where the probabilities of outcomes are unknown or imprecise, leading individuals to face uncertain environments without clear information. Risk, on the other hand, involves scenarios where the probabilities of different outcomes are known and quantifiable, allowing for calculable expectations. Ambiguity seeking describes a preference for choosing options with unclear probabilities, whereas risk aversion reflects a tendency to avoid options with known but potentially unfavorable outcomes.
Psychological Theories Behind Ambiguity Seeking
Psychological theories behind ambiguity seeking highlight an individual's preference for uncertain outcomes when probabilities are unknown, contrasting with risk aversion where probabilities are clear. Models such as Ellsberg's paradox expose how people may favor ambiguous options to explore hidden information or experience novelty, driven by cognitive biases and emotions like curiosity or overconfidence. This tendency challenges classical decision theory, suggesting that ambiguity seeking can arise from psychological motivations rather than purely rational calculations.
Understanding Risk Aversion: Causes and Effects
Risk aversion stems from an individual's preference to minimize uncertainty and potential losses, often driven by psychological factors such as fear of negative outcomes and loss aversion. This behavior influences decision-making processes by favoring options with more predictable results, ultimately impacting financial choices, investment strategies, and consumer behavior. Understanding these causes and effects aids in developing models that predict market trends and optimize risk management techniques.
Comparing Ambiguity Aversion with Risk Aversion
Ambiguity aversion occurs when individuals prefer known risks over unknown probabilities, leading them to avoid options with uncertain likelihoods of outcomes. In contrast, risk aversion involves a preference for options with lower variability in outcomes even when probabilities are known, emphasizing the avoidance of potential losses. The key difference lies in ambiguity aversion's sensitivity to unknown probabilities, whereas risk aversion relates to the known distribution of outcomes and their variance.
Factors Influencing Individual Decision Preferences
Individual decision preferences are shaped by cognitive biases, past experiences, and the perceived uncertainty of outcomes, which drive ambiguity seeking or risk aversion behaviors. Neurological factors, such as activity in the prefrontal cortex and amygdala, influence tolerance levels for ambiguity versus risk during decision-making. Environmental context, including social influence and information availability, also plays a critical role in determining whether individuals prefer ambiguous options or choose to avoid risk.
Real-Life Examples of Ambiguity Seeking
Ambiguity seeking behavior is evident in investors choosing innovative start-ups despite uncertain outcomes, contrasting with risk-averse individuals who prefer established blue-chip stocks for predictable returns. In medical decision-making, patients opting for experimental treatments rather than standard protocols demonstrate ambiguity seeking due to uncertain efficacy but potential high rewards. Entrepreneurs frequently exhibit ambiguity seeking by launching ventures without clear market data, embracing uncertainty to capitalize on novel opportunities.
Practical Implications in Finance and Economics
Ambiguity seeking investors often pursue assets with uncertain probabilities, leading to higher portfolio diversification and potentially greater returns, while risk-averse individuals prefer well-defined risks, favoring safer, more predictable investments like government bonds. In finance, ambiguity seeking can drive market volatility and mispricing due to speculative behavior, whereas risk aversion stabilizes markets by promoting conservative capital allocation and hedging strategies. Economic policies tailored to these behavioral traits influence market efficiency, with ambiguity-tolerant agents supporting innovation and growth, in contrast to risk-averse preferences promoting financial stability and reduced systemic risk.
Behavioral Biases: How Ambiguity Impacts Choices
Ambiguity seeking and risk aversion represent contrasting behavioral biases that significantly influence decision-making under uncertainty. Ambiguity seekers prefer options with unknown probabilities, drawn by incomplete information, whereas risk-averse individuals favor known risks with established probabilities to minimize potential losses. This behavioral divergence affects economic choices, investment strategies, and responses to ambiguous situations, highlighting how ambiguity impacts preferences and cognitive processing during decision-making.
Strategies to Balance Ambiguity and Risk in Decisions
Effective strategies to balance ambiguity seeking and risk aversion in decision-making include employing robust scenario analysis and probabilistic modeling to clarify uncertain outcomes. Incorporating adaptive learning allows decision-makers to update beliefs and strategies dynamically as new information emerges, reducing ambiguity over time. Utilizing diversified portfolios or option-based approaches further mitigates risk while maintaining flexibility to capitalize on ambiguous opportunities.
Ambiguity seeking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com