Global diversification spreads your investment portfolio across various countries and industries, reducing risk and enhancing potential returns. It allows you to capitalize on growth opportunities in emerging markets while cushioning against regional economic downturns. Explore the rest of this article to learn how global diversification can optimize your investment strategy.
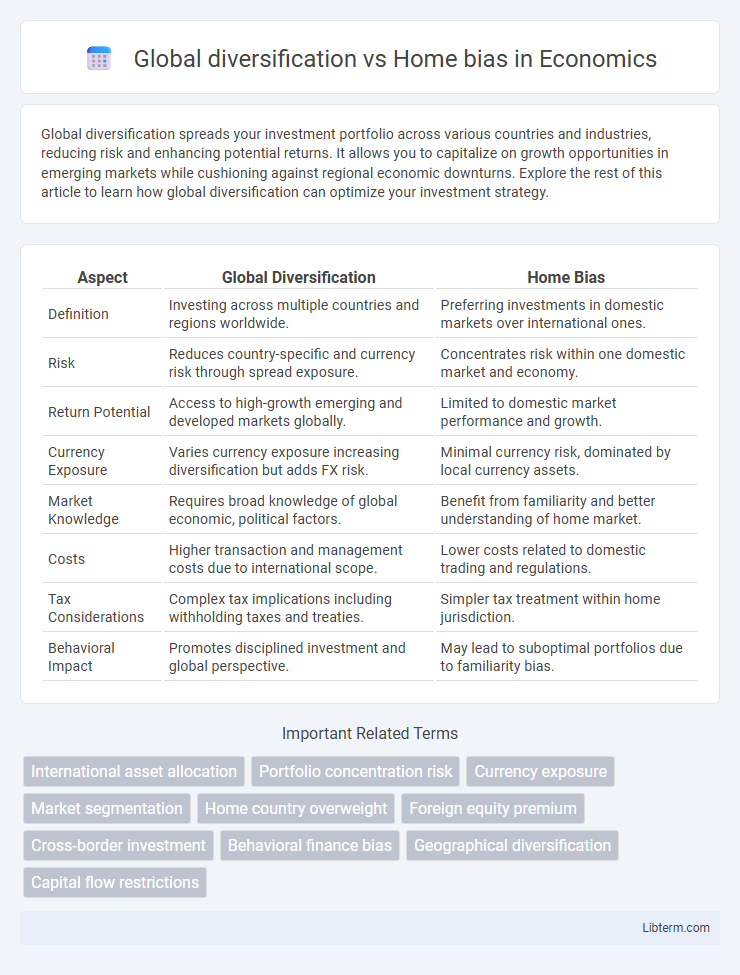
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Global Diversification | Home Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing across multiple countries and regions worldwide. | Preferring investments in domestic markets over international ones. |
| Risk | Reduces country-specific and currency risk through spread exposure. | Concentrates risk within one domestic market and economy. |
| Return Potential | Access to high-growth emerging and developed markets globally. | Limited to domestic market performance and growth. |
| Currency Exposure | Varies currency exposure increasing diversification but adds FX risk. | Minimal currency risk, dominated by local currency assets. |
| Market Knowledge | Requires broad knowledge of global economic, political factors. | Benefit from familiarity and better understanding of home market. |
| Costs | Higher transaction and management costs due to international scope. | Lower costs related to domestic trading and regulations. |
| Tax Considerations | Complex tax implications including withholding taxes and treaties. | Simpler tax treatment within home jurisdiction. |
| Behavioral Impact | Promotes disciplined investment and global perspective. | May lead to suboptimal portfolios due to familiarity bias. |
Understanding Global Diversification
Global diversification involves spreading investments across various countries and asset classes to reduce exposure to domestic market risks and capitalize on international growth opportunities. Understanding global diversification requires recognizing the benefits of currency variation, economic cycles, and market dynamics that differ from those of the home country. This strategy mitigates home bias, which is the tendency of investors to favor domestic assets, potentially limiting portfolio performance and increasing vulnerability to local economic downturns.
Defining Home Bias in Investment
Home bias in investment refers to the tendency of investors to favor domestic assets over foreign ones despite the potential benefits of global diversification. This phenomenon leads to a portfolio concentrated in home country equities, often resulting in lower risk-adjusted returns due to insufficient exposure to international markets. Studies show that home bias limits diversification opportunities, increasing vulnerability to country-specific economic downturns.
Key Benefits of Global Diversification
Global diversification reduces portfolio risk by spreading investments across various international markets, minimizing the impact of country-specific economic downturns. Access to emerging markets and different currency exposures enhances potential returns and hedges against domestic inflation or currency depreciation. Investors benefit from increased opportunities in industries or sectors underrepresented in their home country, leading to a more balanced and resilient investment strategy.
Risks Associated with Home Bias
Home bias in investment portfolios exposes investors to increased risks such as lack of sector and geographic diversification, which can amplify the impact of country-specific economic downturns and political instability. Concentrating assets domestically heightens vulnerability to currency fluctuations and regulatory changes unique to the home market. Global diversification mitigates these risks by spreading exposure across multiple economies, reducing the potential for significant portfolio losses linked to localized events.
Factors Driving Home Bias
Home bias in investment portfolios is primarily driven by familiarity and perceived information advantages regarding local markets, leading investors to favor domestic assets despite global diversification benefits. Behavioral factors, such as patriotism and cognitive biases, reinforce preferences for home country investments, while regulatory constraints and transaction costs also limit cross-border portfolio allocation. Economic factors including exchange rate risk and differences in tax treatment further contribute to the persistence of home bias in international investing.
Performance Comparison: Global vs. Domestic Portfolios
Global diversification in investment portfolios reduces risk by spreading assets across multiple international markets, often leading to enhanced risk-adjusted returns compared to home-biased portfolios concentrated in a single country. Empirical studies reveal that global portfolios typically outperform domestic-only portfolios by capturing growth opportunities in emerging and developed markets, mitigating country-specific economic downturns. Performance comparison shows that portfolios with reduced home bias benefit from superior diversification, higher Sharpe ratios, and more consistent returns over long-term investment horizons.
Barriers to International Investing
Barriers to international investing include currency risk, regulatory differences, and increased transaction costs impacting global diversification strategies. Investors face information asymmetry and political risk that reinforce home bias, limiting portfolio exposure to foreign markets. Overcoming these challenges requires advanced research tools and financial instruments to optimize cross-border investment returns.
Strategies for Reducing Home Bias
Global diversification strategies involve spreading investments across international markets to reduce risk inherent in domestic-only portfolios. Techniques for reducing home bias include incorporating foreign equities, utilizing global ETFs, and employing currency-hedged funds to manage exchange rate volatility. Institutional investors often increase overseas exposure by leveraging emerging market assets and sector diversification to enhance portfolio resilience and returns.
The Role of Emerging Markets in Diversification
Emerging markets play a crucial role in global diversification by offering higher growth potential and unique risk-return profiles compared to developed markets. These markets provide access to rapidly expanding economies, increased consumer demand, and untapped sectors, reducing portfolio concentration risk associated with home bias. Incorporating emerging markets into investment portfolios enhances overall diversification benefits by capturing opportunities unavailable in domestic or traditional developed market assets.
Future Trends in Global Investment Allocation
Global investment allocation is increasingly shifting towards diversification beyond traditional home bias, driven by technological advancements and enhanced access to international markets. Emerging markets and ESG-focused assets are gaining prominence, reflecting evolving investor preferences and regulatory frameworks. Enhanced data analytics and geopolitical shifts also influence portfolio adjustments, emphasizing balanced risk and return globally.
Global diversification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com