Fiscal responsibility involves effectively managing your income, expenses, and savings to maintain financial stability and avoid debt. It requires budgeting, prudent spending, and planning for future financial goals to ensure long-term economic well-being. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips on enhancing your fiscal responsibility.
Table of Comparison
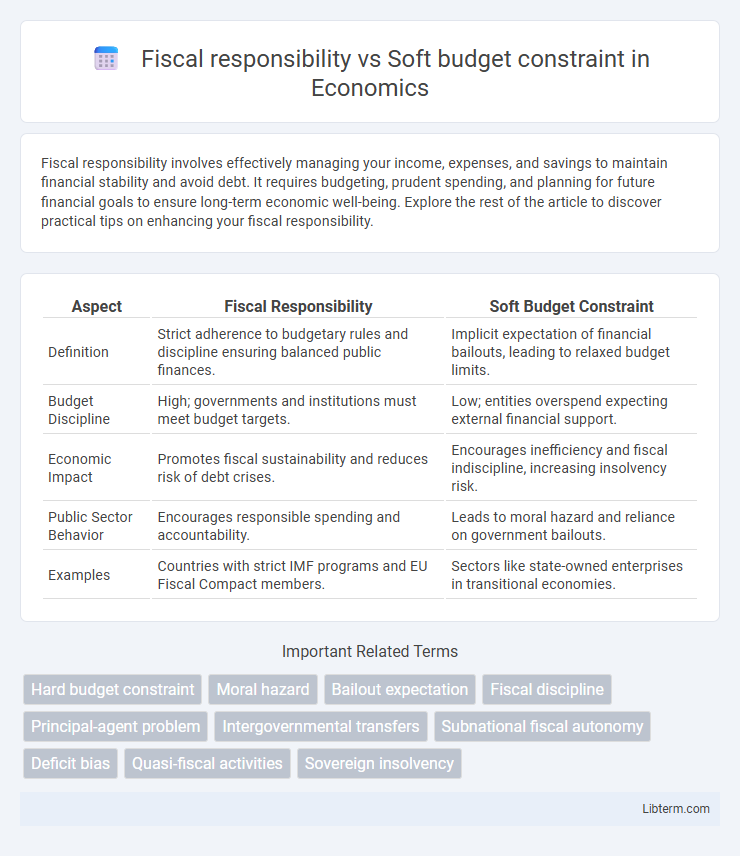
| Aspect | Fiscal Responsibility | Soft Budget Constraint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strict adherence to budgetary rules and discipline ensuring balanced public finances. | Implicit expectation of financial bailouts, leading to relaxed budget limits. |
| Budget Discipline | High; governments and institutions must meet budget targets. | Low; entities overspend expecting external financial support. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes fiscal sustainability and reduces risk of debt crises. | Encourages inefficiency and fiscal indiscipline, increasing insolvency risk. |
| Public Sector Behavior | Encourages responsible spending and accountability. | Leads to moral hazard and reliance on government bailouts. |
| Examples | Countries with strict IMF programs and EU Fiscal Compact members. | Sectors like state-owned enterprises in transitional economies. |
Understanding Fiscal Responsibility: Core Principles
Fiscal responsibility entails maintaining balanced budgets, controlling public debt, and ensuring sustainable government spending to promote long-term economic stability. Key principles include transparency in financial reporting, adherence to fiscal rules, and accountability mechanisms that prevent excessive borrowing and inefficient resource allocation. Understanding these principles helps distinguish fiscal responsibility from soft budget constraints, which occur when institutions rely on external bailouts, leading to persistent financial indiscipline.
The Concept of Soft Budget Constraints Defined
Soft budget constraints refer to situations where governments or organizations are assured financial support despite inefficiencies or overspending, undermining fiscal discipline. This phenomenon often leads to a lack of incentive to reduce deficits or improve financial management, contrasting sharply with the principle of fiscal responsibility which demands strict adherence to budget limits and sustainable spending. The concept highlights how guaranteed bailouts or subsidies distort economic behavior and complicate efforts toward effective public financial management.
Historical Evolution of Fiscal Responsibility
The historical evolution of fiscal responsibility traces back to the rise of modern state finance in the 19th century, emphasizing balanced budgets and debt repayment to maintain government credibility. This shift was driven by increased public scrutiny and the need to avoid unsustainable public debt, contrasting with the soft budget constraint theory, which highlights the tendency of governments and public enterprises to overspend under implicit bailouts. Over time, fiscal responsibility frameworks, including fiscal rules and balanced budget amendments, were institutionalized to counteract the inefficiencies and moral hazards associated with soft budget constraints.
Origins and Implications of Soft Budget Constraints
Soft budget constraints originate from institutional arrangements where organizations or governments expect external financial support despite fiscal mismanagement, undermining hard budget discipline. This phenomenon often occurs in socialist economies or organizations reliant on bailouts, leading to persistent inefficiencies and overinvestment. The implications include distorted resource allocation, reduced incentives for cost control, and fiscal irresponsibility, complicating long-term economic stability and policy enforcement.
Fiscal Responsibility: Benefits for Economic Stability
Fiscal responsibility promotes sustainable government spending and debt management, reducing the risk of fiscal crises and inflationary pressures. Maintaining balanced budgets enhances investor confidence, stabilizes borrowing costs, and supports long-term economic growth. Countries with strong fiscal discipline often experience lower interest rates, improved credit ratings, and increased capacity to respond to economic shocks effectively.
Dangers of Soft Budget Constraints in Public Finance
Soft budget constraints in public finance lead to inefficient resource allocation and persistent budget deficits due to the expectation of bailouts or external financial support. This behavior encourages fiscal indiscipline, undermines accountability, and discourages revenue maximization efforts by government entities. Ultimately, it exacerbates public debt accumulation and can trigger macroeconomic instability, threatening long-term fiscal sustainability.
Case Studies: Countries Practicing Fiscal Responsibility
Countries exemplifying fiscal responsibility, such as Sweden, Germany, and Canada, demonstrate disciplined budget management characterized by strict adherence to balanced budgets and controlled public debt levels. These nations implement rigorous fiscal rules, transparent reporting systems, and independent oversight institutions that effectively prevent soft budget constraints, avoiding recurrent bailouts and fiscal indiscipline. Empirical case studies reveal their success in sustaining macroeconomic stability, fostering investor confidence, and achieving long-term economic growth through prudent expenditure and revenue policies.
Examples of Soft Budget Constraint Outcomes
Soft budget constraints often lead to persistent inefficiencies in state-owned enterprises due to guaranteed financial bailouts, exemplified by the chronic losses and continuous subsidies faced by companies in post-socialist economies like Hungary and Poland. These firms frequently accumulate debt without restructuring incentives, resulting in resource misallocation and stunted economic growth. Fiscal irresponsibility emerges as governments prioritize short-term political gains over sustainable budget policies, amplifying deficits and inflation risks.
Policy Measures to Promote Fiscal Discipline
Fiscal responsibility requires strict adherence to budgetary limits through policies such as balanced budget laws, expenditure caps, and transparent reporting standards. Soft budget constraints, characterized by expectations of bailouts, undermine fiscal discipline and can be mitigated by setting clear rules for subsidies, enhancing oversight mechanisms, and implementing penalty frameworks for non-compliance. Strengthening fiscal institutions and promoting accountability through independent audit bodies are essential policy measures to ensure sustainable public finances and prevent recurrent fiscal slippages.
Balancing Growth: Striking the Right Fiscal Approach
Balancing growth requires a fiscal approach that prioritizes strict fiscal responsibility to avoid the pitfalls of a soft budget constraint, which often leads to inefficient resource allocation and fiscal indiscipline. Implementing credible fiscal rules and maintaining disciplined budget management ensure sustainable economic expansion without excessive debt accumulation. Countries that effectively combine sound fiscal policies with targeted growth investments can achieve long-term stability and robust economic development.
Fiscal responsibility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com